What is the name of the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion?
A. Ionization
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Isotopic decay
Ionization is the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion.
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Choice B is not the best answer because oxidation refers to the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule.
Choice C is not the best answer because reduction refers to the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
Choice D is not the best answer because isotopic decay refers to the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: During the menstrual cycle, which structure in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation?
A. Corpus luteum.
B. Fimbriae
C. Follicle
D. Ovarian ligament.
Answer Explanation
Corpus luteum.
During the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation.
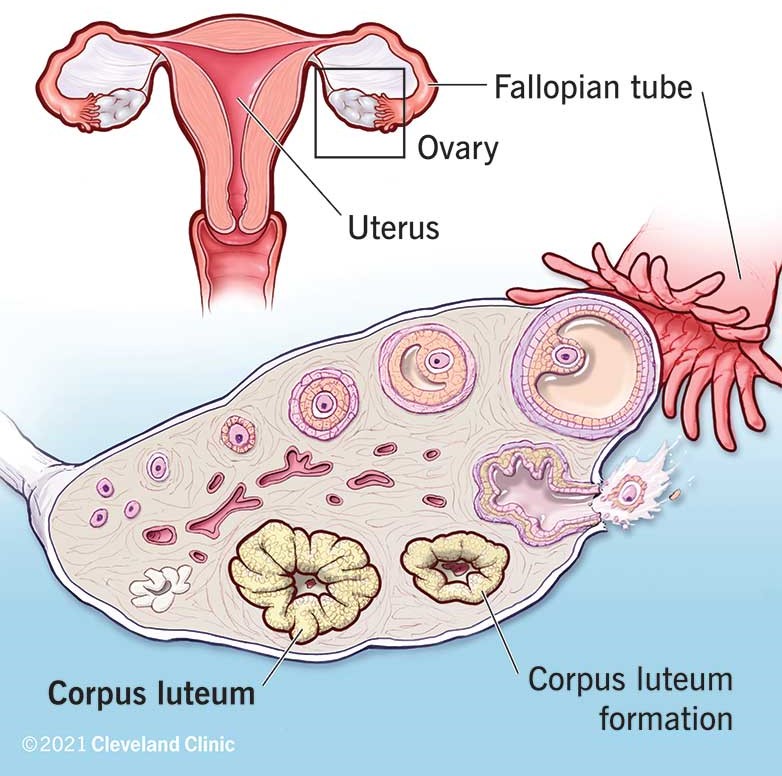
Choice B is incorrect because fimbriae are finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube.
Choice C is incorrect because a follicle is a sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Choice D is incorrect because the ovarian ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the uterus.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
Answer Explanation
Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
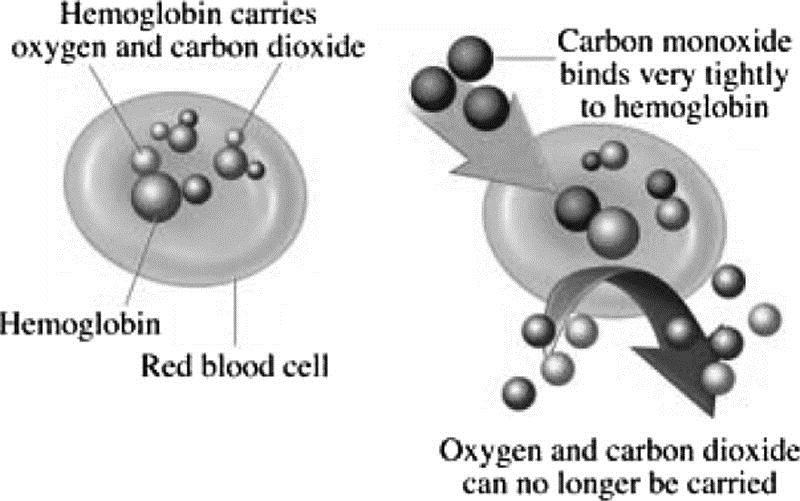
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Q #3: A patient with a history of heart failure is prescribed a medication that increases urine output to reduce fluid buildup. Which of the following statements best describes the mechanism of action of the prescribed medication?
A. Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
B. Blocks beta receptors.
C. Increases sodium and water reabsorption.
D. Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice D - Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The medication prescribed to the patient is a diuretic, which removes water and electrolytes from the body by increasing urination 1.
This helps reduce fluid buildup in the body.
Choice A, Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice B, Blocks beta receptors, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice C, Increases sodium and water reabsorption, is not the correct answer because it would have the opposite effect of reducing fluid buildup.
-
Q #4: A nurse is caring for a patient who has suffered a traumatic brain injury after falling from a height. The nurse knows that the severity of the injury depends on the speed at which the patient hit the ground. Which of the following factors affects the terminal velocity of a falling object?
A. The shape and surface area of the object.
B. The mass and volume of the object.
C. The acceleration and momentum of the object.
D. The height and distance of the fall.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
The shape and surface area of the object.
The terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid is affected by several factors, including its mass and shape.
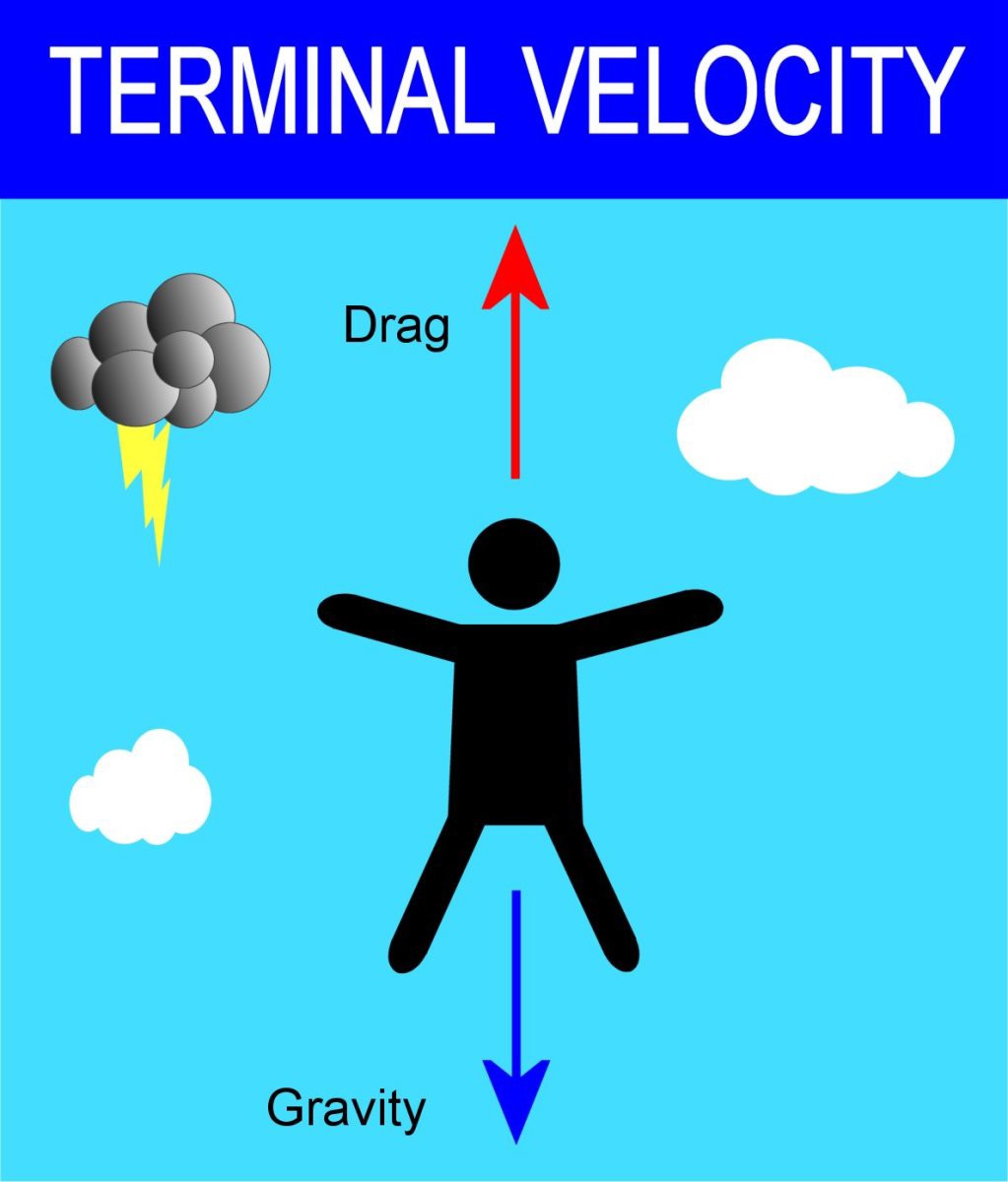
Objects with large surface areas will often experience a large amount of air resistance when they move.
