What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
A. To produce energy for the cell
B. To store genetic information
C. To transport molecules within the cell
D. To synthesize proteins in the cell
Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
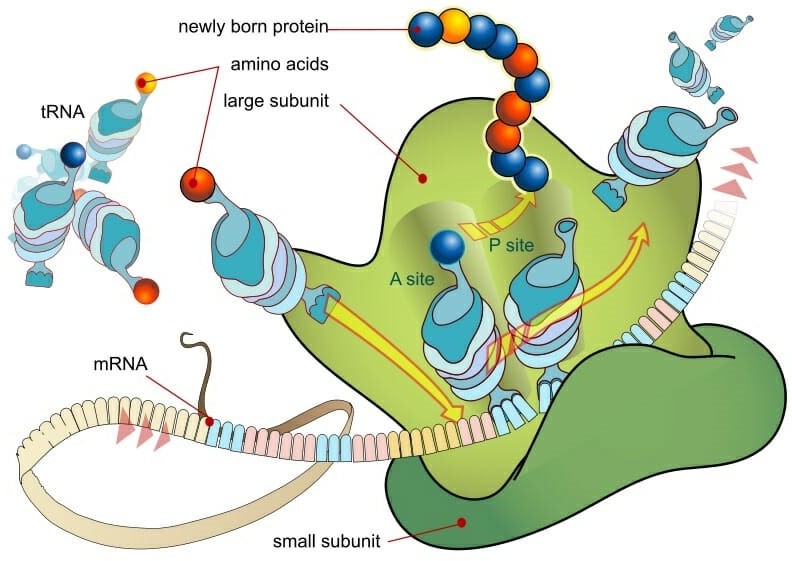
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What are the three types of salivary glands and where are they located in the mouth?
A. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the cheeks, tongue, and roof of the mouth, respectively.
B. Sublingual, submandibular, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
C. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the roof of the mouth, cheeks, and under the jawbone, respectively.
D. Sublingual, parotid, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
Answer Explanation
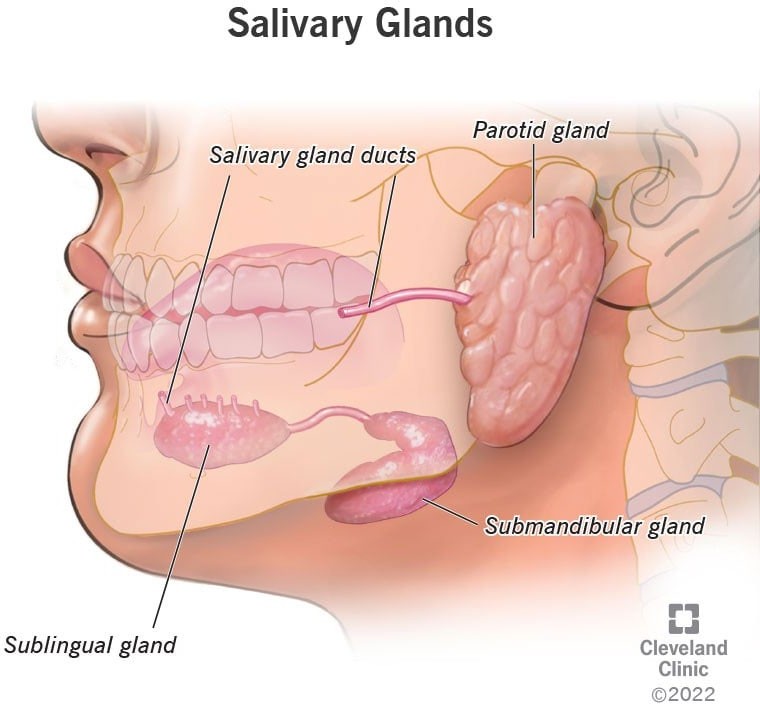
The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands.
- Parotid glands are located just in front of your ears.
- Sublingual glands are located below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth.
- Submandibular glands are located below your jaw.
-
Q #2: What is the molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2)?
