A student notices a pattern of stripes on five tigers. Each of the five tigers has the same stripe pattern. Using his inductive reasoning, what does he logically assume based on this information?
A. The pattern continues to change over time.
B. Natural adaptations cause this pattern to occur
C. Each offspring will have the same stripe pattern
D. Ancestors of the tigers have different stripe patterns
Inductive reasoning involves making specific observations and using them to make broad statements. The student observes that all of the tigers have the same stripe pattern. He can use this observation to make the broad statement that all the tigers’ offspring will have the same stripe pattern.
Inductive reasoning involves drawing a general conclusion from specific observations. This form of reasoning is referred to as the “from the bottom up” approach. Information gathered from specific observations can be used to make a general conclusion about the topic under investigation. In other words, conclusions are based on observed patterns in data.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What is the correct order of the stages of the cell cycle?
A. G1,S,G2,M
B. G2,S,G1,M
C. M,S,G2,G1
D. S,M,G1,G1
Answer Explanation
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
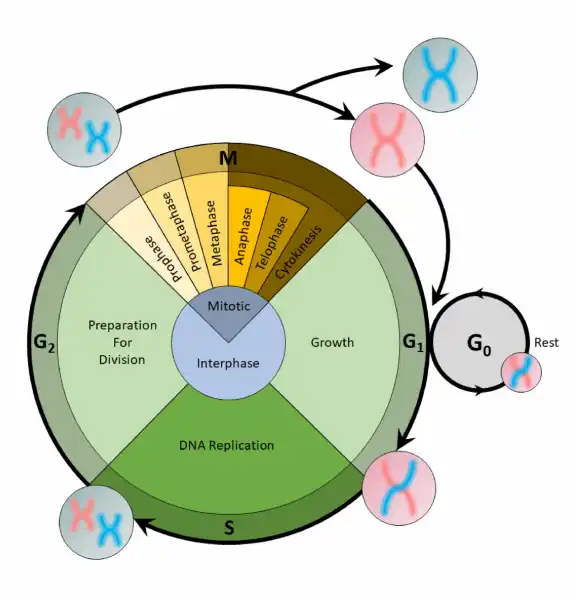
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is supported by the cell theory?
A. Cells are alive and recognized as the building blocks for life.
B. Scientists can identify and differentiate cells by using a microscope
C. Cells are produced from existing cells using meiosis instead of mitosis.
D. Living things are composed of a single cell that remains undifferentiated
Answer Explanation
After scientists were able to view cells under the microscope they formulated the cell theory. One part of this theory concluded that all cells are alive. They also represent the basic unit of life.
All living things are made of cells. Cells are the smallest structural units and basic building blocks of living things. Cells contain everything necessary to keep living things alive. Varying in size and shape, cells carry out specialized functions. This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
-
Q #3: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
Answer Explanation
Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.
-
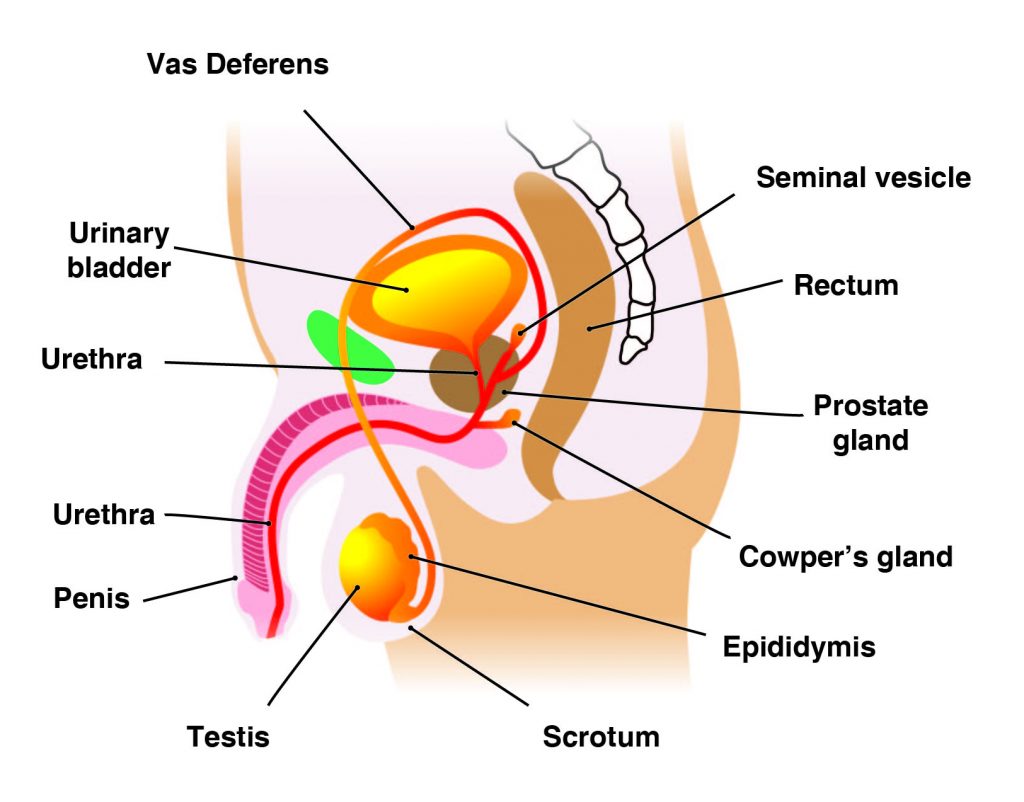
Q #4: Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
Answer Explanation
The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
-
Q #5: If a person smells something sweet, what form of information is this initially perceived as in the nervous system?