Choice B is incorrect because the volume of the object does not affect its terminal velocity.
Choice C is incorrect because the acceleration and momentum of the object do not affect its terminal velocity.
Choice D is incorrect because the height and distance of the fall do not affect the terminal velocity of a falling object.
-
Q #5: Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
Answer Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
-
Q #6: Which factor is primarily responsible for the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis?
A. Hydrostatic pressure of the solution.
B. Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
C. Temperature of the solution.
D. Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules .
Answer Explanation
Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
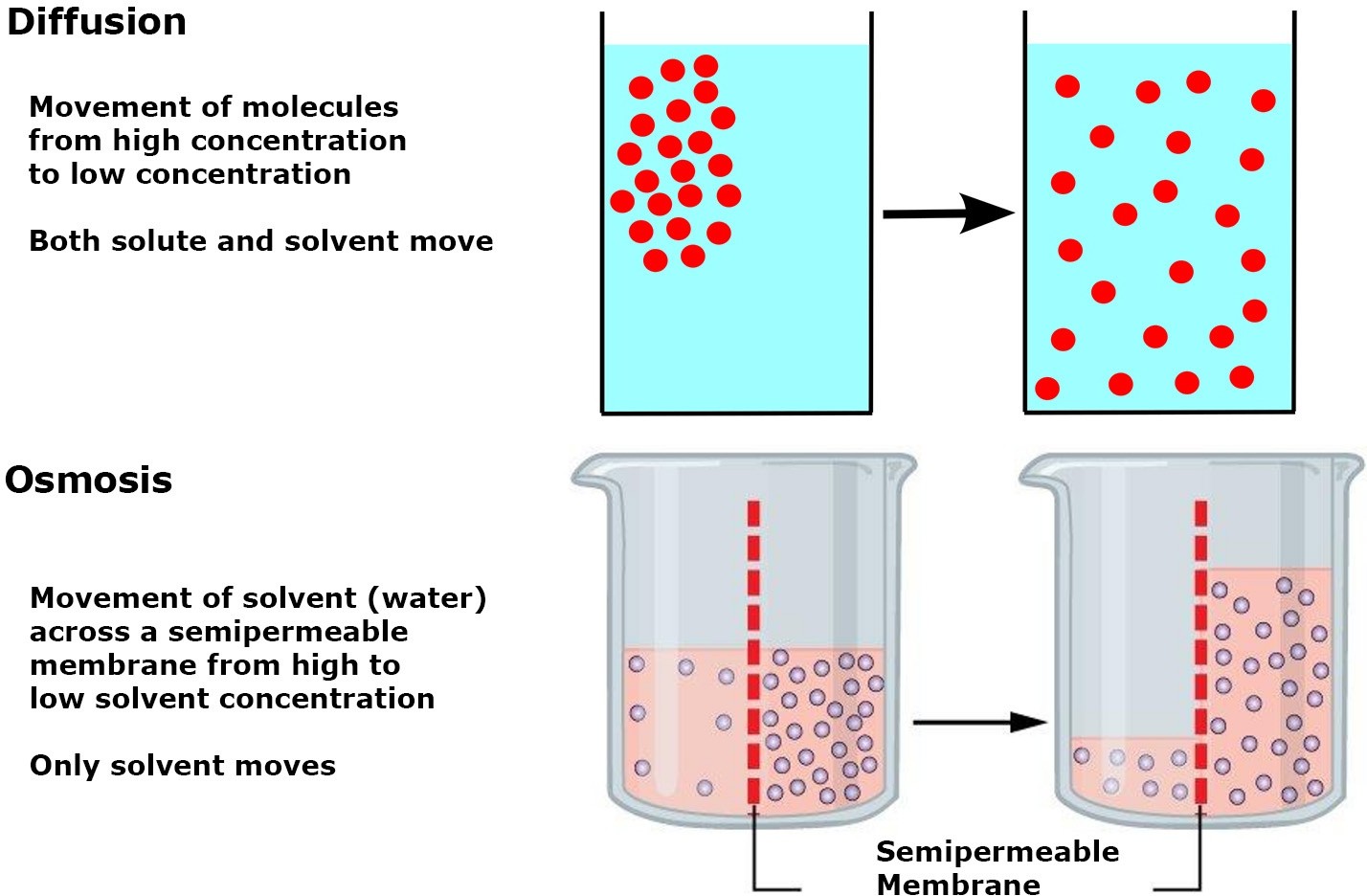
The concentration of solute particles in the solution is the primary factor that determines the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis.
Hydrostatic pressure (choice A) can affect the movement of water across cell membranes but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Temperature (choice C) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules (choice D) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
