After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
Answer Explanation
Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
-
Q #2: Which part of the digestive system comes before the stomach?
A. mouth
B. esophagus
C. ileum
D. colon
Answer Explanation
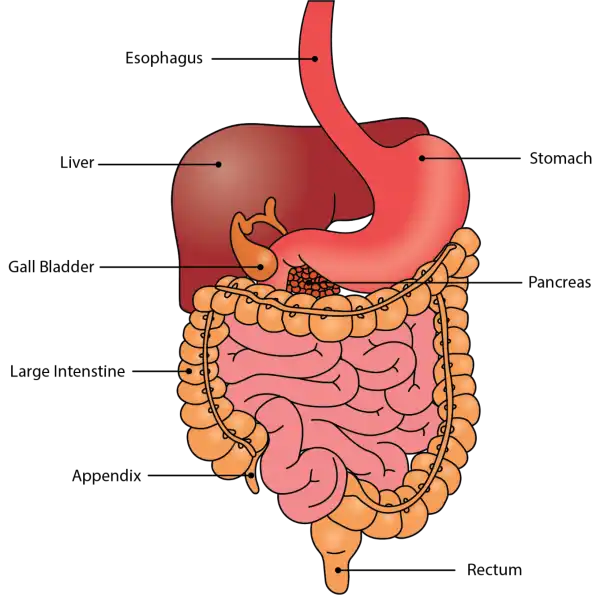
Oral Cavity is the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestine is about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colon is about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
-
Q #3: In which state of matter are the intermolecular forces between particles in a substance the strongest?
A. Gas
B. Liquid
C. Plasma
D. Solid
Answer Explanation
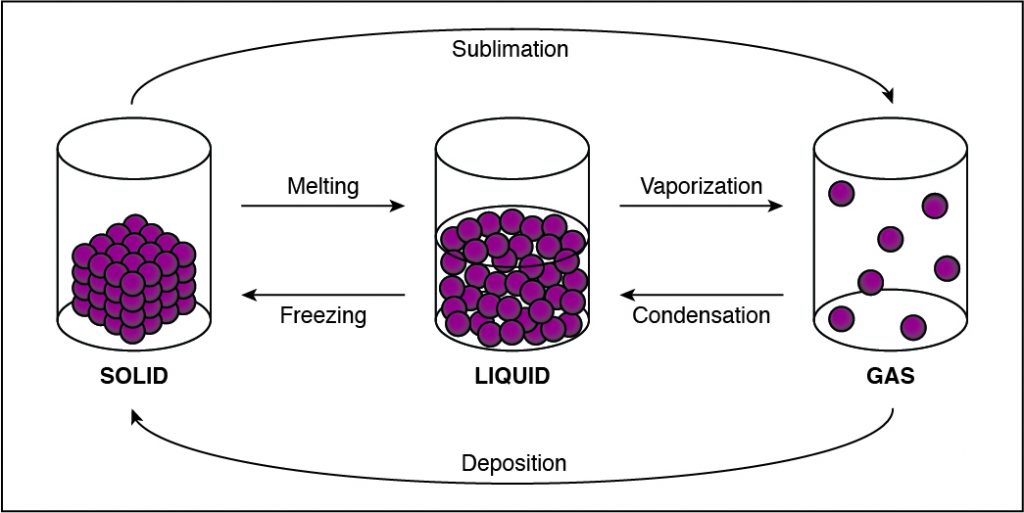
In solids, particles are usually closer together than in other states of matter because of the strong cohesive forces between the particles.
- Solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas differ from one another in the amount of energy that the particles have and the strength of the cohesive forces that hold the particles together.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
-
Q #4: The diffusion of nutrients through the walls of the digestive system is critical to homeostasis in the body. Where does the majority of this diffusion take place in the digestive system?
A. Stomach
B. Esophagus
C. Oral cavity
D. Small intestine
Answer Explanation
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestines, located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestines (jejunum). Once food has mixed with acid in the stomach, it moves into the duodenum, where it then mixes with bile from the gallbladder and digestive juices secreted from the pancreas. In the duodenum, absorption of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients begins.
-
Q #5: Which is true regarding the Urinary system?
