In which state of matter do the particles of iron have the lowest amount of cohesion?
A. Solid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
B. Liquid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
C. Gaseous iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
D. The particles have the same amount of cohesion in all states of matter.
The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines
A. the primary structure of a codon
B. the primary structure of a protein
C. the primary structure of a nucleotide
D. the primary structure of a nucleic acid.
Answer Explanation
The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines the primary structure of a protein. The components necessary for translation are located in the cytoplasm. Translation is the making of proteins by mRNA binding to a ribosome with the start codon that initiates the production of amino acids. A peptide bond forms and connects the amino acids together. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s structure, which determines its function.
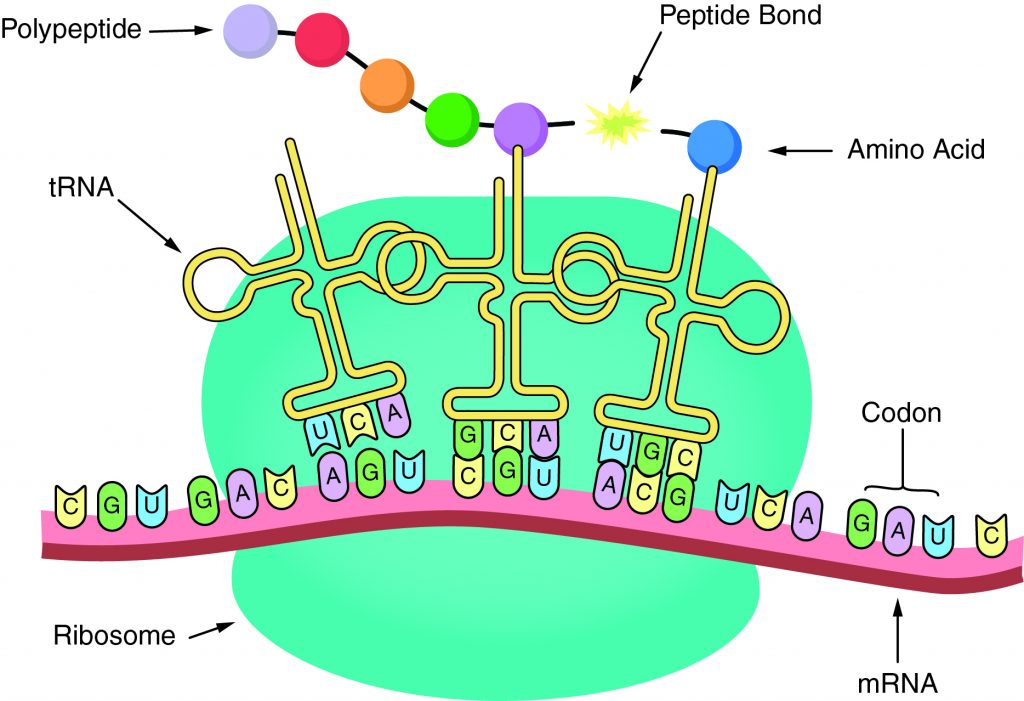
-
Q #2: What organelle is only associated with plant cells?
A. Cell wall
B. Ribosome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Golgi apparatus
Answer Explanation
Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells. Chloroplasts are photosynthetic compounds used to make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
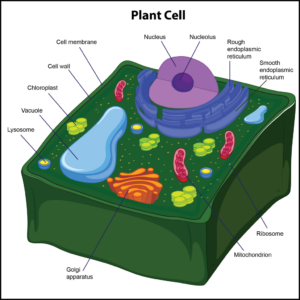
-
Q #3: Where is skeletal muscle found?
A. Inside the heart
B. Attached to bone
C. Lining the walls of the bladder
D. Within the gastrointestinal tract
Answer Explanation
Skeletal muscle: This muscle cell is striated, long, and cylindrical. There are many nuclei in a skeletal muscle cell. Attached to bones in the body, skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily, meaning that it is under conscious control.
Smooth muscle: This muscle consists of nonstriated muscle cells that are spindle-shaped. Like cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contain one nucleus. This muscle type is found in the walls of internal organs like the bladder and stomach. Smooth muscle contraction is involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle: This muscle consists of muscle cells that are striated, short, and branched. These cells contain one nucleus, are branched, and are rectangular. Cardiac muscle contraction is an involuntary process, which is why it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. This muscle is found in the walls of the heart.