A. Linear
B. Trigonal planar
C. Bent
D. Tetrahedral
Answer Explanation
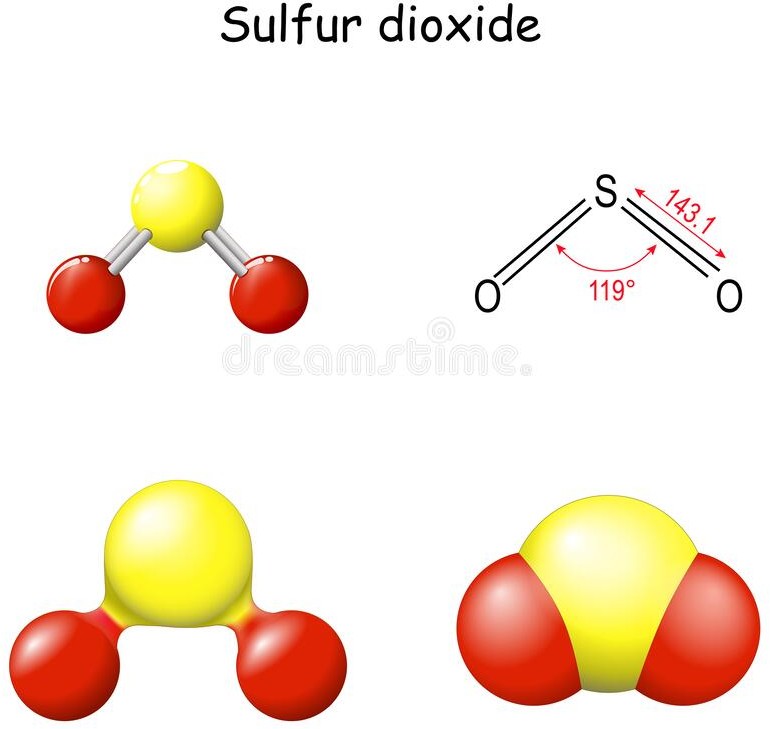
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
-
Q #3: A researcher collects data on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month. This data would be most useful to analyze which of the following:
A. traffic paterns during rush hour
B. pedestrian movement during the day
C. air pollution levels in the area
D. noise levels in the area
Answer Explanation
The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic paterns during rush hour.
-
Q #4: What is the name of the valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle in the heart?
A. Aortic valve
B. Mitral valve
C. Tricuspid valve
D. Pulmonary valve
Answer Explanation
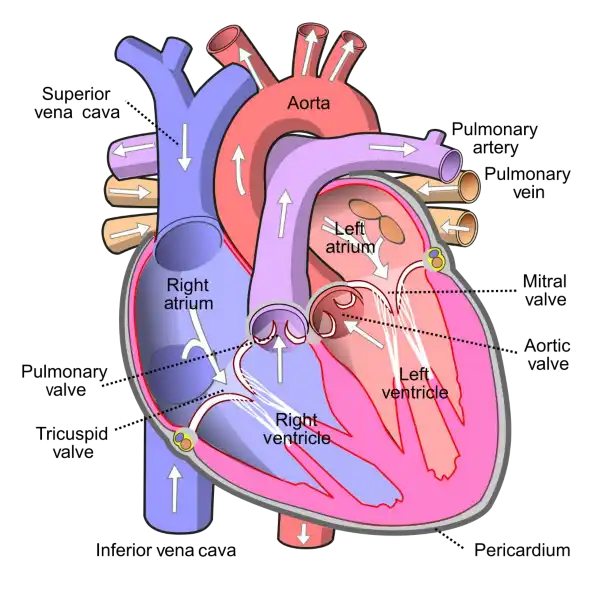
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
-
Q #5: What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
A. Calcium binds to tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
B. Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to initiate the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
C. Calcium activates the motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction.
D. Calcium is required for the relaxation of muscles after contraction.
Answer Explanation
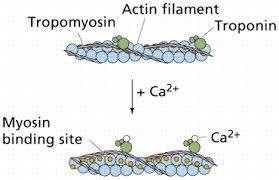
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
-
Q #6: Which of the following is an example of an exothermic reaction?