-
Q #7: What is a control group used for in scientific studies?
A. To establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
B. To establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
C. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable.
D. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
Answer Explanation
A control group is used in scientific studies to establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
The control group serves as a baseline or comparison group that does not receive the treatment or intervention being tested.
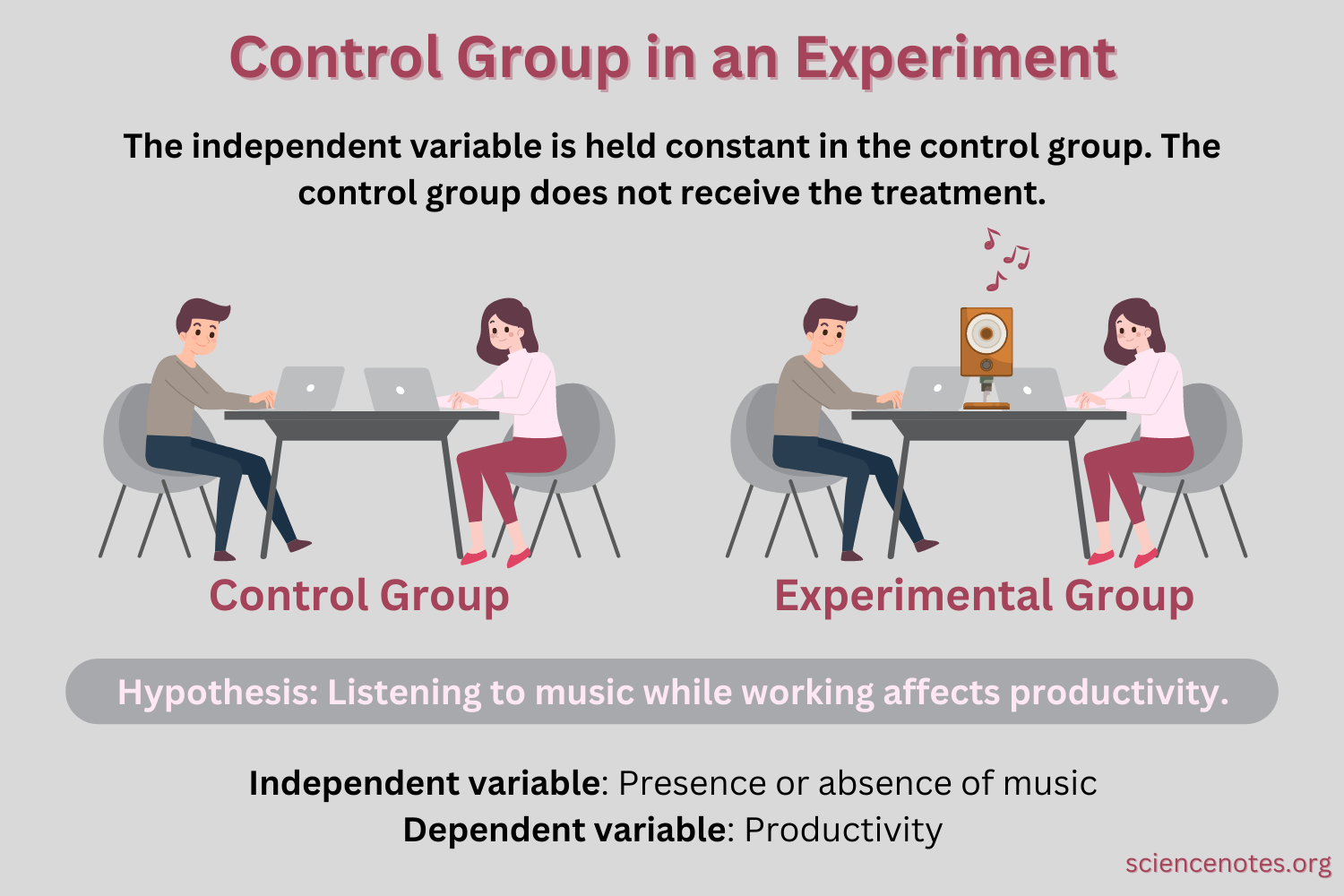
By comparing the results of the control group to the experimental group, researchers can determine if any observed changes are due to the independent variable or if they are due to chance or other factors.
Choice B is incorrect because a control group is not used to establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
Choice C is incorrect because while a control group can help control for the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable, its primary purpose is to isolate the effect of the independent variable.
Choice D is incorrect because a control group is not used to control for the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
-
Q #8: Which cytotoxic lymphocyte granules contain serine proteases that induce apoptosis in target cells?.
A. Perforins.
B. Cytokines.
C. Granzymes.
D. Interferons.
Answer Explanation
Granzymes.
Granzymes are a family of serine proteases that are stored in and secreted from the cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells.
They work in synergy with perforin, a pore-forming toxin, to induce apoptosis in target cells.
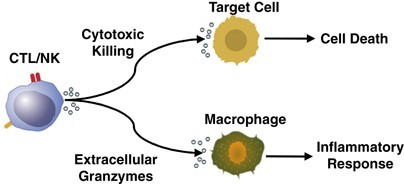
Perforin is necessary for the delivery of granzyme B to the target cell cytosol where caspase-dependent and -independent pathways to apoptosis are activated.
Perforins (choice A) are pore-forming toxins that work in synergy with granzymes to induce apoptosis in target cells.
Cytokines (choice B) are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
Interferons (choice D) are a type of cytokine that play a role in immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
-
Q #9: Which gland, located in the mediastinum, plays a key role in the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes?
A. Thymus
B. Parathyroid
C. Adrenal
D. Pituitary
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Thymus.
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ located in the mediastinum.