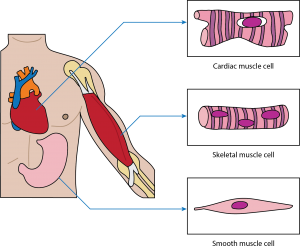
-
Q #4: In the following single-replacement reaction, ______ replaces ______. Cl2+2NaI→2NaCl+I2
A. sodium, iodine
B. chlorine, iodine
C. chlorine, sodium
D. sodium, chlorine
Answer Explanation
In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) is an element in the reaction that replaces iodine in the compound sodium iodide (NaI). This allows chlorine to form a compound with sodium (NaCl) and leaves iodine (I2) as an element.
Synthesis reactions involve two or more reactants (A and B) combining to form one product (AB). In the example provided, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) begin as separate elements. At the end of the reaction, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are bonded in a molecule of water (H2O).
Decomposition reactions have only one reactant (AB) that breaks apart into two or more products (A and B). In the example above, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breaks apart into two smaller molecules: water (H2O) and oxygen (O2).
Single-replacement reactions involve two reactants, one compound (AB) and one element (C). In this type of reaction, one element replaces another to form a new compound (AC), leaving one element by itself (B). In the example, zinc replaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid (HCl). As a result, zinc forms a compound with chlorine, zinc chloride (ZnCl2), and hydrogen (H2) is left by itself.
Double-replacement reactions involve two reactants, both of which are compounds made of two components (AB and CD). In the example, silver nitrate, composed of silver (Ag1+) and nitrate (NO31-) ions, reacts with sodium chloride, composed of sodium (Na1+) and chloride (Cl1-) ions. The nitrate and chloride ions switch places to produce two compounds that are different from those in the reactants.
Combustion reactions occur when fuels burn, and they involve specific reactants and products, as seen in the examples below. Some form of fuel that contains carbon and hydrogen is required. Examples of such fuels are methane, propane in a gas grill, butane in a lighter, and octane in gasoline. Notice that these fuels all react with oxygen, which is necessary for anything to burn. In all combustion reactions, carbon dioxide, water, and energy are produced. When something burns, energy is released, which can be felt as heat and seen as light.
-
Q #5: Which is classified as a type of acid-base reaction that produces a salt?
A. Combination
B. Decomposition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Neutralization
Answer Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes, neutralization reactions also occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as an ionic compound that includes any cation except H+ and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
-
Q #6: Fertilization (the fusing of one sperm and an ovum) results in a(n) _____.
A. embryo
B. fetus
C. infant
D. zygote
Answer Explanation
Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating a zygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
-
Q #7: An atom has 28 protons, 32 neutrons, and 28 electrons. What is the name of this isotope?
A. Nickel-32
B. Nickel-60
C. Germanium-56
D. Germanium-60
Answer Explanation
The number of protons, 28, gives the atomic number, which identifies this atom as nickel. The mass is the number after the dash in the isotope name, which is determined by adding the numbers of protons and neutrons (28 + 32 = 60).
-
Q #8: Which blood group is a universal donor?
A. A
B. B
C. AB
D. O
Answer Explanation
A person can be a universal blood donor or acceptor. A universal blood donor has type O blood, while a universal blood acceptor has type AB blood.
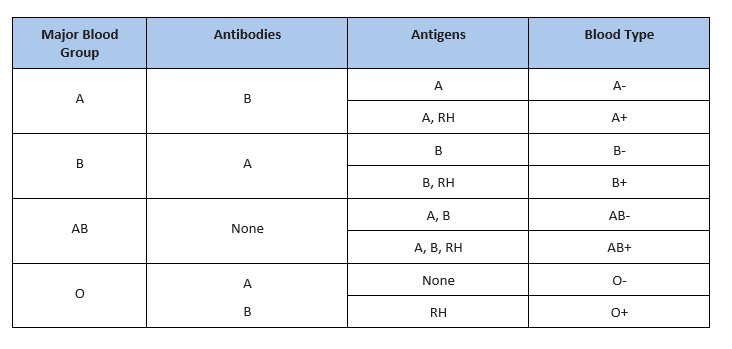
There are several different types or groups of blood, and the major groups are A, B, AB, and O. Blood group is a way to classify blood according to inherited differences of red blood cell antigens found on the surface of a red blood cell. The type of antibody in blood also identifies a particular blood group. Antibodies are proteins found in the plasma. They function as part of the body’s natural defense to recognize foreign substances and alert the immune system.
