What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
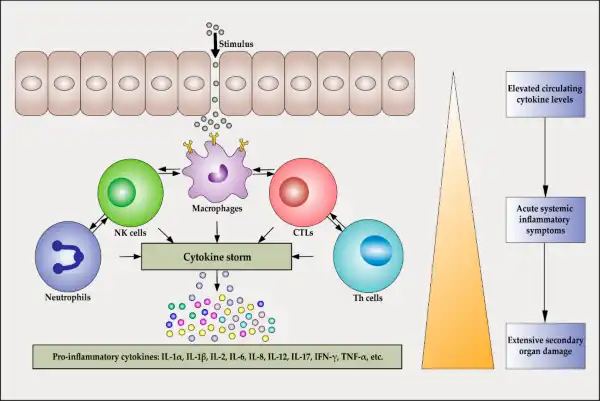
Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.
Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
Answer Explanation
Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.

Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is true regarding the role of oncogenes in cancer development?
A. Mutations in oncogenes always result in the inhibition of cell division.
B. Oncogenes are only found in human cells and not in any other organism.
C. Genes that regulate cell division are not found in any viruses.
D. Genes that regulate cell division can become oncogenes when mutated.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice D.
Genes that regulate cell division can become oncogenes when mutated.
Oncogenes are mutated genes that can contribute to the development of cancer.
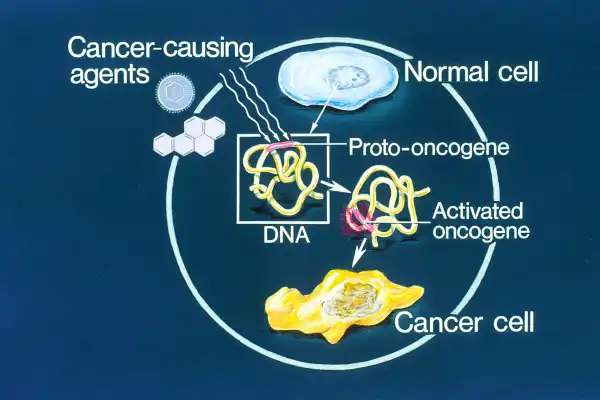
In their non-mutated state, everyone has genes which are referred to as proto- oncogenes.
When proto-oncogenes are mutated or increased in numbers due to DNA damage, the proteins produced by these genes can affect the growth, proliferation, and survival of the cell, and potentially result in the formation of a malignant tumor.
Choice A is incorrect because mutations in oncogenes do not always result in the inhibition of cell division.
Instead, they can contribute to the development of cancer by affecting cell growth.
Choice B is incorrect because oncogenes are not only found in human cells but can be present in other organisms as well.
Choice C is incorrect because genes that regulate cell division can be found in viruses. -
Q #3: What is the organelle that encapsulates the contents of the cell and plays a vital role in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell?.
A. Ribosome
B. Nucleus
C. Mitochondria
D. Plasma membrane.
Answer Explanation
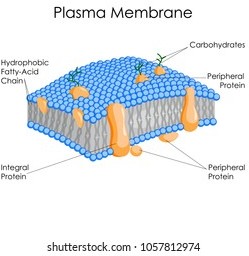
The plasma membrane is the organelle that encapsulates the contents of the cell and plays a vital role in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
It is a selectively permeable barrier that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment.
Choice A is incorrect because ribosomes are organelles involved in protein synthesis, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Choice B is incorrect because the nucleus is an organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because mitochondria are organelles involved in energy production, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
-
Q #4: Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
Answer Explanation
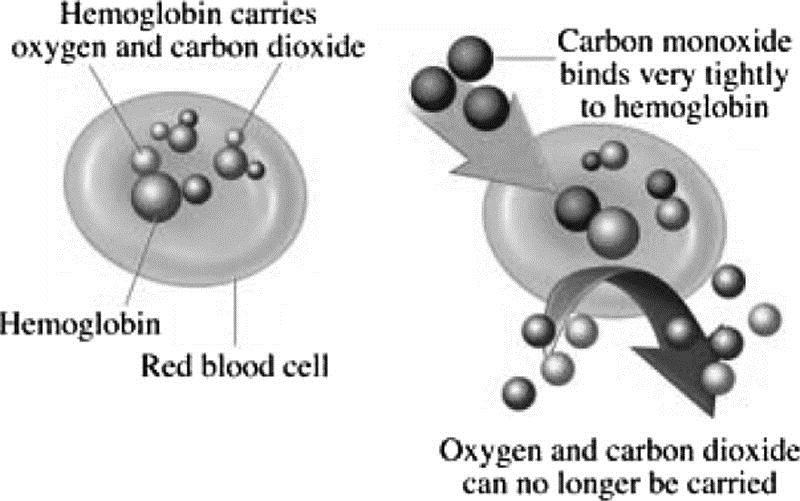
Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Q #5: What is the name of the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion?
A. Ionization
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Isotopic decay
Answer Explanation
Ionization is the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion.
