How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
Answer Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
Answer Explanation
Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
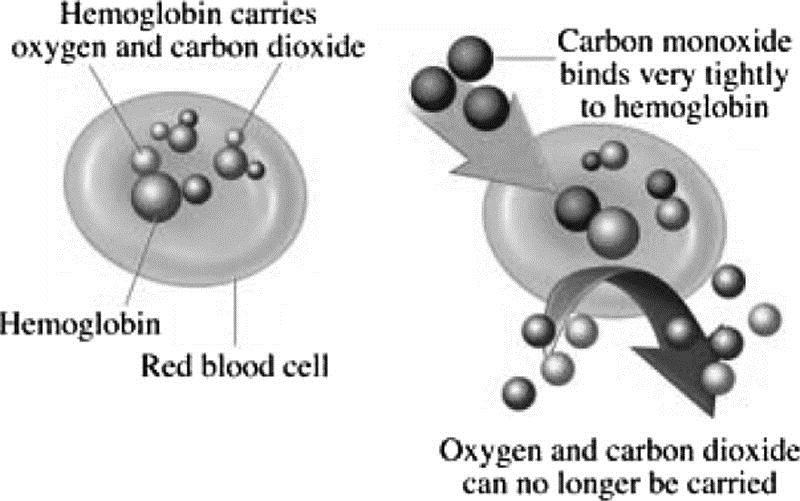
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Q #3: What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
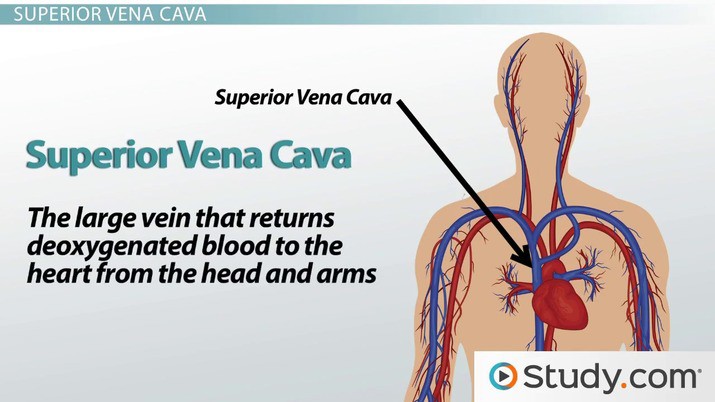
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
-
Q #4: Which subatomic particle contributes to the positive charge of an atom?
A. Proton
B. Neutron
C. Electron
D. Nucleon
Answer Explanation
Protons contribute to the positive charge of an atom.
Protons are subatomic particles with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom.
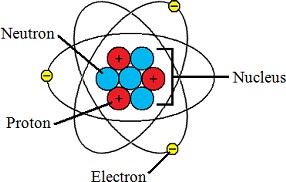
Choice B is incorrect because neutrons are neutral and do not have a charge. Choice C is incorrect because electrons have a negative charge.
Choice D is incorrect because nucleons refer to both protons and neutrons, but only protons contribute to the positive charge of an atom.
