The covalent bonds between the monomers of an enzyme macromolecule are:
A. Ester bonds
B. Peptide bonds
C. Phosphodiester bonds
D. Glycosidic bonds
The correct answer is b. Peptide bonds. Enzymes are proteins, and proteins are made up of amino acid monomers linked together by peptide bonds. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
a. Ester bonds are covalent bonds that form between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
c. Phosphodiester bonds are covalent bonds that form between a phosphate group and two hydroxyl
groups.
d. Glycosidic bonds are covalent bonds that form between two monosaccharides.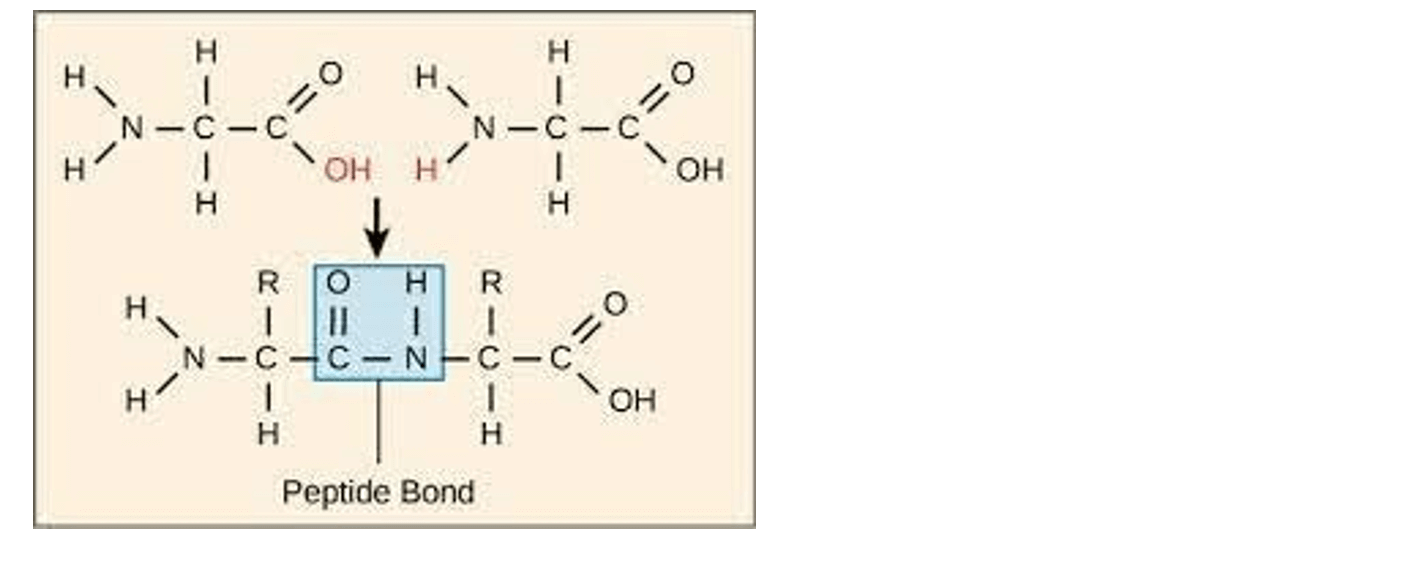
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: The mitochondrial inner membrane carries out the same function in cellular respiration as the ________ membrane of chloroplasts in photosynthesis. Which of the following correctly completes the sentence above?
A. Thylakoid
B. Epithelial
C. Nuclear
D. Tonoplast
Answer Explanation
The thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts is where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place, while the mitochondrial inner membrane is where the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis occur during cellular respiration.
The tonoplast is the membrane that surrounds the central vacuole in plant cells. It is not involved in cellular respiration or photosynthesis.