A. Kidneys makes urine, Kidney help regulate water balance.
B. As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium.
C. Eliminates metabolic wastes., Kidneys makes urine., Kidney help regulate water balance.
D. Kidney help regulate water balance, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, Eliminates metabolic wastes
Answer Explanation
Kidneys makes urine is incorrect. Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase is incorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance is correct. Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is correct. There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes is correct. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
-
Q #6: What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
Answer Explanation
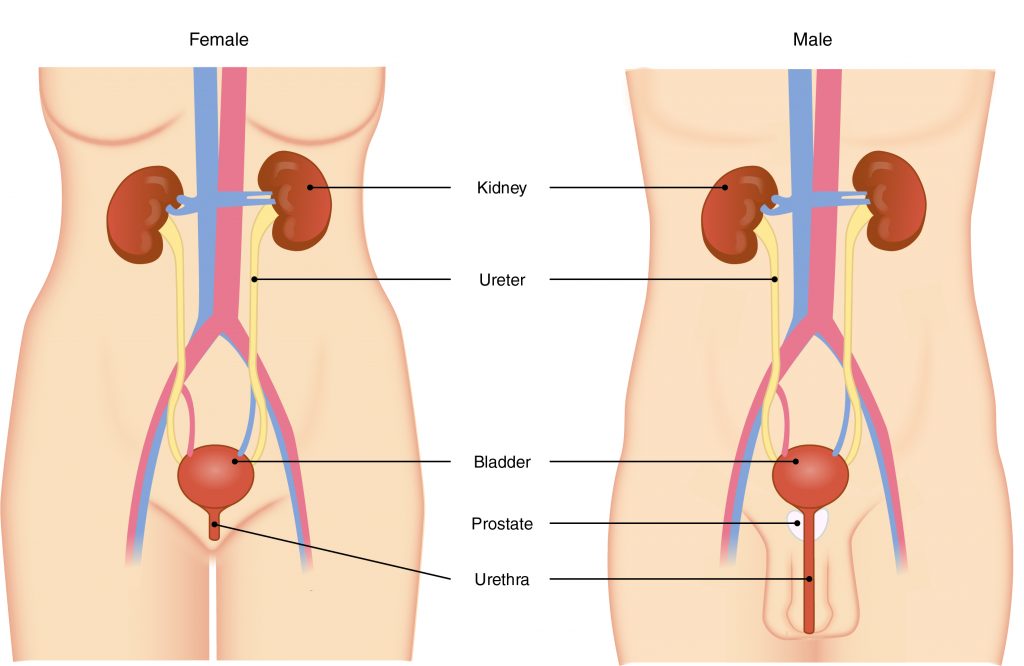
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
-
Q #7: Which of the following determines the strength of an acidic solution?
A. Litmus paper that turns red
B. Litmus paper that turns blue
C. Measured pH value equal to 7
D. Measured pH value less than 7
Answer Explanation
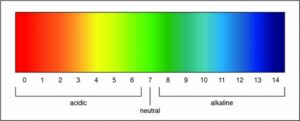
Both litmus paper and a pH scale can be used to indicate whether a solution is acidic. However, a pH scale can also determine the strength of an acid.
Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
-
Q #8: During which of the following phase changes will the cohesion between the particles in a substance decrease?
A. Condensation
B. Deposition
C. Freezing
D. Vaporization
Answer Explanation
If the cohesion between particles decreases, then the particles must be undergoing a phase change that allows particles to move farther apart. This happens when a substance vaporizes and turns from liquid to gas. Any phase change that moves to the right in the diagram above requires energy to be added to the system because the substance has more energy at the end of the phase change. The phase changes are melting, vaporization (boiling), and sublimation. When energy is added, particles move faster and can break away from each other more easily as they move to a state of matter with a higher amount of energy. This is most commonly done by heating the substance.
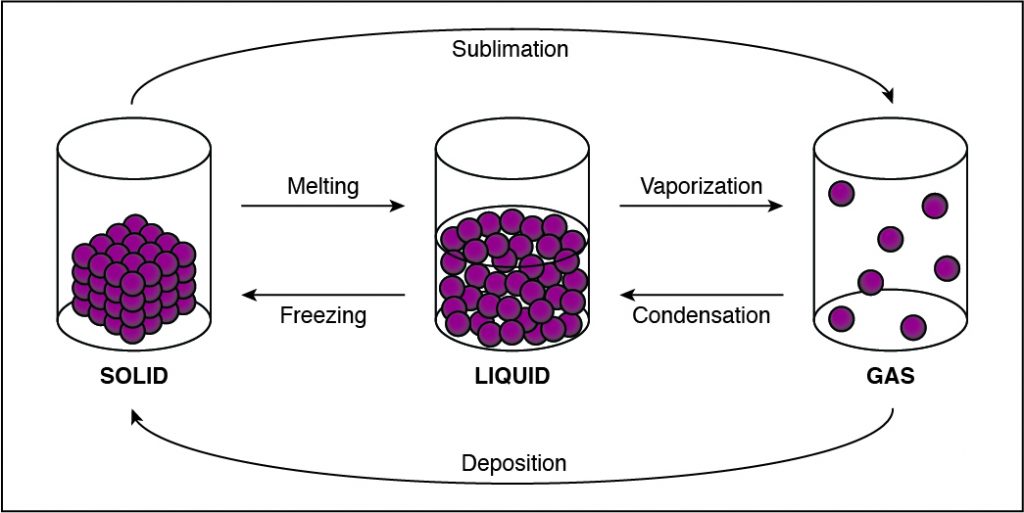
-
Q #9: Which is classified as a type of acid-base reaction that produces a salt?
A. Combination
B. Decomposition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Neutralization
Answer Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes, neutralization reactions also occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as an ionic compound that includes any cation except H+ and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
-
Q #10: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
Answer Explanation
Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