-
Q #5: What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
Answer Explanation
Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
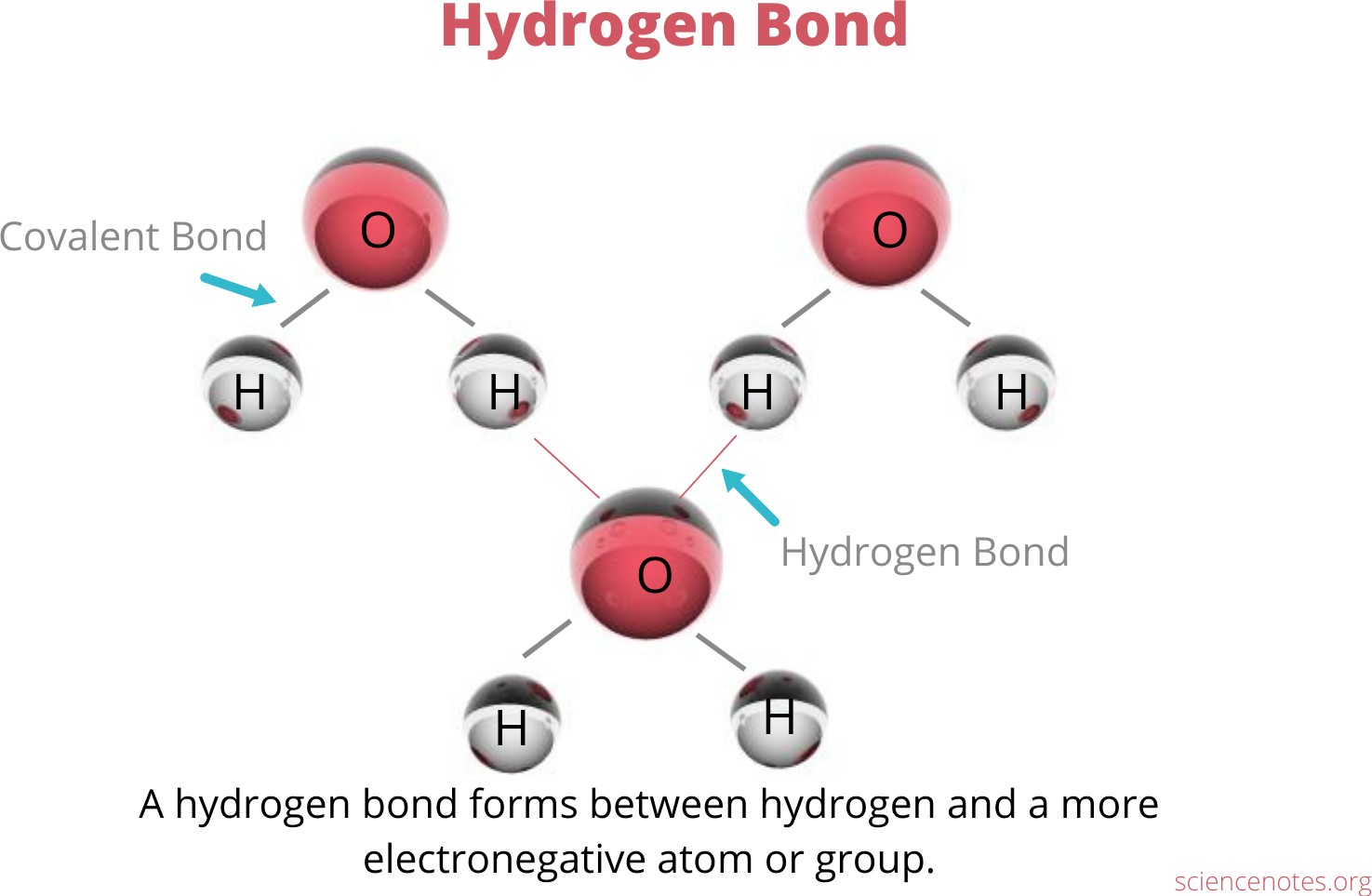
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
-
Q #6: What is the name of the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion?
A. Ionization
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Isotopic decay
Answer Explanation
Ionization is the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion.
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Choice B is not the best answer because oxidation refers to the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule.
Choice C is not the best answer because reduction refers to the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
Choice D is not the best answer because isotopic decay refers to the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
-
Q #7: Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
-
Q #8: What is the function of the neuromuscular junction?
A. To connect muscle fibers to motor neurons
B. To bind acetylcholine to nAChRs
C. To depolarize the muscle cell membrane D.
D. To activate voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane .
Answer Explanation
The neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract.