The other options, epithelial and nuclear, are not related to these processes.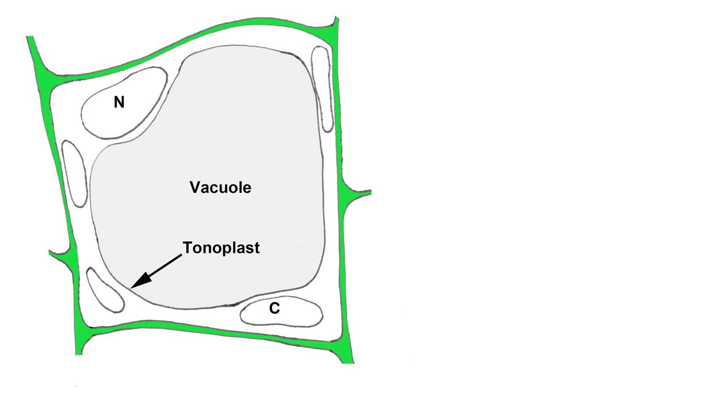
-
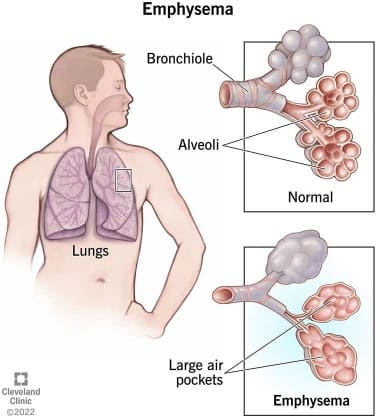
Q #2: Emphysema caused by damage to alveoli from toxins and pollutants is likely to result in the body having difficulty performing which of the following actions?
A. Releasing histamine and acetylcholine
B. Exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide
C. Absorbing food
D. Producing enzymes
Answer Explanation
Emphysema is a lung condition that is caused by damage to the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. When the alveoli are damaged, the body has difficulty exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide. This can lead to shortness of breath and other respiratory problems. The other options are not directly related to the function of the alveoli or the effects of emphysema.
-
Q #3: Experiments cannot validate hypotheses, only falsify them. The statement above can be restated in which of the following ways?
A. a. Until disproved, an explanation for an observation is valid.
B. b. Certain concepts cannot be subjected to direct experimentation.
C. c. A hypothesis that has not been falsified remains provisional.
D. d. Proving a hypothesis exempts it from further testing
Answer Explanation
The statement "Experiments cannot validate hypotheses, only falsify them" can be restated as "A hypothesis that has not been falsified remains provisional." This means that a hypothesis is considered valid until it is disproved by experimental evidence. However, even if a hypothesis has not been falsified, it is still considered provisional and subject to further testing and scrutiny.
a."Until disproved, an explanation for an observation is valid" is similar to the correct answer but does not capture the provisional nature of a hypothesis.
b."Certain concepts cannot be subjected to direct experimentation" is not a restatement of the original statement.
d. "Proving a hypothesis exempts it from further testing" is incorrect because no hypothesis can be definitively proven and all hypotheses are subject to further testing and scrutiny.
-
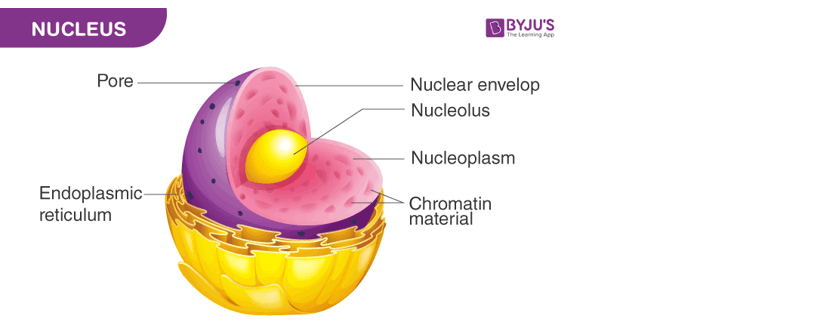
Q #4: Genetic information describing the characteristics of an organism is found in which of the following?
A. Nuclei
B. Membranes
C. Cilia
D. Ribosomes
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is a. Nuclei. Genetic information describing the characteristics of an organism is found in the nuclei of its cells. The nucleus contains the organism's DNA, which carries the genetic information that determines its traits.
b. Membranes are structures that surround and enclose cells and organelles, but they do not contain genetic information.
c. Cilia are hair-like structures that protrude from the surface of some cells and are involved in movement, but they do not contain genetic information.
d. Ribosomes are organelles that are involved in protein synthesis, but they do not contain genetic information.
