If a person smells something sweet, what form of information is this initially perceived as in the nervous system?
A. Cognitive
B. Integrative
C. Motor
D. Sensory
A sensory nerve is a nerve that carries sensory signals from the external environment to the brain to the central nervous system. It is also an afferent nerve, long dendrites of sensory neurons, which sends sensory information towards the central nervous system (CNS). This information is what is sensed, using the five senses from external environment, sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch.
Motor nerves have only efferent fibers, long axons of motor neurons, that carry impulses away from the CNS to the effectors, which are typically tissues and muscles of the body.
Interneurons are nerve cells that act as a bridge between motor and sensory neurons in the CNS. These neurons help form neural circuits, which helps neurons communicate with each other.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
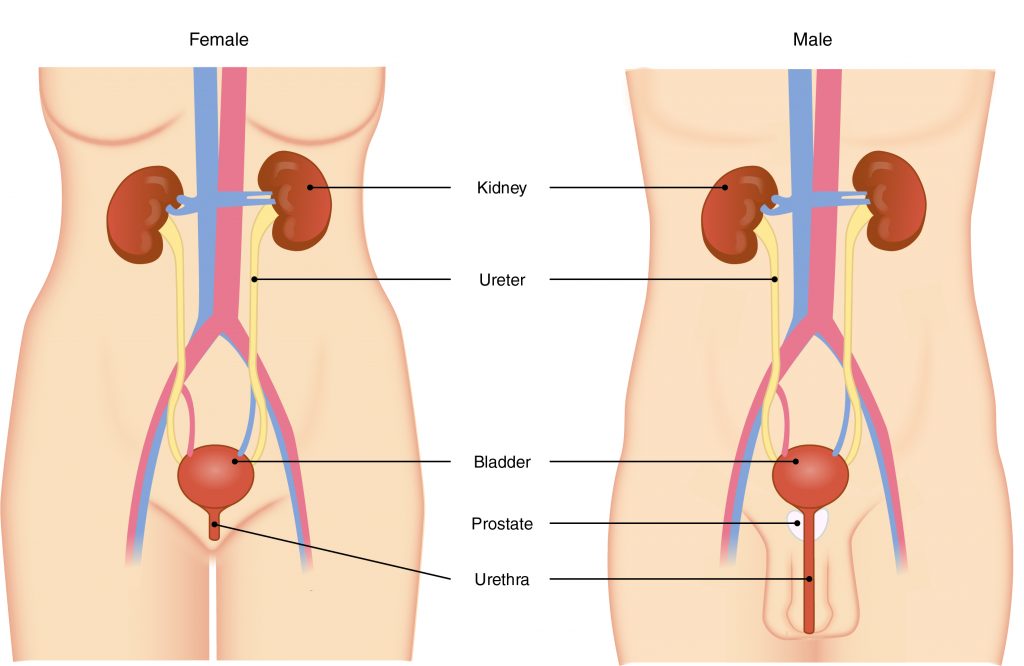
Q #1: What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
Answer Explanation
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
-
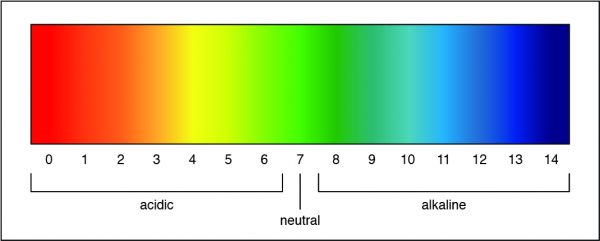
Q #2: What solution has a pH of 7?
A. Aniline
B. Pyridine
C. Pure water
D. Sodium hydroxide
Answer Explanation
A pH of 7 is a neutral solution, which is how pure water is classified. Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
-
Q #3: Which choice best describes homeostasis?
A. A functional system of the body
B. Blood flow to every cell in the body
C. A relatively constant environment within the body
D. Neural pathways that have integrated into the body
Answer Explanation
Homeostasis is the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body. Each cell of the body is surrounded by a small amount of fluid, and the normal functions of each cell depend on the maintenance of its fluid environment within a narrow range of conditions, including temperature, volume, and chemical content. These conditions are known as variables. For example, body temperature is a variable that can increase in a hot environment or decrease in a cold environment.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms in the human body: negative and positive.
- Negative Feedback: Most systems of the body are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, which maintain homeostasis. Negative means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted. The maintenance of normal blood pressure is a negative-feedback mechanism. Normal blood pressure is important because it is responsible for moving blood from the heart to tissues.
- Positive Feedback: Positive-feedback mechanisms are not homeostatic and are rare in healthy individuals. Positive means that when a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response of the system is to make the deviation even greater. Positive feedback therefore usually creates a cycle leading away from homeostasis and, in some cases, results in death. Inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of positive feedback.
-
Q #4: After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
Answer Explanation
Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.