A. Melting ice
B. Burning wood
C. Cooking an egg
D. Dissolving sugar in water
Answer Explanation
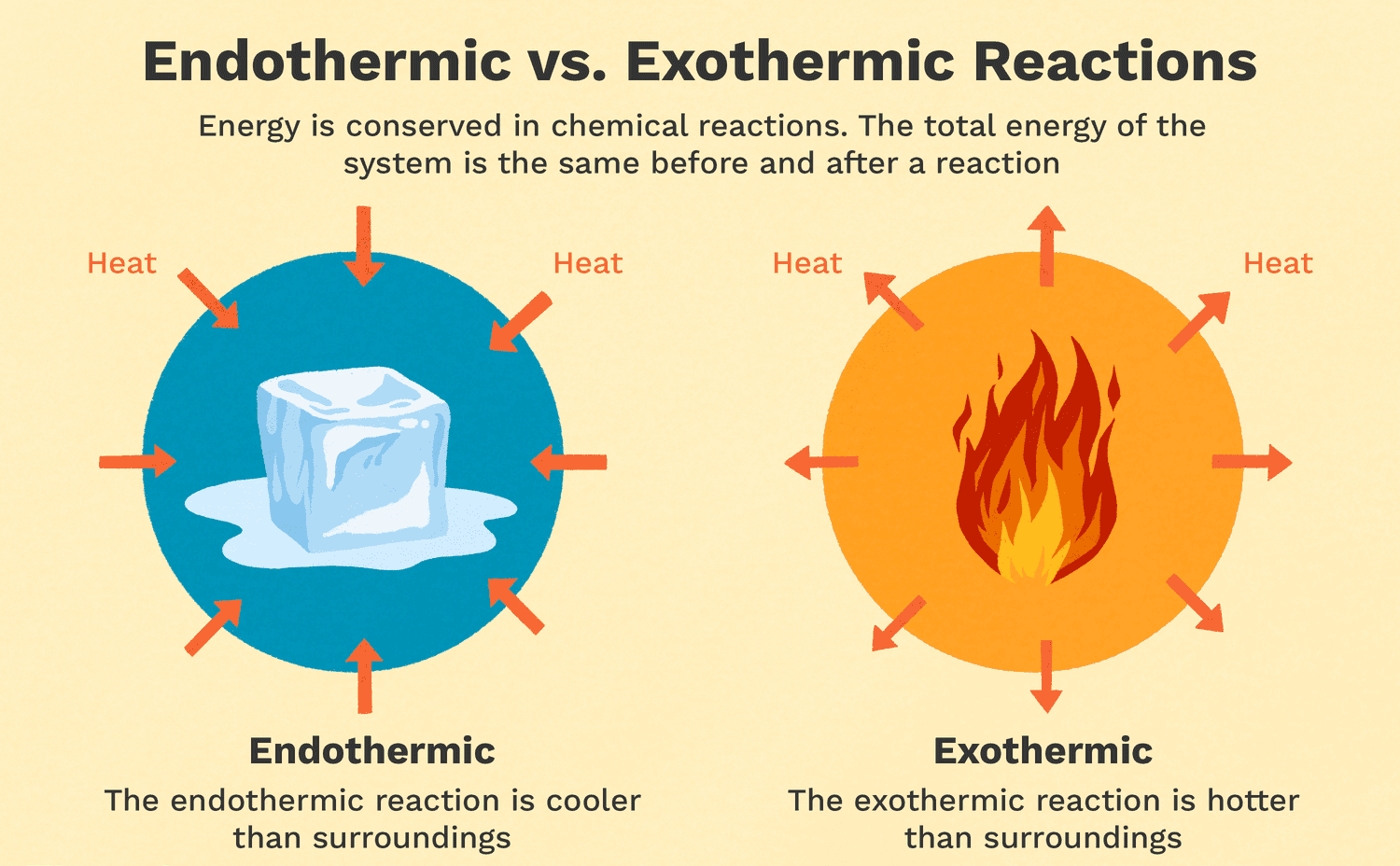
Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. Burning wood is an example of an exothermic reaction because it releases heat and light. As the wood reacts with oxygen in the air, it undergoes a combustion reaction that releases energy in the form of heat and light. Melting ice is an endothermic reaction because it requires energy input to melt the solid ice into liquid water. Cooking an egg is a chemical reaction that involves denaturing the proteins in the egg, but it is not necessarily exothermic or endothermic. Dissolving sugar in water is also not an example of an exothermic reaction because it does not release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound.