-
Q #5: Lipids absorbed in the small intestine will first enter which of the following structures?
A. Veins
B. Arteries
C. Lacteal vessels
D. Interstitial spaces
Answer Explanation
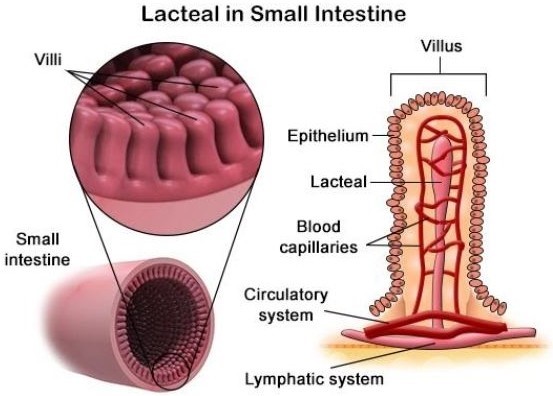
The correct answer is c. Lacteal vessels. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine will first enter lacteal vessels, which are small lymphatic vessels located in the villi of the small intestine. These vessels transport the absorbed lipids to the lymphatic system, where they eventually enter the bloodstream.
a. Veins and b. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood throughout the body. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine do not directly enter these vessels.
d. Interstitial spaces are spaces between cells and tissues that contain interstitial fluid. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine do not directly enter these spaces.
-
Q #6: Hikers who found a human body at high altitude in the Italian Alps thought the man had died recently, but tests indicated he was shot with an arrow more than 5,300 years ago. Which of the following would be the best reason for prolonged preservation of the body?
A. The ultraviolet rays at such a high altitude caused all his molecules to be preserved.
B. The food that the person ate contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body.
C. The body was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found.
D. The arrow wound caused blood to flow out of the body which led the enzymes that would break down tissue to be cleared from the body.
Answer Explanation
The best reason for the prolonged preservation of the body is that it was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after death and remained frozen until it was found. Freezing can preserve a body by slowing down or stopping the decomposition process.
The other options are not as likely to have caused prolonged preservation.
Ultraviolet rays can damage molecules rather than preserve them. Toxins in food would not necessarily kill all bacteria that could cause decomposition. Blood loss from an arrow wound would not necessarily clear all enzymes that could break down tissue.
-
Q #7: Which of the following is the function of a totipotent cell?
A. Develops into any kind of cell
B. Fights infectious diseases
C. Aids in the maturation of sex cells
D. Carries electrical impulses
Answer Explanation
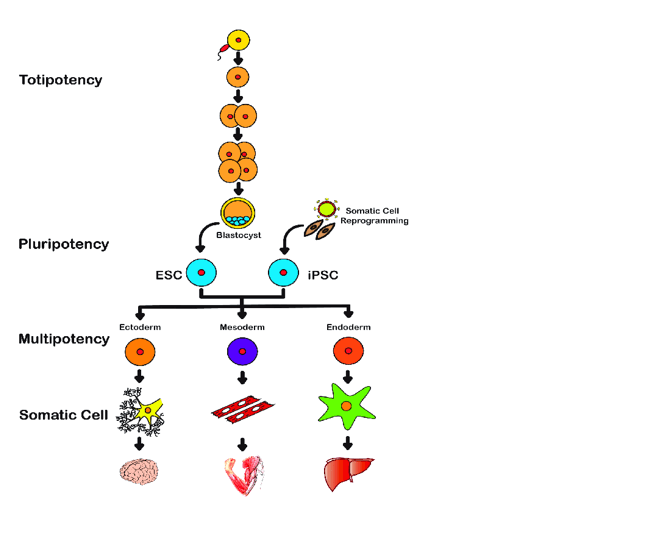
The function of a totipotent cell is to develop into any kind of cell ¹. Totipotent cells have the capacity to produce all adult cell types and can enter the germ line, contributing genetic material to succeeding generations ?. They have the ability to self-replicate, producing daughter cells that are identical to the parent ?.
The other options are incorrect because they do not accurately describe the function of a totipotent cell. Fighting infectious diseases, aiding in the maturation of sex cells, and carrying electrical impulses are not functions performed by totipotent cells.
-
Q #8: Which of the following functions does the myelin sheath perform for a nerve cell?