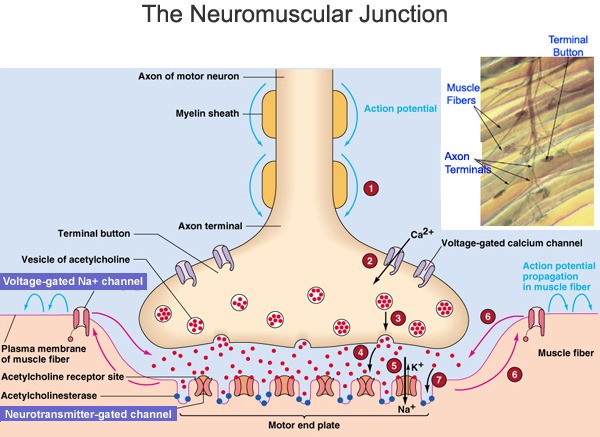
The activation of many muscle fibers together causes muscles to contract, which in turn can produce movement.
Choice B is incorrect because binding acetylcholine to nAChRs is a process that occurs at the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function of the neuromuscular junction itself.
Choice C is incorrect because depolarizing the muscle cell membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
Choice D is incorrect because activating voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
-
Q #9: Which of the following allows a limited range of immune cells to detect and respond rapidly to a wide range of pathogens that share common structures?
A. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
B. Cytokines
C. Chemokines
D. T cells .
Answer Explanation
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are a class of receptors that can directly recognize the specific molecular structures on the surface of pathogens.
PRRs play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system and are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens.
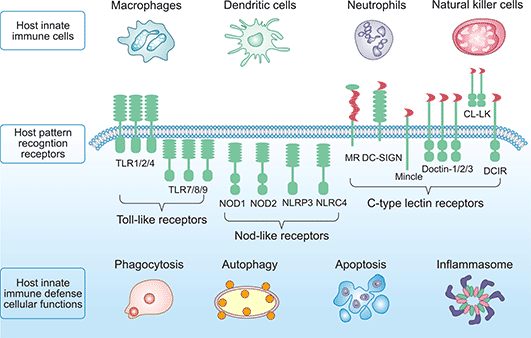
Choice B is incorrect because cytokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that regulate immunity.
Choice C is incorrect because chemokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that attract immune cells to sites of infection.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are not receptors but rather white blood cells that assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
-
Q #10: Which gland, located in the mediastinum, plays a key role in the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes?
A. Thymus
B. Parathyroid
C. Adrenal
D. Pituitary
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Thymus.
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ located in the mediastinum.
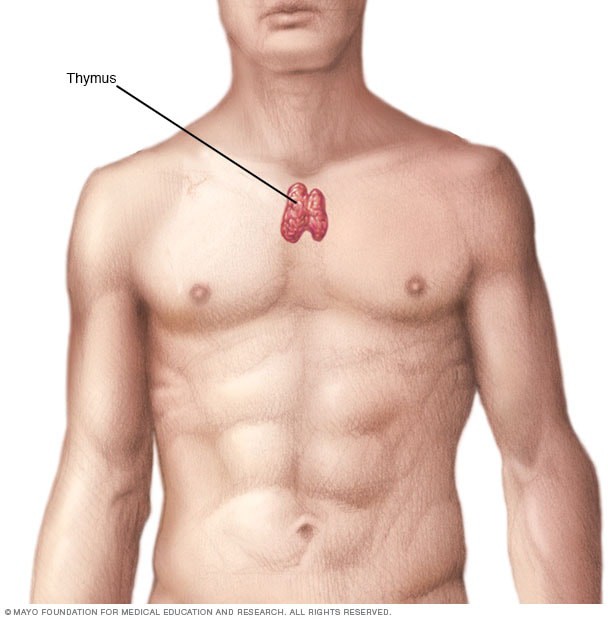
It plays a key role in the maturation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
Choice B.
Parathyroid is incorrect because the parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands located in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels in the blood.
Choice C.
Adrenal is incorrect because the adrenal glands are endocrine glands located above the kidneys that produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Choice D.
Pituitary is incorrect because the pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located at the base of the brain that produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