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Choice B is not the best answer because oxidation refers to the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule.
Choice C is not the best answer because reduction refers to the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
Choice D is not the best answer because isotopic decay refers to the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
-
Q #6: Which of the following refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand?
A. Orthopnea
B. Hypoxia
C. Tachypnea
D. Bradypnea
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Orthopnea.
Orthopnea refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand.
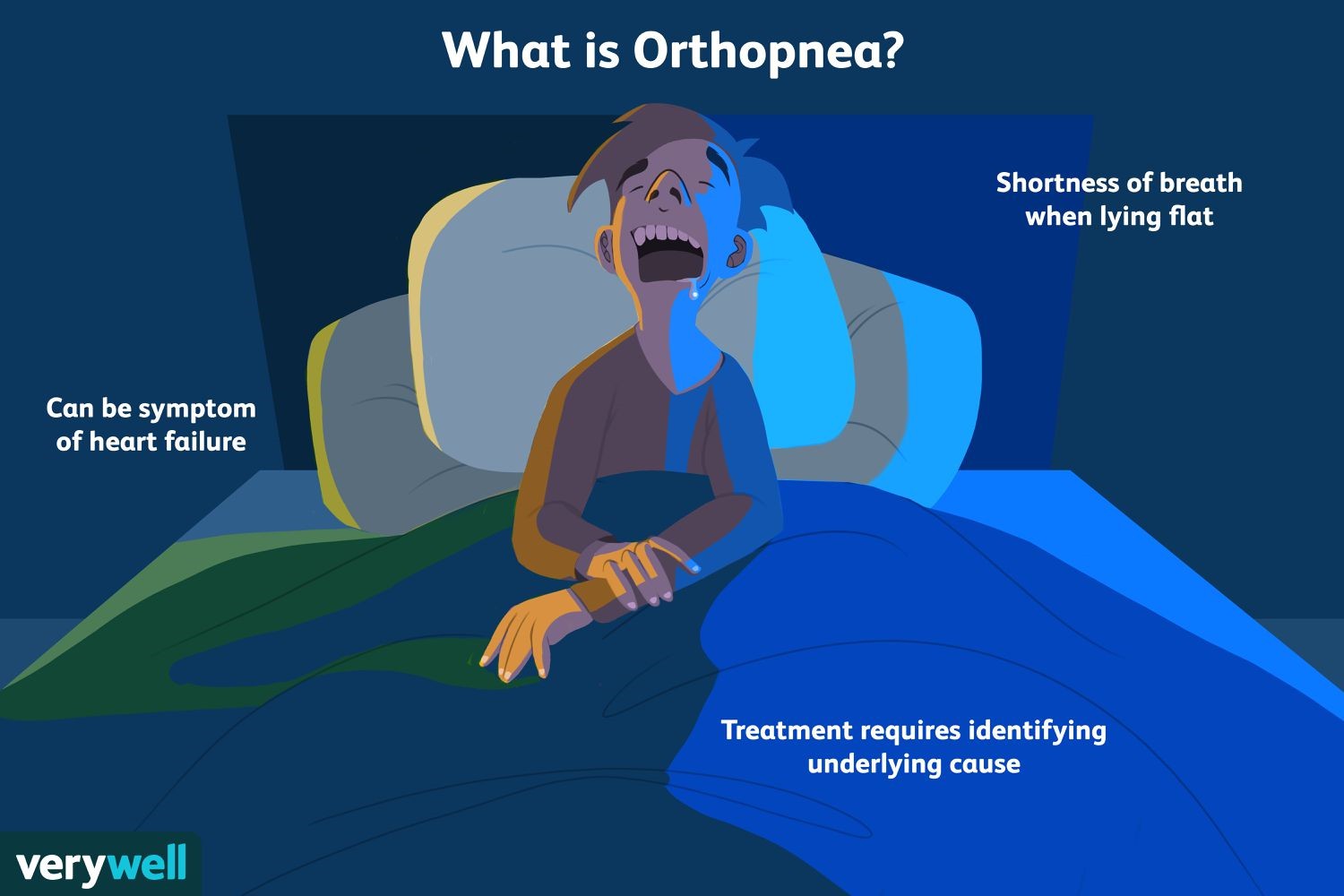
Choice B, Hypoxia, is not the correct answer because it refers to a condition in which there is a lack of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Choice C, Tachypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to rapid breathing.
Choice D, Bradypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to abnormally slow breathing.
-
Q #7: In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between what?.
A. Control group and treatment group.
B. Independent variable and dependent variable.
C. Experimental group and non-experimental group.
D. High level and low level of the independent variable.
Answer Explanation
In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between the control group and treatment group.
This means researchers can correctly measure the entire effect of the treatment without interference from confounding variables.