-
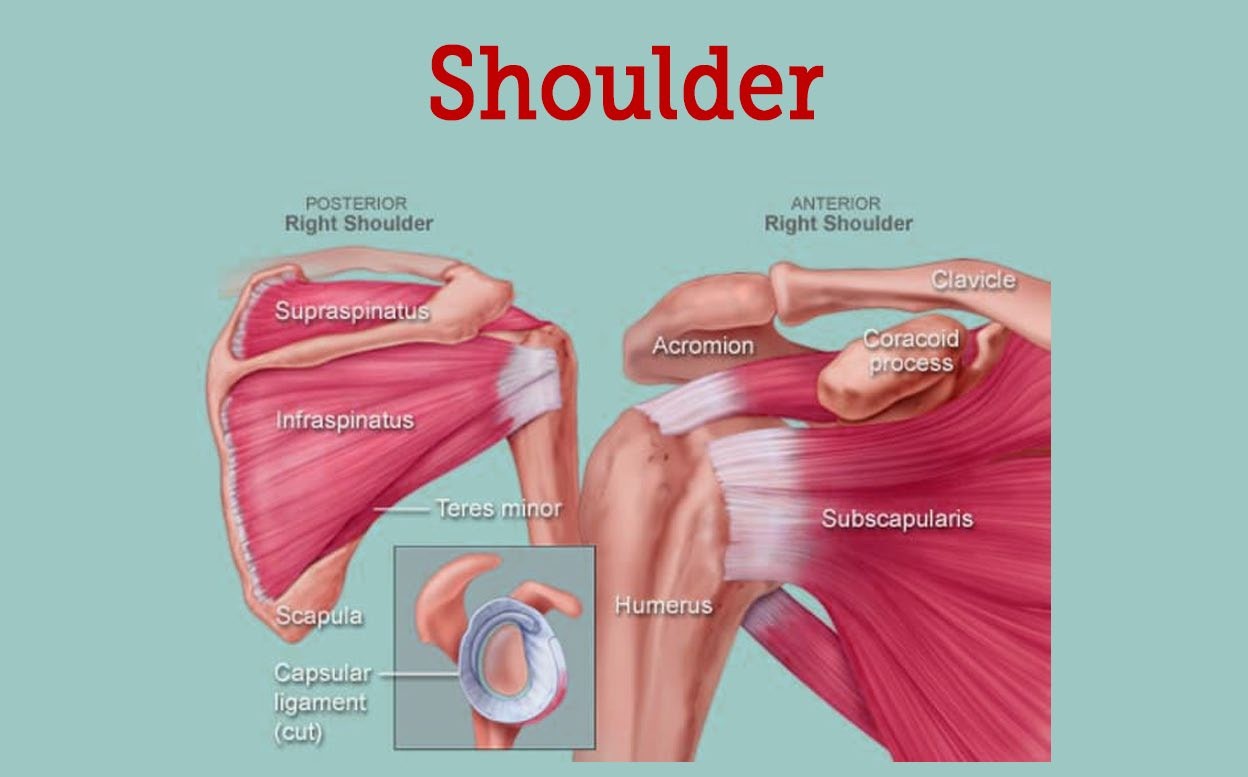
Q #7: What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
A. Elbow joint
B. Hip joint
C. Knee joint
D. Shoulder joint
Answer Explanation
-
Q #8: What are the five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards?
A. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
B. Thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
C. Lumbar, thoracic, cervical, coccygeal, sacral
D. Sacral, lumbar, cervical, thoracic, coccygeal
Answer Explanation
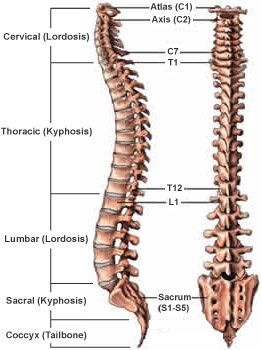
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
- Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
- Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
- Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
- Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
-
Q #9: What is the name of the genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Klinefelter syndrome
C. Down syndrome
D. Huntington's disease
Answer Explanation
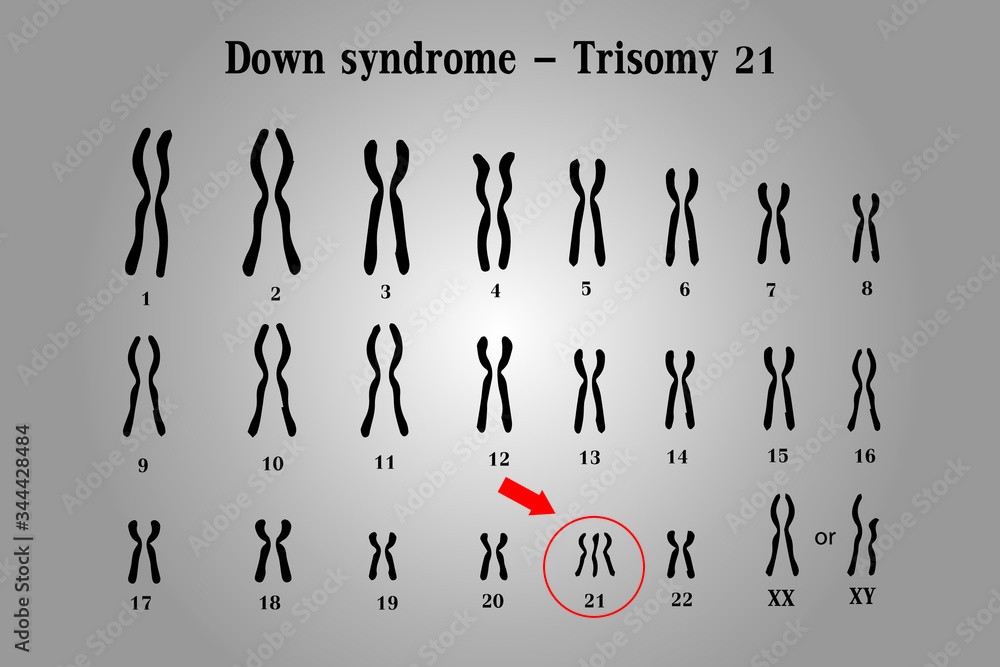
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is also known as trisomy 21, because affected individuals have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two.
The extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome occurs due to a random error in cell division, which leads to the production of an abnormal gamete (egg or sperm) with an extra copy of the chromosome. When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, and develops into a fetus with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is characterized by a range of physical and intellectual symptoms, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, heart defects, and increased risk of certain medical conditions such as leukemia and Alzheimer's disease. However, the severity and expression of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
-
Q #10: Which of the following is an example of a double-blind study?
A. Participants are randomly assigned to a treatment group or a control group
B. Participants and researchers both know which group participants are assigned to
C. Participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but researchers do
D. Both participants and researchers do not know which group participants are assigned to
Answer Explanation
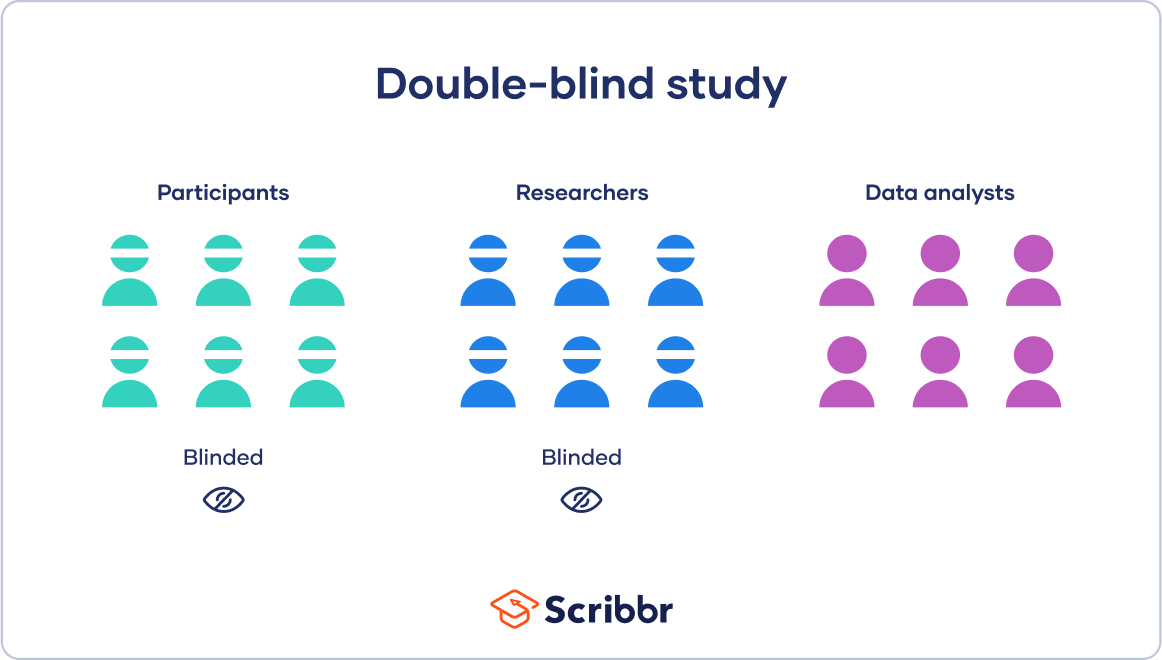
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to. Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind. Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to. Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
