A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis. What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following is a consequence of increased viscosity of a fluid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. The fluid will have a lower density.
C. The fluid will have a higher flow rate.
D. The fluid will have a higher pressure.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
-
Q #2: What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
Answer Explanation
Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
-
Q #3: Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
Answer Explanation
Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
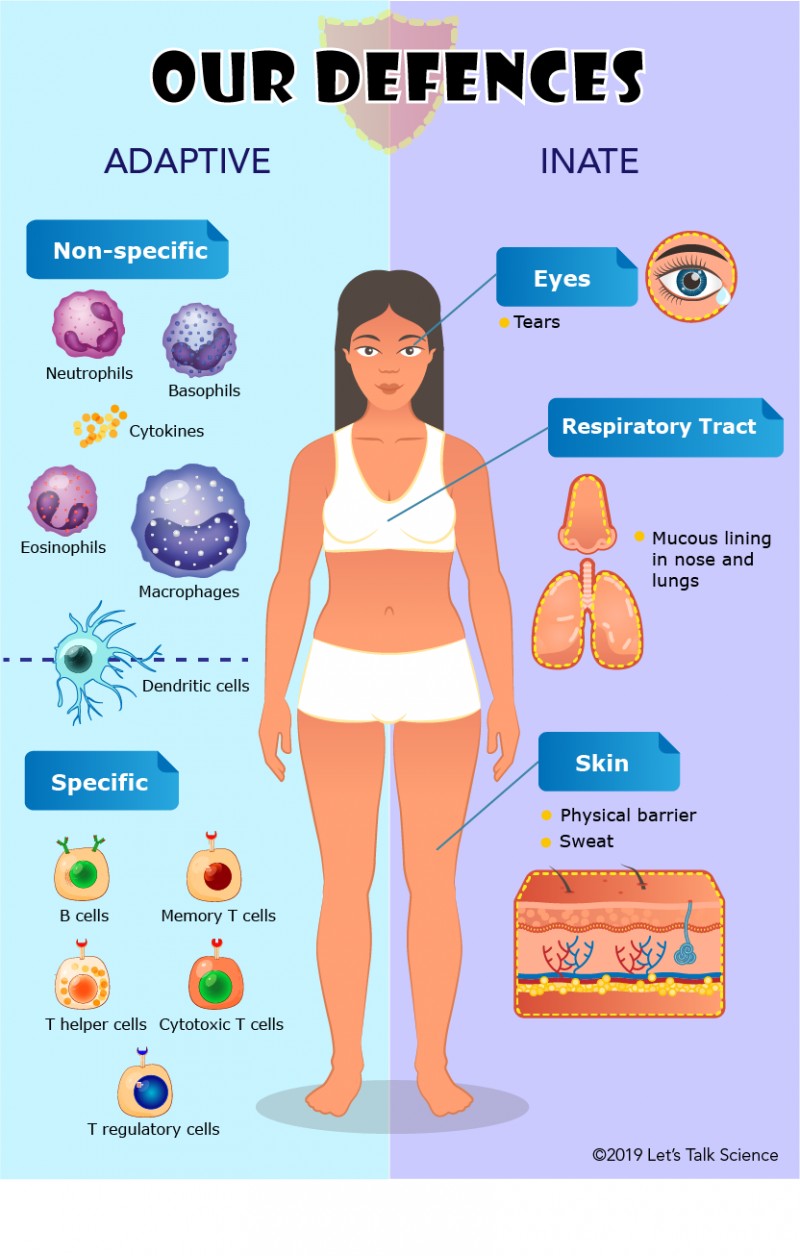
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
-
Q #4: Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
Answer Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
-
Q #5: A nurse is caring for a patient who has been declared brain dead and is awaiting organ donation. Which of the following interventions is most important to preserve the viability of the organs?
A. Administering antibiotics to prevent infection.
B. Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
C. Providing emotional support to the family members.
D. Applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
Early identification and management of potential organ donors must take into consideration specific pathophysiologic changes for medical optimization 1.
The VIPPS (ventilation, infusion and pumping, pharmacological treatment, and specificities) strategy is a mnemonic method that brings together key aspects of the restoration of oxygen delivery to tissues during hemodynamic instability plus organ optimization strategies.
Choice A is incorrect because administering antibiotics to prevent infection is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Choice C is incorrect because providing emotional support to family members, while important, is not an intervention that directly affects organ viability.