-
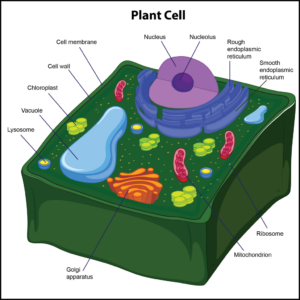
Q #5: What organelle is only associated with plant cells?
A. Cell wall
B. Ribosome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Golgi apparatus
Answer Explanation
Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells. Chloroplasts are photosynthetic compounds used to make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
-
Q #6: What is the correct order of the stages of the cell cycle?
A. G1,S,G2,M
B. G2,S,G1,M
C. M,S,G2,G1
D. S,M,G1,G1
Answer Explanation
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
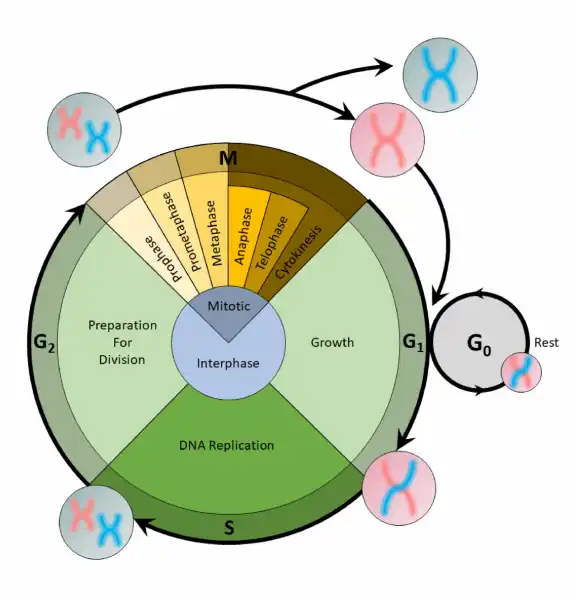
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
-
Q #7: _____ is dependent not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of substance available.
A. Condensation
B. Deposition
C. Evaporation
D. Melting
Answer Explanation
Unlike condensation, deposition, and melting, evaporation is dependent not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of a substance available.
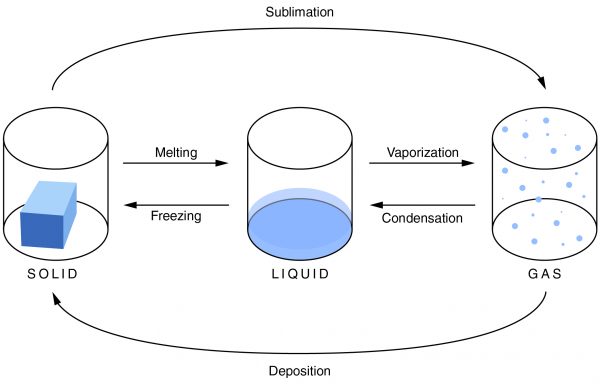
Condensation is the change of a gas or vapor to a liquid. A change in the pressure and the temperature of a substance causes this change. The condensation point is the same as the boiling point of a substance. It is most noticeable when there is a large temperature difference between an object and the atmosphere. Condensation is also the opposite of evaporation.
Evaporation is the change of a liquid to a gas on the surface of a substance. This is not to be confused with boiling, which is a phase transition of an entire substance from a liquid to a gas. The evaporation point is the same as the freezing point of a substance. As the temperature increases, the rate of evaporation also increases. Evaporation depends not only on the temperature, but also on the amount of substance available.
Freezing is the change of a liquid to a solid. It occurs when the temperature drops below the freezing point. The amount of heat that has been removed from the substance allows the particles of the substance to draw closer together, and the material changes from a liquid to a solid. It is the opposite of melting.
Melting is the change of a solid into a liquid. For melting to occur, enough heat must be added to the substance. When this is done, the molecules move around more, and the particles are unable to hold together as tightly as they can in a solid. They break apart, and the solid becomes a liquid.
Sublimation is a solid changing into a gas. As a material sublimates, it does not pass through the liquid state. An example of sublimation is carbon dioxide, a gas, changing into dry ice, a solid. It is the reverse of deposition.
Deposition is a gas changing into a solid without going through the liquid phase. It is an uncommon phase change. An example is when it is extremely cold outside and the cold air comes in contact with a window. Ice will form on the window without going through the liquid state.
-
Q #8: Why did it take many years for the cell theory to be developed?
A. Advancements in microscopy took place slowly.
B. Cells were difficult to isolate for experimental analysis
C. Researchers believed a cell formed from preexisting cells
D. Scientists already proved that cells were essential for life.
Answer Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
-
Q #9: What structure plays a role in air conduction?
A. Alveolus
B. Capillary
C. Lung
D. Trachea
Answer Explanation
The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
-
Q #10: In which state of matter do the particles of iron have the lowest amount of cohesion?
A. Solid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
B. Liquid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
C. Gaseous iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
D. The particles have the same amount of cohesion in all states of matter.
Answer Explanation
The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
