Genetic information describing the characteristics of an organism is found in which of the following?
A. Nuclei
B. Membranes
C. Cilia
D. Ribosomes
The correct answer is a. Nuclei. Genetic information describing the characteristics of an organism is found in the nuclei of its cells. The nucleus contains the organism's DNA, which carries the genetic information that determines its traits.
b. Membranes are structures that surround and enclose cells and organelles, but they do not contain genetic information.
c. Cilia are hair-like structures that protrude from the surface of some cells and are involved in movement, but they do not contain genetic information.
d. Ribosomes are organelles that are involved in protein synthesis, but they do not contain genetic information.
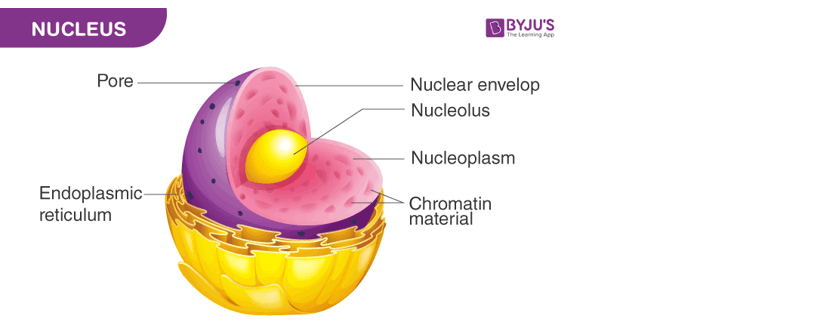
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
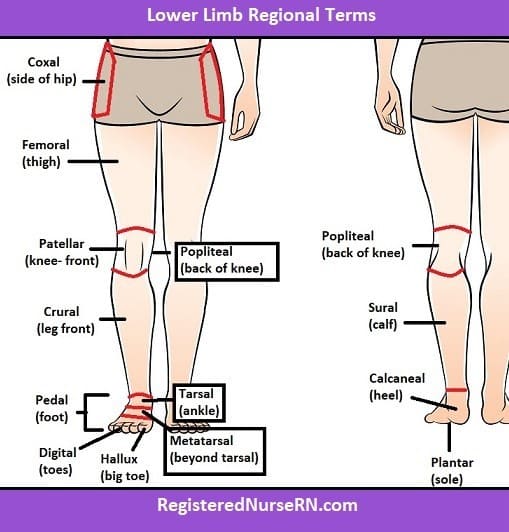
Q #1: In which of the following regions of the body are the tibia and fibula?
A. Coxal
B. Antecubital
C. Tarsal
D. Crural
Answer Explanation
The tibia and fibula are located in the crural region of the body, which is the lower leg between the knee and ankle. The coxal region refers to the hip area, the antecubital region is the front of the elbow, and the tarsal region is the ankle and foot.
-
Q #2: Use the table below to answer the question. Object Mass (g) Time of fall (sec) 1 5.0 2.0 2 5.0 1.0 3 30.0 0.5 4 35.0 1.5 Which of the following conclusions is supported by the data?
A. Objects A and B will fall at the same rate.
B. The greater the mass of an object, the faster it will fall.
C. The time of fall is independent of the mass of the object.
D. Air resistance could be greater for A than for B.
Answer Explanation
-
Q #3: The mitochondrial inner membrane carries out the same function in cellular respiration as the ________ membrane of chloroplasts in photosynthesis. Which of the following correctly completes the sentence above?
A. Thylakoid
B. Epithelial
C. Nuclear
D. Tonoplast
Answer Explanation
The thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts is where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place, while the mitochondrial inner membrane is where the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis occur during cellular respiration.
The tonoplast is the membrane that surrounds the central vacuole in plant cells. It is not involved in cellular respiration or photosynthesis.