Choice D is incorrect because applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
-
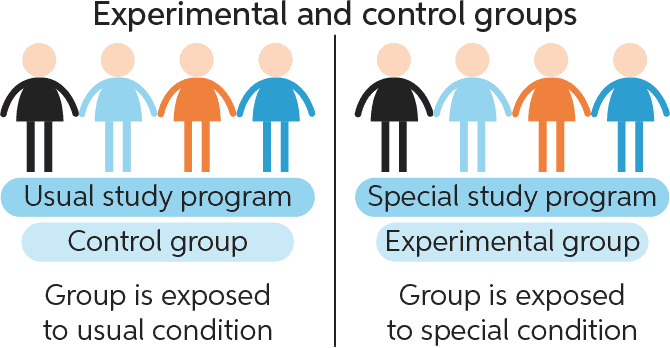
Q #6: In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between what?.
A. Control group and treatment group.
B. Independent variable and dependent variable.
C. Experimental group and non-experimental group.
D. High level and low level of the independent variable.
Answer Explanation
In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between the control group and treatment group.
This means researchers can correctly measure the entire effect of the treatment without interference from confounding variables.
Choice B) Independent variable and dependent variable is incorrect because these are not groups but rather variables.
The independent variable is manipulated by the experimenters while the dependent variable is measured to see if it changes as a result of the manipulation.
Choice C) Experimental group and non-experimental group is incorrect because a non-experimental group is not a term used in experimental design.
The correct term for the group that does not receive the treatment is control group.
Choice D) High level and low level of the independent variable is incorrect because these are levels of the independent variable, not groups.
In an experiment, there can be multiple levels of the independent variable, but they are applied to different groups (e.g.
control group, treatment group).
-
Q #7: Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
Answer Explanation
Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
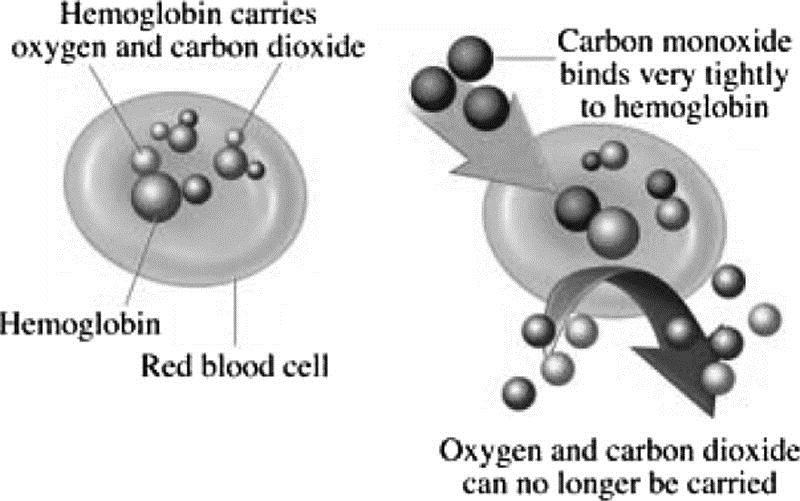
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Q #8: Which of the following structures in the nephron is responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients?
A. Distal tubule
B. Proximal tubule
C. Glomerulus
D. Loop of Henle
Answer Explanation
Proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is responsible for reabsorbing all the nutrients and most of the water.