A. Insulation
B. Regeneration
C. Sensory perception
D. Nutrition
Answer Explanation
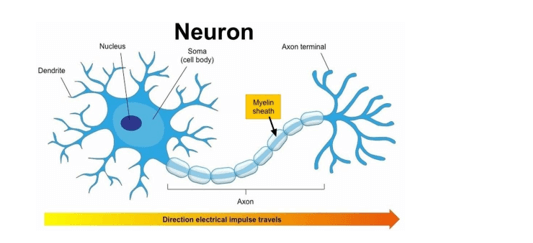
The myelin sheath is a protective membrane that wraps around parts of certain nerve cells.
Its fatty-protein coating provides protective insulation for your nerve cell like the plastic insulation covering that encases the wires of an electrical cord ².
This allows the electrical impulses to travel quickly and efficiently between one nerve cell and the next. The other options are incorrect because they do not describe the functions of the myelin sheath.
Regeneration, sensory perception, and nutrition are not functions performed by the myelin sheath for a nerve cell.
-
Q #9: Which of the following summarizes a change that takes place as a solid turns to a liquid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. Particles become less ordered.
C. Particles move closer together.
D. Intermolecular forces between particles become stronger.
Answer Explanation
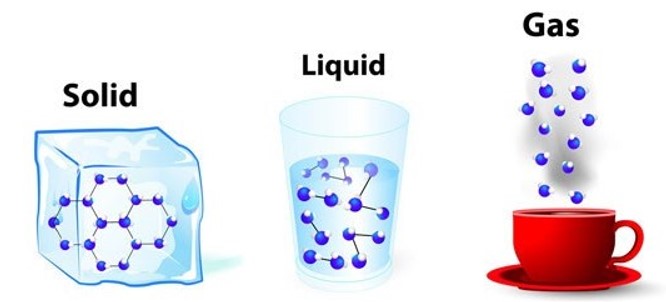
A change that takes place as a solid turns to a liquid is that particles become less ordered ¹. When a solid is heated, its particles gain energy and begin to vibrate more rapidly ². As the temperature increases, the particles gain enough energy to overcome the forces holding them in place and begin to move more freely
². This results in a loss of order as the solid melts and becomes a liquid.
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe a change that takes place as a solid turns to a liquid. Particles do not have a decrease in mobility, move closer together, or experience stronger intermolecular forces between them as a solid turns to a liquid.
-
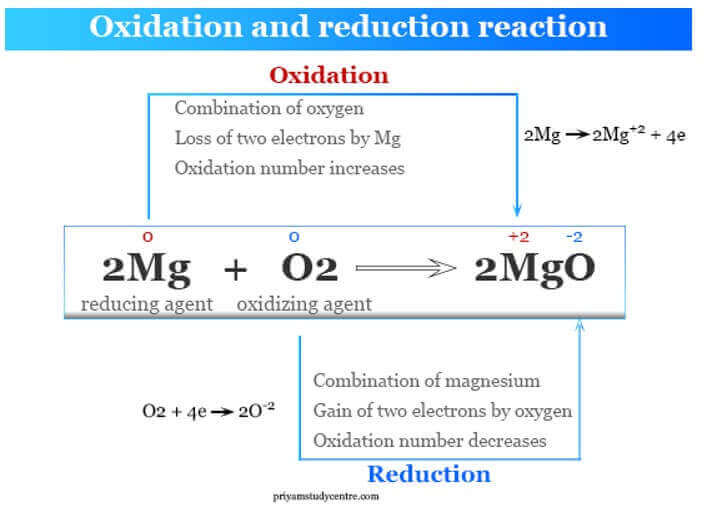
Q #10: Which of the following occurs in an oxidation reaction?
A. Removal of oxygen
B. Addition of carbon
C. Addition of neutrons
D. Removal of electrons
Answer Explanation
An oxidation reaction occurs when there is a removal of electrons ¹. Oxidation is the loss of electrons during a reaction by a molecule, atom or ion ¹. When oxidation occurs, the oxidation state of the chemical species increases ¹.
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe what occurs in an oxidation reaction. Removal of oxygen, addition of carbon, and addition of neutrons are not processes that occur in an oxidation reaction.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
