As soon as an invader, known as a(n) _____, enters the body, the body begins to fight.
A. antibody
B. pathogen
C. trigger
D. vaccination
Pathogen is an infectious foreign body that enters the body and causes disease or illness to the person. There are five types of pathogens: viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and worms. Pathogens have antigen proteins found on their surface and are unique to each pathogen.
Antibody is a protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances (antigens). There are many different antibodies found in the body. Each one is unique and protects the body against the specific antigen that it detects at any given time. If there are no antibodies for a specific antigen, the more likely you are to develop an illness.
Vaccinations are the introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen or of a harmless microbe with the protein of a pathogen on its surface into the body. Often administered through needle injection, to stimulate the immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease Immunity protects the body from a disease when exposed to it.
There are four types of immunity: natural/passive, natural/active, artificial/passive, and artificial/ active.
- Natural/passive – Babies receive immunities from breastmilk.
- Natural/active – The body produces antibodies to combat an illness when a person becomes sick.
- Artificial/passive – This immunity is temporary and requires doses of serum to maintain the immunity.
- Artificial/active – A vaccination provides artificial/active immunity.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
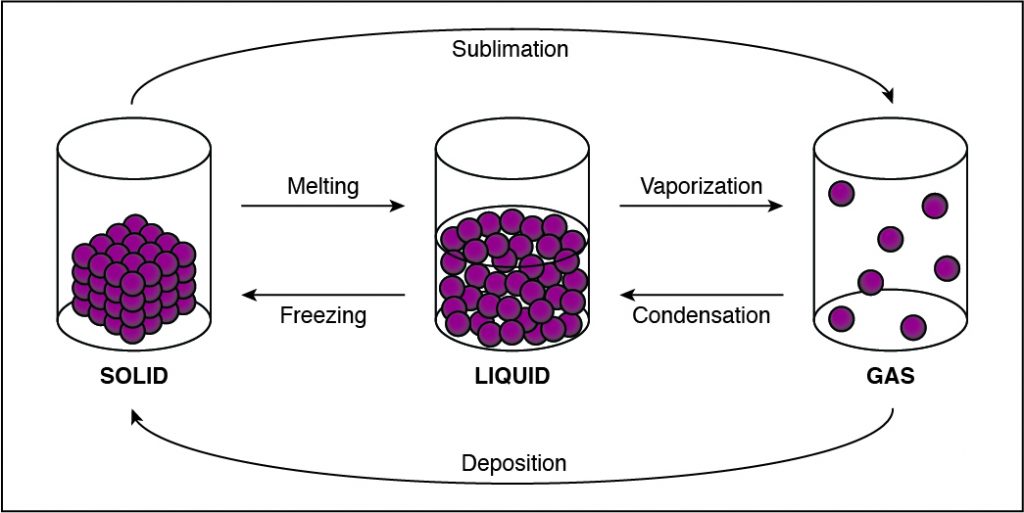
Q #1: During which of the following phase changes will the cohesion between the particles in a substance decrease?
A. Condensation
B. Deposition
C. Freezing
D. Vaporization
Answer Explanation
If the cohesion between particles decreases, then the particles must be undergoing a phase change that allows particles to move farther apart. This happens when a substance vaporizes and turns from liquid to gas. Any phase change that moves to the right in the diagram above requires energy to be added to the system because the substance has more energy at the end of the phase change. The phase changes are melting, vaporization (boiling), and sublimation. When energy is added, particles move faster and can break away from each other more easily as they move to a state of matter with a higher amount of energy. This is most commonly done by heating the substance.
-
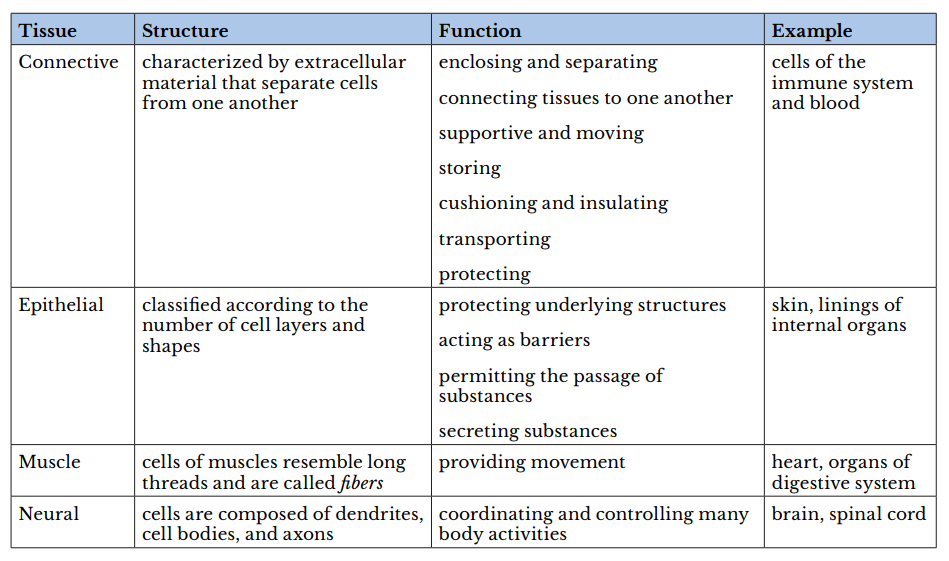
Q #2: Which of the following types of tissues include cells of the immune system and of the blood?