A. Cognitive
B. Integrative
C. Motor
D. Sensory
Answer Explanation
A sensory nerve is a nerve that carries sensory signals from the external environment to the brain to the central nervous system. It is also an afferent nerve, long dendrites of sensory neurons, which sends sensory information towards the central nervous system (CNS). This information is what is sensed, using the five senses from external environment, sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch.
Motor nerves have only efferent fibers, long axons of motor neurons, that carry impulses away from the CNS to the effectors, which are typically tissues and muscles of the body.
Interneurons are nerve cells that act as a bridge between motor and sensory neurons in the CNS. These neurons help form neural circuits, which helps neurons communicate with each other.
-
Q #6: After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
Answer Explanation
Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.
-
Q #7: What type of reaction is described by the following equation? ZnBr2(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2KBr(aq)
A. Synthesis
B. Decomposition
C. Single-Replacement
D. Double-Replacement
Answer Explanation
In this reaction, two elements are trading places hence double-replacement. In the reactants, zinc and bromide ions are together, and potassium and hydroxide ions are together. In the products, zinc and hydroxide ions are together, and potassium and bromide ions are together.
-
Q #8: An atom has 28 protons, 32 neutrons, and 28 electrons. What is the name of this isotope?
A. Nickel-32
B. Nickel-60
C. Germanium-56
D. Germanium-60
Answer Explanation
The number of protons, 28, gives the atomic number, which identifies this atom as nickel. The mass is the number after the dash in the isotope name, which is determined by adding the numbers of protons and neutrons (28 + 32 = 60).
-
Q #9: What body system is the skeletal system most closely associated with when hematopoiesis happens?
A. Urinary system
B. Digestive system
C. Muscular system
D. Cardiovascular system
Answer Explanation
The cardiovascular system is closely associated with hematopoiesis because it includes the heart and blood vessels, which are responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. Hematopoiesis, the process of blood cell formation, primarily occurs in the bone marrow, which is part of the skeletal system. However, the cardiovascular system plays a crucial role in transporting these blood cells to various parts of the body once they are produced in the bone marrow.
So, while the skeletal system provides the site for hematopoiesis, the cardiovascular system is responsible for distributing the blood cells, making it the most closely associated system in this context.
-
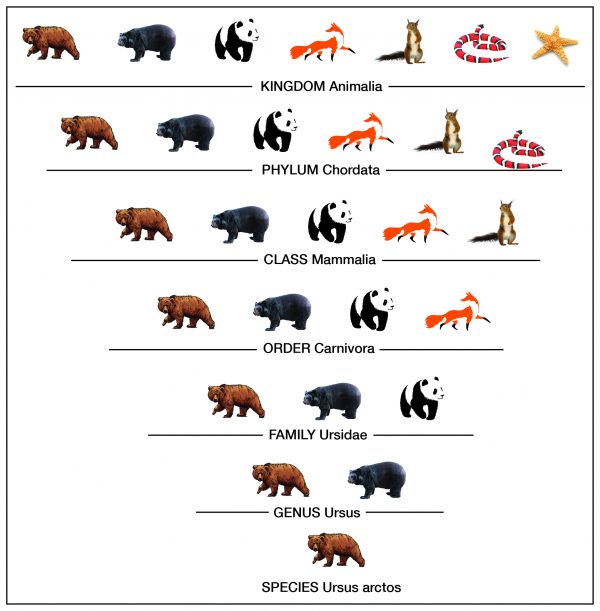
Q #10: Which sequence describes the hierarchy level of biological organization?
A. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
B. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
C. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
D. Species, kingdom, genus, class, family, phylum, and order
Answer Explanation
Taxonomy is the process of classifying, describing, and naming organisms. There are seven levels in the Linnaean taxonomic system, starting with the broadest level, kingdom, and ending with the species level. For example, in the image the genus level contains two types of bears, but the species level shows one type. Additionally, organisms in each level are found in the level above it. For example, organisms in the order level are part of the class level. This classification system is based on physical similarities across living things. It does not account for molecular or genetic similarities.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