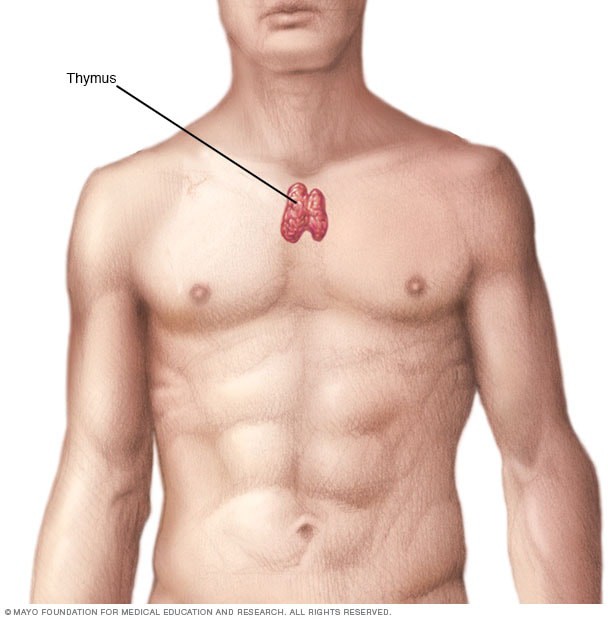
It plays a key role in the maturation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
Choice B.
Parathyroid is incorrect because the parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands located in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels in the blood.
Choice C.
Adrenal is incorrect because the adrenal glands are endocrine glands located above the kidneys that produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Choice D.
Pituitary is incorrect because the pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located at the base of the brain that produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions.
-
Q #10: What is a primer in DNA sequencing?
A. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
B. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a "starter" for the template.
C. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
D. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a "starter" for the template.
Answer Explanation
A primer is a short single-stranded DNA fragment used in certain laboratory techniques, such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
In the PCR method, a pair of primers hybridizes with the sample DNA and defines the region that will be amplified.
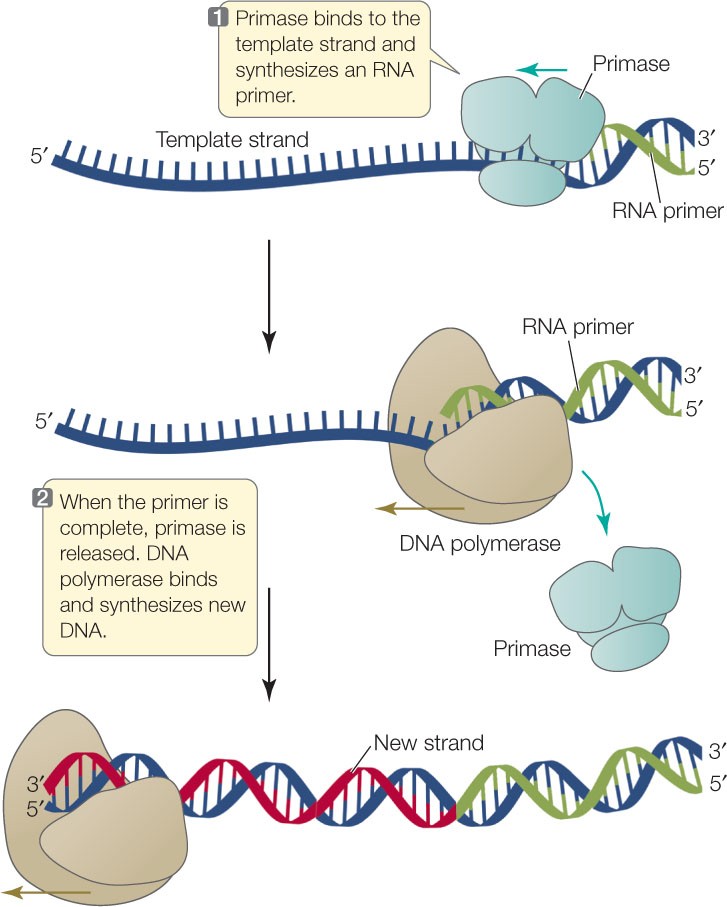
Choice A) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a “starter” for the polymerase is incorrect because primers are single-stranded, not double-stranded.
Choice B) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because it does not make sense for a primer to bind to itself.
Choice D) A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because primers bind to the template DNA, not to the polymerase.
Note: DNA primers are used instead of RNA primers in DNA sequencing and PCR because DNA is more stable, specific, and compatible with the enzymes and processes involved in these techniques.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