A. Connective
B. Epithelial
C. Muscle
D. Neural
Answer Explanation
A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function and similar extracellular substances located between the cells. The table below describes the four primary tissues found in the human body.
body.
-
Q #3: Which example is part of the scientific method?
A. A student reads about a new way to harness energy from the sun.
B. A researcher studies the effects of car exhaust on how people breathe.
C. A researcher analyzes how many plants respond well to a new fertilizer
D. A student discovers how insulin plays a role in the development of diabetes
Answer Explanation
One step of the scientific method is to analyze information or data collected from the experiment to conclude whether the hypothesis is supported.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
-
Q #4: An intracellular chemical signal can be produced in the cell membrane. Once it is produced, where does it go?
A. To a different cell
B. To another part of the same cell
C. To a region right outside the cell
D. To an area with a high ion concentration
Answer Explanation
There are two major types of receptor molecules that respond to an intercellular chemical signal:
- Intracellular receptors: These receptors are located in either the cytoplasm or the nucleus of the cell. Signals diffuse across the cell membrane and bind to the receptor sites on intracellular receptors, of the same cell.
- Membrane-bound receptors: These receptors extend across the cell membrane, with their receptor sites on the outer surface of the cell membrane. They respond to intercellular chemical signals that are large, water-soluble molecules that do not diffuse across the cell membrane.
-
Q #5: Why did it take many years for the cell theory to be developed?
A. Advancements in microscopy took place slowly.
B. Cells were difficult to isolate for experimental analysis
C. Researchers believed a cell formed from preexisting cells
D. Scientists already proved that cells were essential for life.
Answer Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
-
Q #6: What raw inorganic material would an autotroph most likely use to create chemical energy for growth?
A. carbon dioxide
B. minerals in soil
C. decaying matter
D. sugar molecules
Answer Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophs are organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
-
Q #7: Which statement best represents Mendel’s experiments with garden peas?
A. As a result, Mendel developed several theories that have since been disproved.
B. Mendel realized he was on an incorrect track, which led him to other experimental media
C. As a result, Mendel developed foundational conclusions that are still valued and followed today.
D. Mendel collaborated with others interested in genetics to develop heredity guidelines we still use today
Answer Explanation
Mendel developed theories of genetics that scientists around the world use today.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants either self-pollinate or cross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are either dominant or recessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information called genes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual is homozygous for that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual is heterozygous for that trait. Each copy of a factor, or gene, is called an allele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, or phenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is its genotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
-
Q #8: As soon as an invader, known as a(n) _____, enters the body, the body begins to fight.
A. antibody
B. pathogen
C. trigger
D. vaccination
Answer Explanation
Pathogen is an infectious foreign body that enters the body and causes disease or illness to the person. There are five types of pathogens: viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and worms. Pathogens have antigen proteins found on their surface and are unique to each pathogen.
Antibody is a protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances (antigens). There are many different antibodies found in the body. Each one is unique and protects the body against the specific antigen that it detects at any given time. If there are no antibodies for a specific antigen, the more likely you are to develop an illness.
Vaccinations are the introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen or of a harmless microbe with the protein of a pathogen on its surface into the body. Often administered through needle injection, to stimulate the immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease Immunity protects the body from a disease when exposed to it.
There are four types of immunity: natural/passive, natural/active, artificial/passive, and artificial/ active.
- Natural/passive – Babies receive immunities from breastmilk.
- Natural/active – The body produces antibodies to combat an illness when a person becomes sick.
- Artificial/passive – This immunity is temporary and requires doses of serum to maintain the immunity.
- Artificial/active – A vaccination provides artificial/active immunity.
-
Q #9: What structure plays a role in air conduction?
A. Alveolus
B. Capillary
C. Lung
D. Trachea
Answer Explanation
The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
-
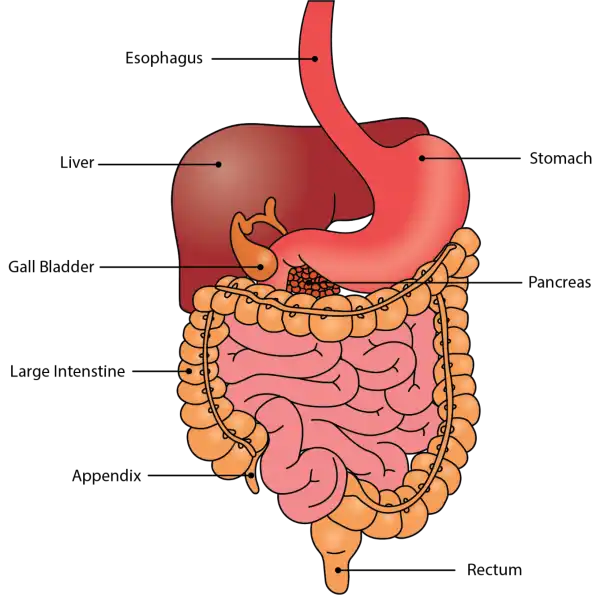
Q #10: Which part of the digestive system comes before the stomach?
A. mouth
B. esophagus
C. ileum
D. colon
Answer Explanation
Oral Cavity is the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestine is about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colon is about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