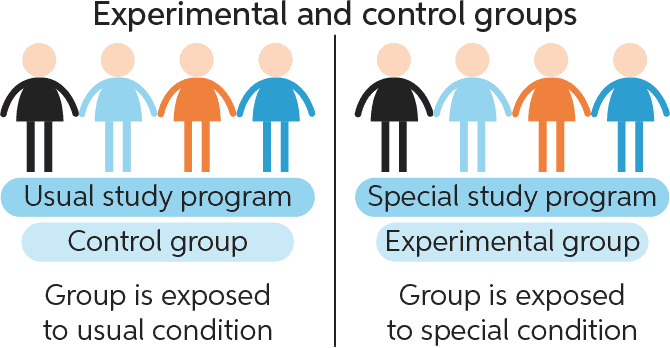
Choice B) Independent variable and dependent variable is incorrect because these are not groups but rather variables.
The independent variable is manipulated by the experimenters while the dependent variable is measured to see if it changes as a result of the manipulation.
Choice C) Experimental group and non-experimental group is incorrect because a non-experimental group is not a term used in experimental design.
The correct term for the group that does not receive the treatment is control group.
Choice D) High level and low level of the independent variable is incorrect because these are levels of the independent variable, not groups.
In an experiment, there can be multiple levels of the independent variable, but they are applied to different groups (e.g.
control group, treatment group).
-
Q #8: Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
Answer Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
-
Q #9: A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder. The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
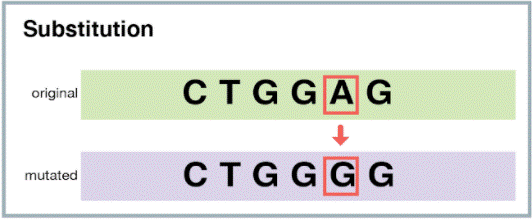
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
-
Q #10: Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
Answer Explanation
Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
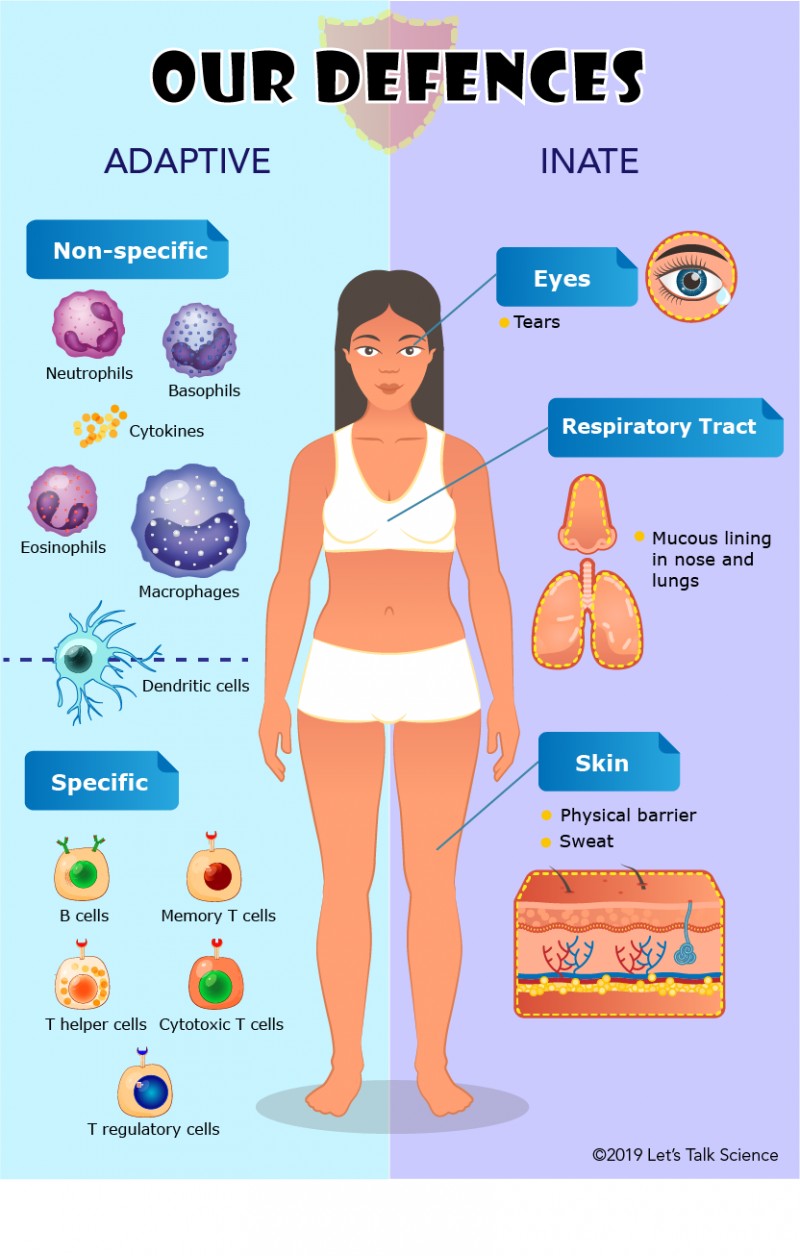
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