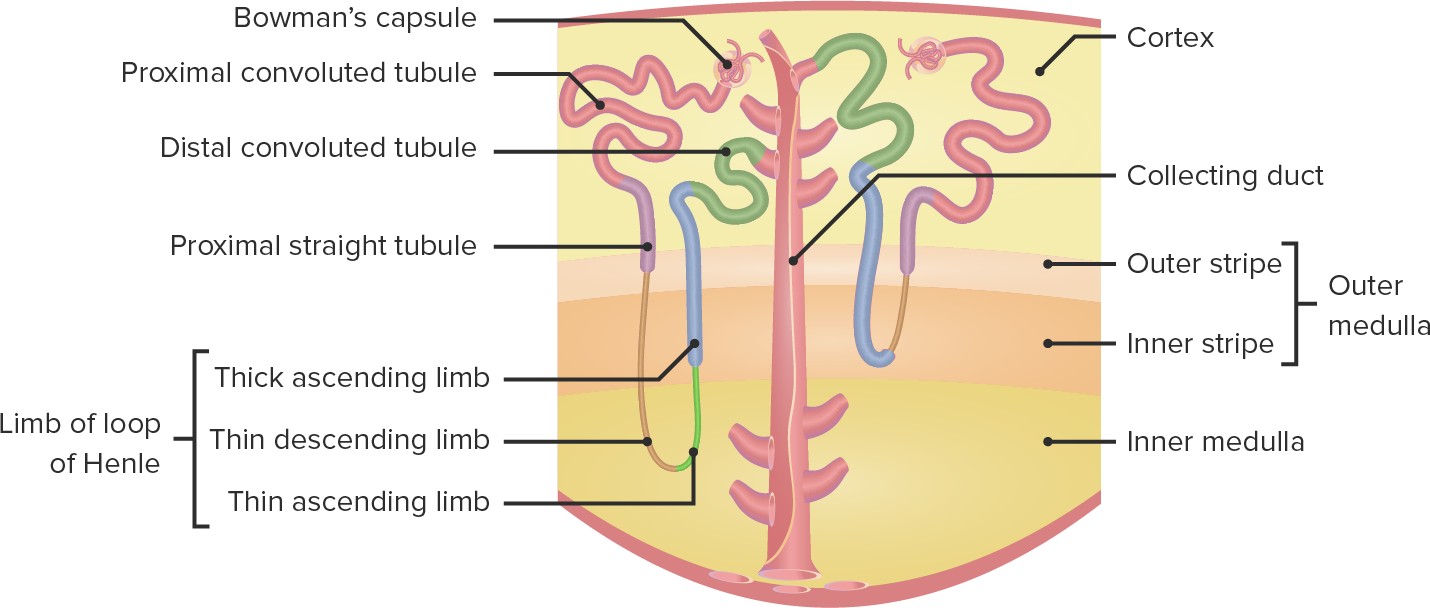
Choice A is incorrect because the distal tubule is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
Choice C is incorrect because the glomerulus is responsible for filtering fluid and solutes out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate.
Choice D is incorrect because the Loop of Henle is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
-
Q #9: A patient with a history of heart failure is prescribed a medication that increases urine output to reduce fluid buildup. Which of the following statements best describes the mechanism of action of the prescribed medication?
A. Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
B. Blocks beta receptors.
C. Increases sodium and water reabsorption.
D. Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice D - Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The medication prescribed to the patient is a diuretic, which removes water and electrolytes from the body by increasing urination 1.
This helps reduce fluid buildup in the body.
Choice A, Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice B, Blocks beta receptors, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice C, Increases sodium and water reabsorption, is not the correct answer because it would have the opposite effect of reducing fluid buildup.
-
Q #10: How do neurons communicate with each other?
A. Through electrical signals only
B. Through chemical signals only
C. Through electrical and chemical signals
D. Through mechanical signals only.
Answer Explanation
Neurons communicate with each other through both electrical and chemical signals.
The electrical signal, or action potential, runs from the cell body area to the axon terminals, through a thin fiber called axon.
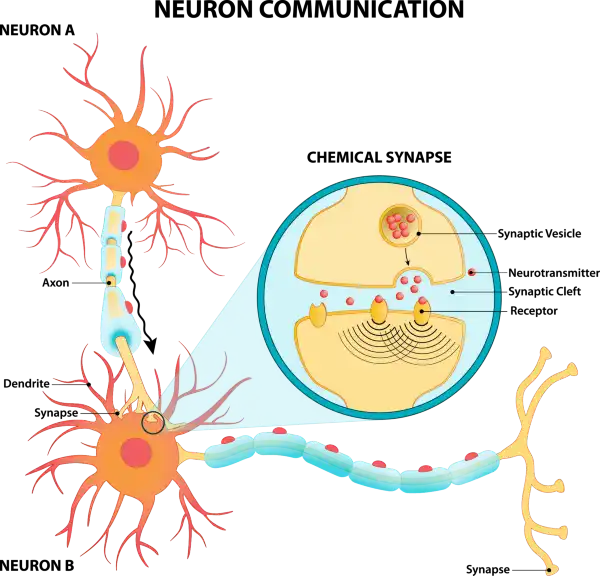
Neurons also communicate with one another at junctions called synapses.
At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell.
Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers.
Choice A is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through electrical signals but also through chemical signals.
Choice B is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through chemical signals but also through electrical signals.
Choice D is incorrect because neurons do not communicate through mechanical signals.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
