The ________ circulation picks up oxygen for cellular use and drops off carbon dioxide for removal from the body.
A. pulmonary
B. interlobular
C. respiratory
D. bronchial
Our blood flow is separated into two major pathways, listed below:
- Systemic circulation - this comes from the left side of the heart and pumps blood to all working tissues, including the brain, muscle, heart, and other organs, and then into the right side of the heart.
- Pulmonary system - this comes from the right side of the heart, and pumps blood to the alveolar sacs within the lungs, and then into the left side of the heart
In pulmonary circulation: The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: If a portion of strand of DNA bases reads 5’ AGCTAGCGT 3’, what would the sequence of bases on the complementary strand read?
A. 5’ UCGAUCGCA 3’
B. 3’ TCGATCGCA 5’
C. 5’ TCGUTCGCU 3’
D. 3’ AGCTAGCGT 5’
Answer Explanation
The complimentary base pairing of DNA states that A pairs with T while C pairs with G. From the give sequence, the complimentary DNA strand will be 3’ TCGATCGCA 5’
-
Q #2: Punnett square In a certain plant, red flowers are dominant over white flowers. A plant heterozygous for red flowers and a plant with white flowers are crossed. Which of the following is the expected proportion of phenotypes in the next generation?
A. 4 red, 0 white
B. 2 red, 2 white
C. 1 red, 3 white
D. 3 red, 1 white
Answer Explanation
We use the Punnet square to find the population of the resulting offspring from the crossing of a plant heterozygous for red flowers with a plant with white flowers.
Let R be the dominant allele for red while r is the recessive allele color for red. Therefore, the phenotype for parent 1 which is heterozygous for red flower will be Rr and the second parent with white flowers will be rr.
We cross the two phenotypes in a Punnet square as follows
r
r
R
Rr
Rr
r
rr
rr
Thus, there are 2 heterozygous offspring with red flowers and 2 offspring with white flowers.
-
Q #3: Which of these infectious agents do not have nucleic acid?
A. viroids
B. viruses
C. bacteria
D. prions
Answer Explanation
-
Q #4: Which of the following sequences on a DNA molecule would be complementary to GCTTATAT?
A. TAGGCGCG
B. ATCCGCGC
C. CGAATATA
D. TGCCTCTC
Answer Explanation
-
Q #5: Nitrogen gas is an extremely stable molecule because its structure contains which of the following?
A. Resonance bonds
B. Ionic bonds
C. Triple covalent bonds
D. Hydrogen bonds
Answer Explanation
The Lewis structure of nitrogen gas is shown below. Triple bonds are stronger than double or single bonds. Therefore, we can infer that the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms makes nitrogen gas more stable.
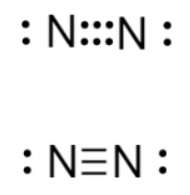
-
Q #6: Which of the following are used to determine a person’s DNA sequence?
A. Genes
B. Enzymes
C. Hormones
D. Blood types
Answer Explanation
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity and it is the DNA that make up genes. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up metabolic and cellular reactions in our bodies. Hormones are responsible for controlling the action of certain cells or organs in our bodies. Blood types are of four types, A, B, AB, and O.
-
Q #7: The ________ circulation picks up oxygen for cellular use and drops off carbon dioxide for removal from the body.
A. pulmonary
B. interlobular
C. respiratory
D. bronchial
Answer Explanation
Our blood flow is separated into two major pathways, listed below:
- Systemic circulation - this comes from the left side of the heart and pumps blood to all working tissues, including the brain, muscle, heart, and other organs, and then into the right side of the heart.
- Pulmonary system - this comes from the right side of the heart, and pumps blood to the alveolar sacs within the lungs, and then into the left side of the heart
In pulmonary circulation: The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide.
-
Q #8: The Life Cycle of HIV Which of the following allows the AIDS virus, which contains RNA, to insert viral DNA into the DNA of a host T-cell after the AIDS virus enters the cell?
A. Receptor proteins located on the surface of the virus
B. The protein that makes up the capsid of the virus
C. Reverse transcriptase, an enzyme encoded by the virus
D. The phospholipids found on the envelope of the virus
Answer Explanation
The AIDS virus (HIV virus) is Class VI or Group VI in the Baltimore Classification. Based on the Baltimore Classification, this specifically involves the reverse transcriptase enzyme and it is encoded by the virus.
This is the enzyme that will produce DNA molecules from the viral RNA. This is the mechanism involved where it will use the reverse transcriptase enzyme to insert viral DNA into the genetic material of the host cell.
-
Q #9: Which of these processes occurs in the mouth?
A. Ingestion
B. Mechanical digestion
C. Chemical digestion
D. All of the above
Answer Explanation
All of these processes occur in the mouth. Ingestion involves taking food into the mouth, mechanical digestion includes the physical breakdown of food through chewing and mixing with saliva, and chemical digestion begins with the action of enzymes in saliva, such as amylase, which starts to break down carbohydrates.
-
Q #10: Which of the following is the atomic number of an atom that has 12 protons and 12 neutrons?
A. 144
B. 12
C. 24
D. 1
Answer Explanation
elements are arranged on the periodic table based on their atomic number. This identity is critical in evaluating the chemical families of elements in chemistry. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus while electrons are found outside the nucleus of the atom. It is the number of protons of an atom that gives its atomic number. Therefore, an atom with 12 protons has an atomic number of 12.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