The other options, epithelial and nuclear, are not related to these processes.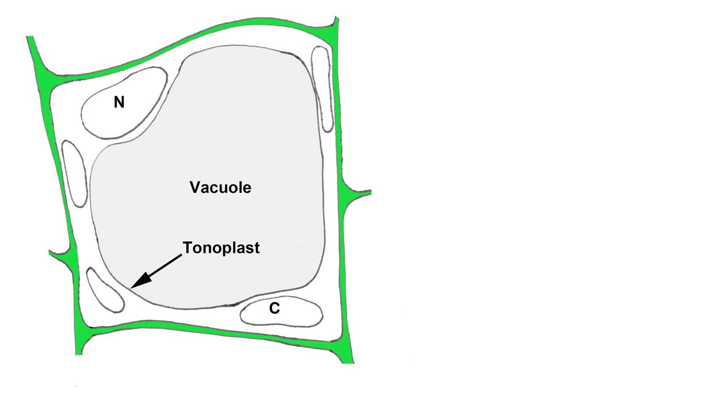
-
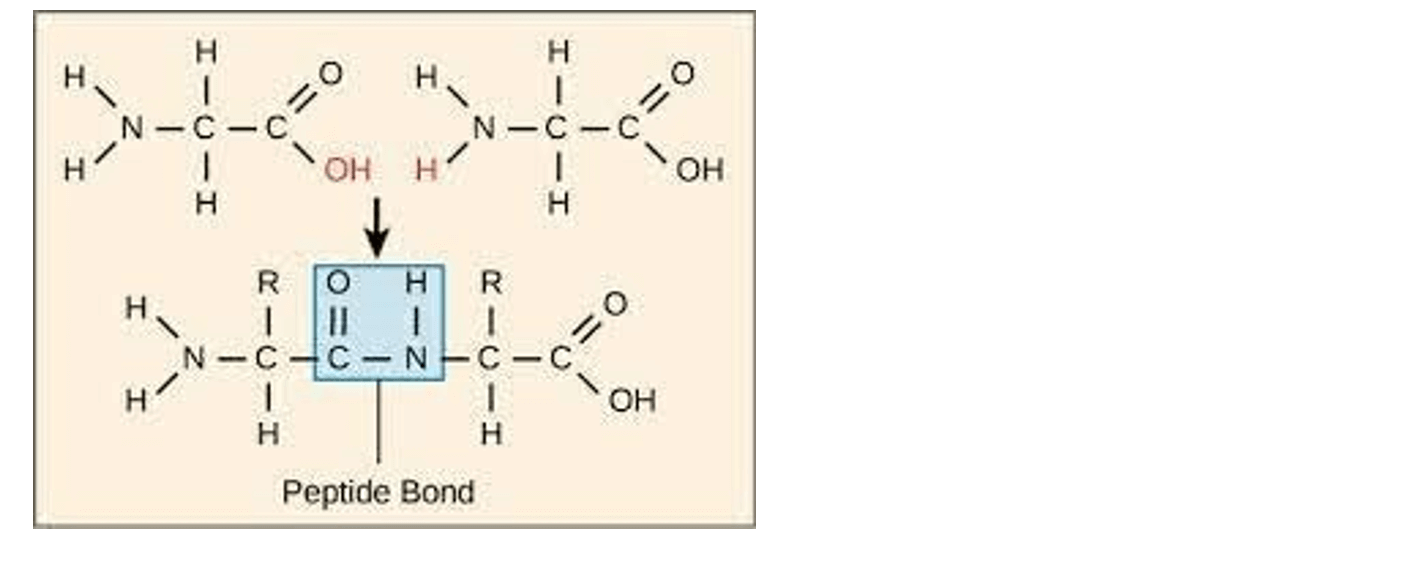
Q #4: The covalent bonds between the monomers of an enzyme macromolecule are:
A. Ester bonds
B. Peptide bonds
C. Phosphodiester bonds
D. Glycosidic bonds
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is b. Peptide bonds. Enzymes are proteins, and proteins are made up of amino acid monomers linked together by peptide bonds. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
a. Ester bonds are covalent bonds that form between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
c. Phosphodiester bonds are covalent bonds that form between a phosphate group and two hydroxyl
groups.
d. Glycosidic bonds are covalent bonds that form between two monosaccharides.
-
Q #5: Which of the following is a protein present in blood plasma?
A. Monocytes
B. Platelets
C. Fibrinogen
D. Lymphocytes
Answer Explanation
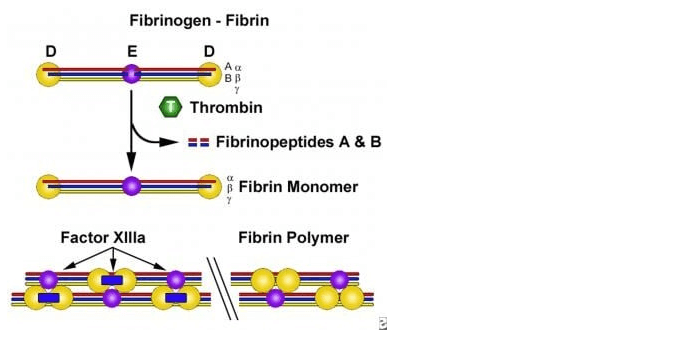
The correct answer is c. Fibrinogen. Fibrinogen is a protein present in blood plasma that plays a key role in blood clotting. When an injury occurs and bleeding begins, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin, which forms a mesh-like structure that helps to trap blood cells and form a clot.
A. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell, not a protein present in blood plasma.
B. Platelets are cell fragments that play a role in blood clotting, but they are not a protein present in blood plasma.
D. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell, not a protein present in blood plasma.
-
Q #6: For which of the following reasons does a chloride ion have a negative charge?
A. It gained an electron
B. It lost an electron.
C. It lost a proton.
D. It gained a proton.
Answer Explanation
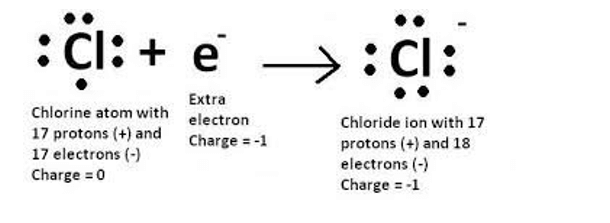
A chloride ion has a negative charge because it gained an electron. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged because it now has more electrons than protons. In the case of a chloride ion, the neutral chlorine atom gains an electron to become a negatively charged chloride ion.
The other options are incorrect because they do not result in a negative charge. Losing an electron would result in a positive charge. Losing or gaining a proton would change the identity of the atom and is not related to the formation of a chloride ion.
-
Q #7: Which of the following structures is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Endoplasmic reticulum
B. Cell membrane
C. Chloroplast
D. Golgi apparatus
Answer Explanation
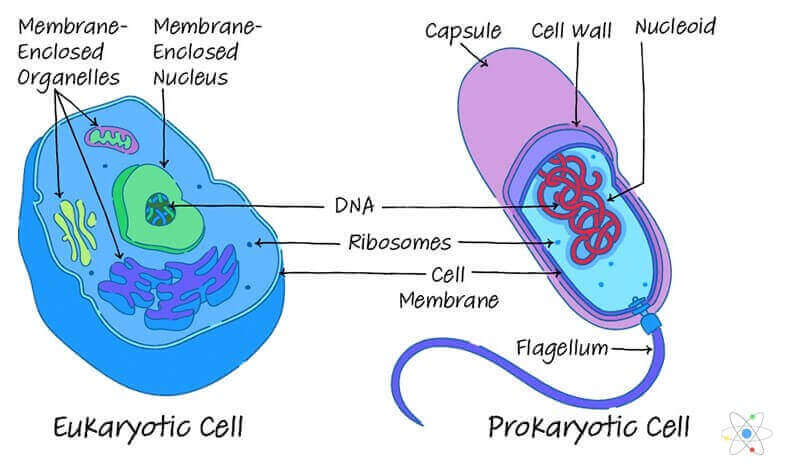
The structure that is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the cell membrane ². The cell membrane is a thin layer that surrounds the cell and separates its internal environment from the external environment ². It is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell ².
The other options are not correct because they are not present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, and Golgi apparatus are organelles that are only found in eukaryotic cells ².
-
Q #8: Which of the following correctly orders structures from simple to complex?
A. Cells, tissues, atoms, organs
B. Atoms, organs, tissues, cells
C. Atoms, cells, tissues, organs
D. Organs, tissues, cells, atoms
Answer Explanation
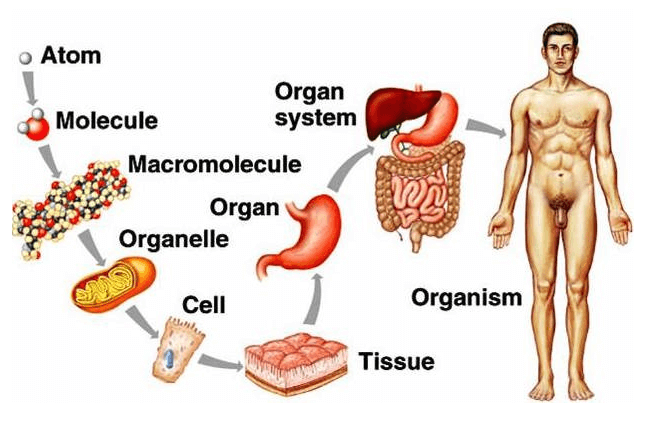
The correct answer is c. Atoms, cells, tissues, organs. This is the correct order of structures from simple to complex. Atoms are the smallest and simplest units of mater. Cells are made up of atoms and are the basic units of life.
Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Organs are made up of different types of tissues and perform more complex functions.
A. Cells, tissues, atoms, organs is not the correct order from simple to complex.
B. Atoms, organs, tissues, cells is not the correct order from simple to complex.
D. Organs, tissues, cells, atoms is not the correct order from simple to complex.
-
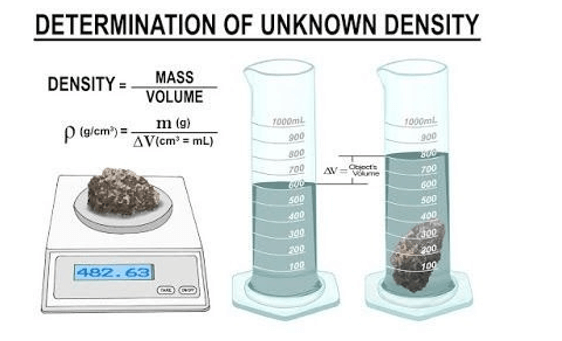
Q #9: To accurately measure the density of a series of small irregular solids made of plastic, wood, fibreglass, and glass, a student will need which of the following laboratory tools?
A. Graduated cylinder, water, weighing balance
B. Graduated cylinder, spectrophotometer, water
C. Graduated beaker, metric ruler, water
D. Weighing balance, Bunsen burner, metric ruler
Answer Explanation
To accurately measure the density of a series of small irregular solids made of plastic, wood, fiberglass, and glass, a student will need a graduated cylinder, water, and a weighing balance. The student can use the water displacement method to determine the volume of each solid by measuring the volume of water displaced when the solid is submerged in a graduated cylinder filled with water. The mass of each solid can be measured using a weighing balance. The density can then be calculated by dividing the mass by the volume.
The other options are not correct because they do not provide the necessary tools to accurately measure the density of the solids. A spectrophotometer is used to measure light absorption and is not necessary for measuring density. A graduated beaker is less accurate than a graduated cylinder for measuring volume. A Bunsen burner is used for heating and is not necessary for measuring density.
-
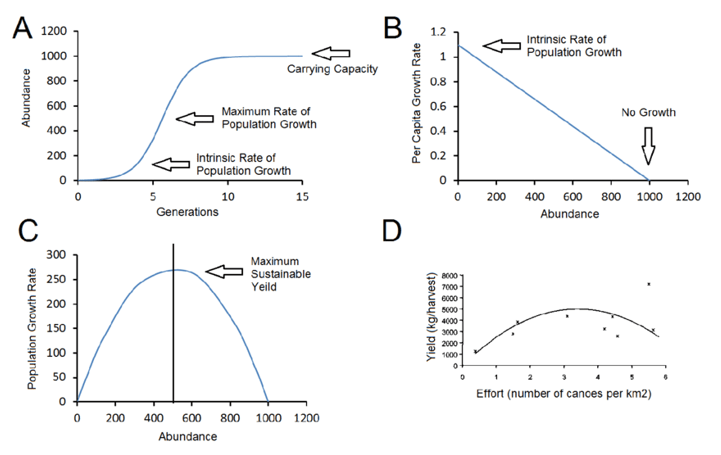
Q #10: Which of the following growth curves shows a population that is at its carrying capacity?
A. B
B. C
C. A
D. D
Answer Explanation
A population is said to be at its carrying capacity when it has reached the maximum number of individuals that can be sustained in a particular environment over a prolonged period of time, given the available resources and the prevailing environmental conditions.
In other words, carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that a given ecosystem can support without being depleted of resources or experiencing environmental degradation. Once a population reaches its carrying capacity, its growth rate slows down and stabilizes, as individuals start to compete more intensely for resources such as food, water, and shelter, and mortality rates increase.
Carrying capacity is an important concept in ecology and population biology because it helps to explain the dynamics of natural populations and how they are influenced by changes in the environment, such as climate change, habitat loss, and human activities.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
