What is the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions?
A. Isotonic contractions produce no movement while isometric contractions produce movement.
B. Isotonic contractions produce movement while isometric contractions produce no movement.
C. Isotonic contractions generate tension in the muscle while isometric contractions involve shortening of the muscle fibers.
D. Isotonic contractions involve contraction of individual muscle fibers while isometric contractions involve the entire muscle.
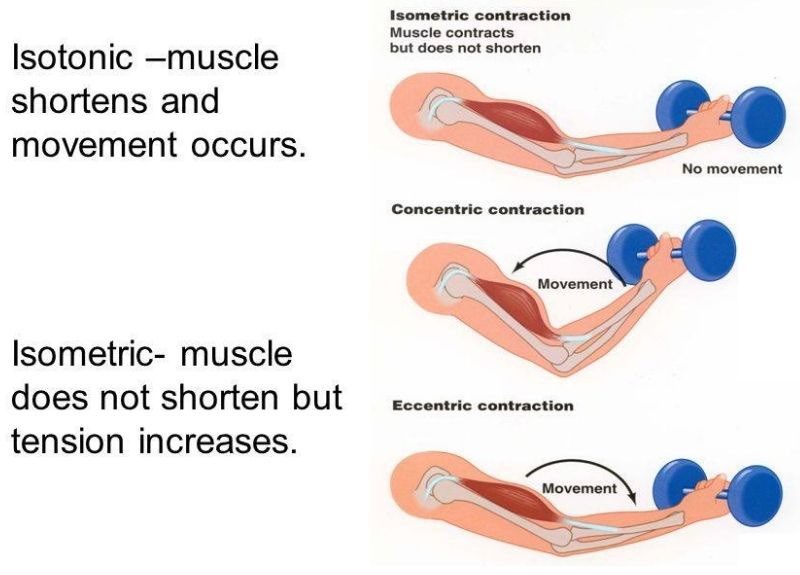
Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
 |
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following statements is true regarding vaccines?
A. Vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against
B. Vaccines work by providing passive immunity to the individual
C. Vaccines work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of the pathogen
D. Vaccines only provide protection against bacterial infections
Answer Explanation
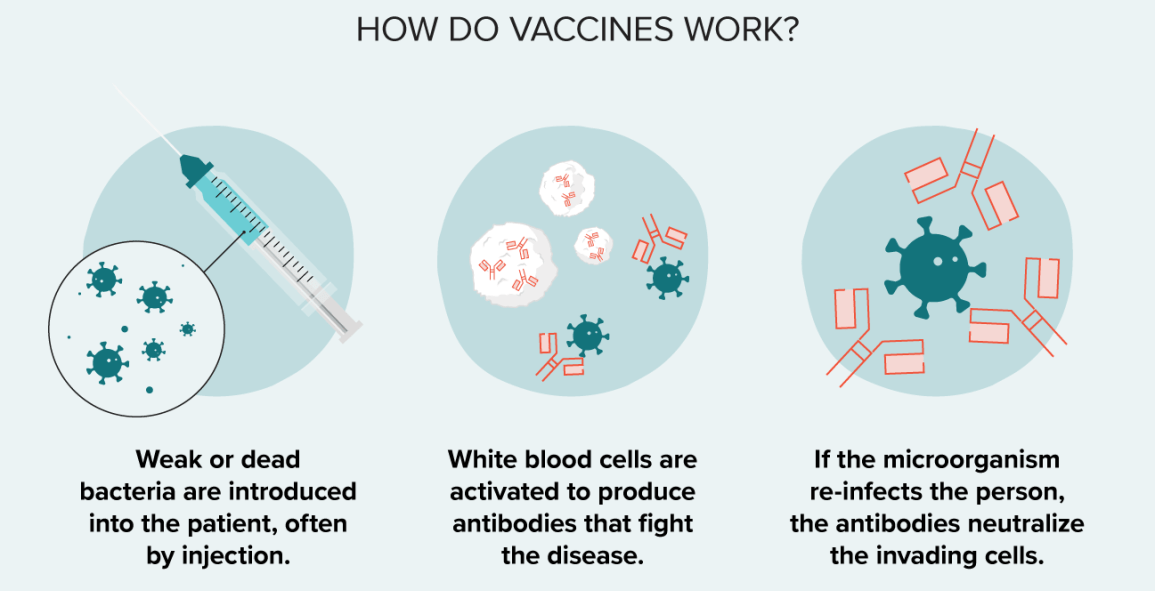
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is NOT one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body?
A. Epithelial
B. Nervous
C. Connective
D. Exocrine glandular
Answer Explanation
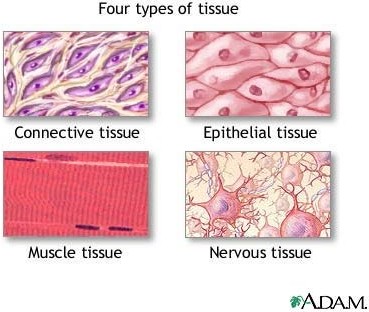
Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body. The four primary tissue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
-
Q #3: What are the five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards?
A. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
B. Thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
C. Lumbar, thoracic, cervical, coccygeal, sacral
D. Sacral, lumbar, cervical, thoracic, coccygeal
Answer Explanation
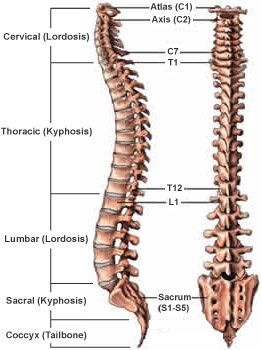
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
- Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
- Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
- Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
- Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
-
Q #4: What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
A. Calcium binds to tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
B. Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to initiate the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
C. Calcium activates the motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction.
D. Calcium is required for the relaxation of muscles after contraction.
Answer Explanation
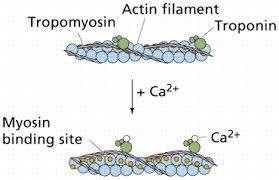
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
-
Q #5: Which of the following describes the process of osmosis?
A. Movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
B. Movement of substances against a concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
C. Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
D. Movement of substances into a cell by engulfing them with the plasma membrane.
Answer Explanation
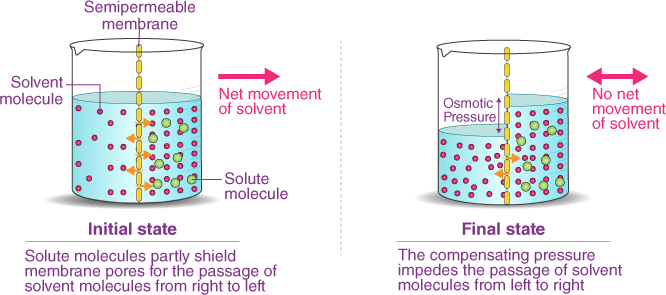
Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
-
Q #6: Which of the following units is used to indicate length?
A. kg
B. L
C. s
D. m
Answer Explanation
The unit used to indicate length is the meter (m). It is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
-
Q #7: What is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants?
A. Chlorophyll a
B. Chlorophyll b
C. Carotenoids
D. Anthocyanins
Answer Explanation
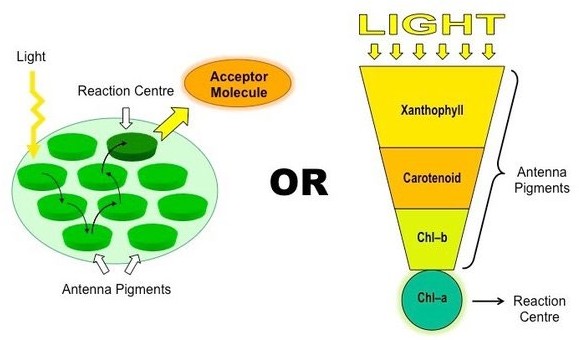
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants. It is a green pigment that is essential for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant. Chlorophyll a absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll that is also involved in photosynthesis, but it is not as abundant as chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll b absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and orange parts of the spectrum and reflects yellow-green light.
Carotenoids are pigments that are present in many plants and are involved in photosynthesis as well as protecting the plant from damage caused by excess light. Carotenoids are responsible for the orange, yellow, and red colors of many fruits and vegetables.
Anthocyanins are pigments that give plants their red, purple, and blue colors. While they are not directly involved in photosynthesis, they play a role in atracting pollinators and protecting the plant from damage caused by UV radiation.
-
Q #8: Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
A. Transport of nutrients to the body
B. Pumping of blood to the lungs
C. Exchange of gases between the body and the environment
D. Digestion of food in the stomach
Answer Explanation
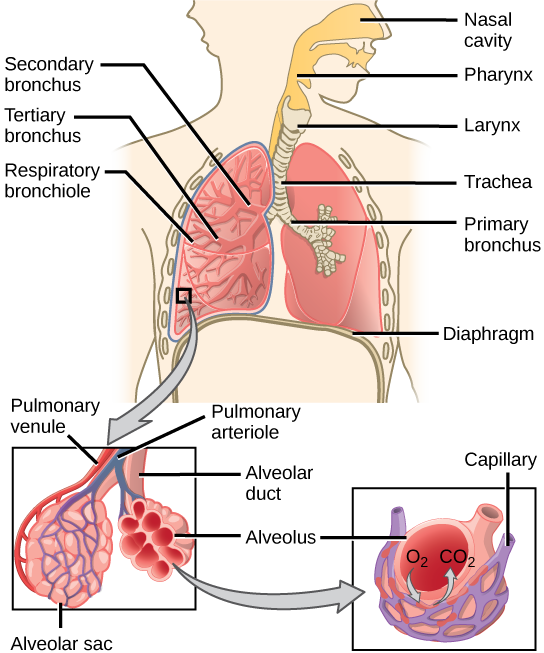
One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
-
Q #9: What is the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions?
A. Isotonic contractions produce no movement while isometric contractions produce movement.
B. Isotonic contractions produce movement while isometric contractions produce no movement.
C. Isotonic contractions generate tension in the muscle while isometric contractions involve shortening of the muscle fibers.
D. Isotonic contractions involve contraction of individual muscle fibers while isometric contractions involve the entire muscle.
Answer Explanation
Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.

-
Q #10: What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
A. Elbow joint
B. Hip joint
C. Knee joint
D. Shoulder joint
Answer Explanation
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