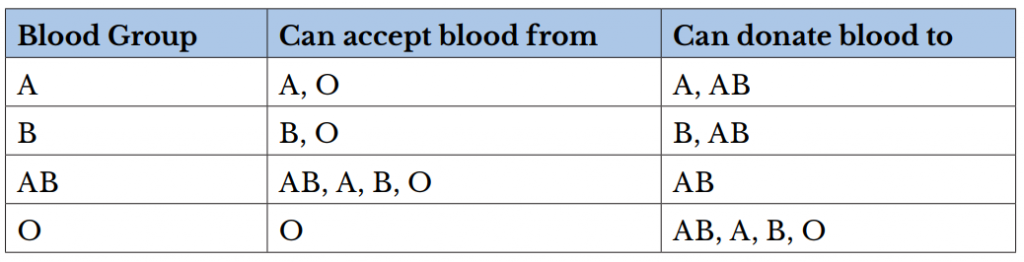
Depending on which antigen is inherited, parental offspring will have one of the four major blood groups. Collectively, the following major blood groups comprise the ABO system:
- Blood group A: Displays type A antigens on the surface of a red blood cell and contains B antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group B: Displays type B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface and contains A antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group O: Does not display A or B antigens on the surface of a red blood cell. Both A and B antibodies are in the plasma.
- Blood group AB: Displays type A and B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface, but neither A nor B antibodies are in the plasma
In addition to antigens, the Rh factor protein may exist on a red blood cell’s surface. Because this protein can be either present (+) or absent (-), it increases the number of major blood groups from four to eight: A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, and AB-.
-
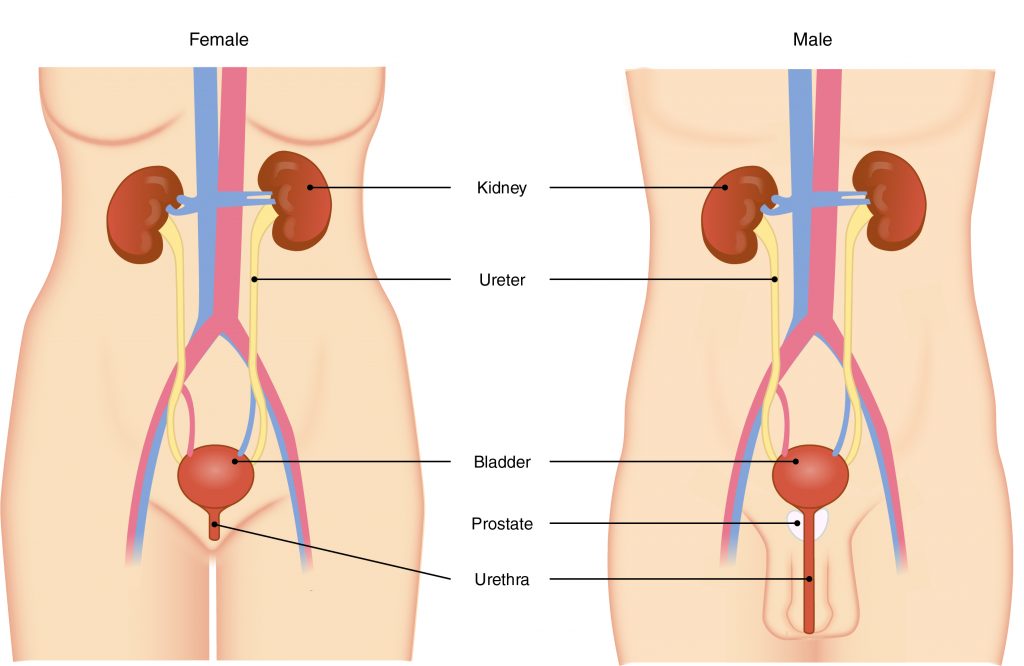
Q #9: What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
Answer Explanation
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
-
Q #10: What type of reaction is described by the following equation? ZnBr2(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2KBr(aq)
A. Synthesis
B. Decomposition
C. Single-Replacement
D. Double-Replacement
Answer Explanation
In this reaction, two elements are trading places hence double-replacement. In the reactants, zinc and bromide ions are together, and potassium and hydroxide ions are together. In the products, zinc and hydroxide ions are together, and potassium and bromide ions are together.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
