What is the purpose of using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) in the laboratory?
A. To separate DNA fragments by size.
B. To amplify specific regions of DNA.
C. To sequence DNA fragments.
D. To analyze protein expression levels.
The correct answer is choice B.
To amplify specific regions of DNA.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a laboratory technique used to make many copies of a specific region of DNA.
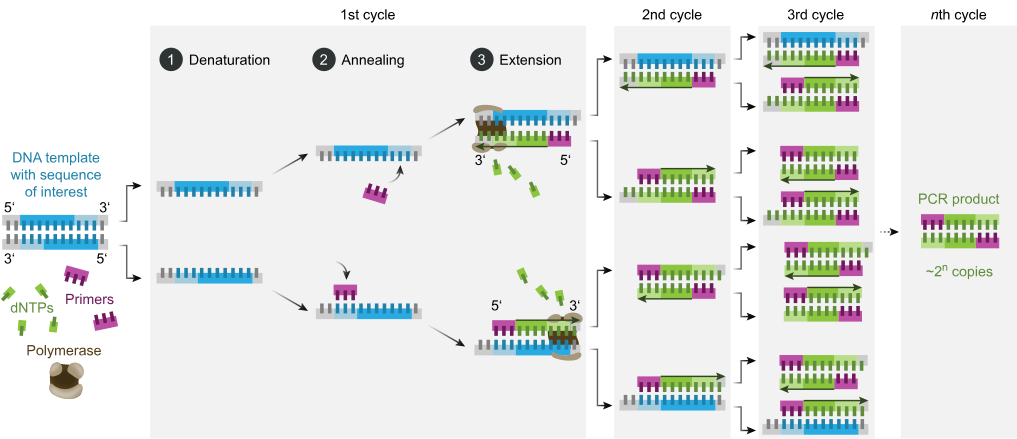 |
The goal of PCR is to make enough of the target DNA region that it can be analyzed or used in some other way.
PCR has many research and practical applications, including DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
Choice A is incorrect because PCR does not separate DNA fragments by size. Choice C is incorrect because PCR does not sequence DNA fragments.
Choice D is incorrect because PCR does not analyze protein expression levels.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand?
A. Orthopnea
B. Hypoxia
C. Tachypnea
D. Bradypnea
Answer Explanation
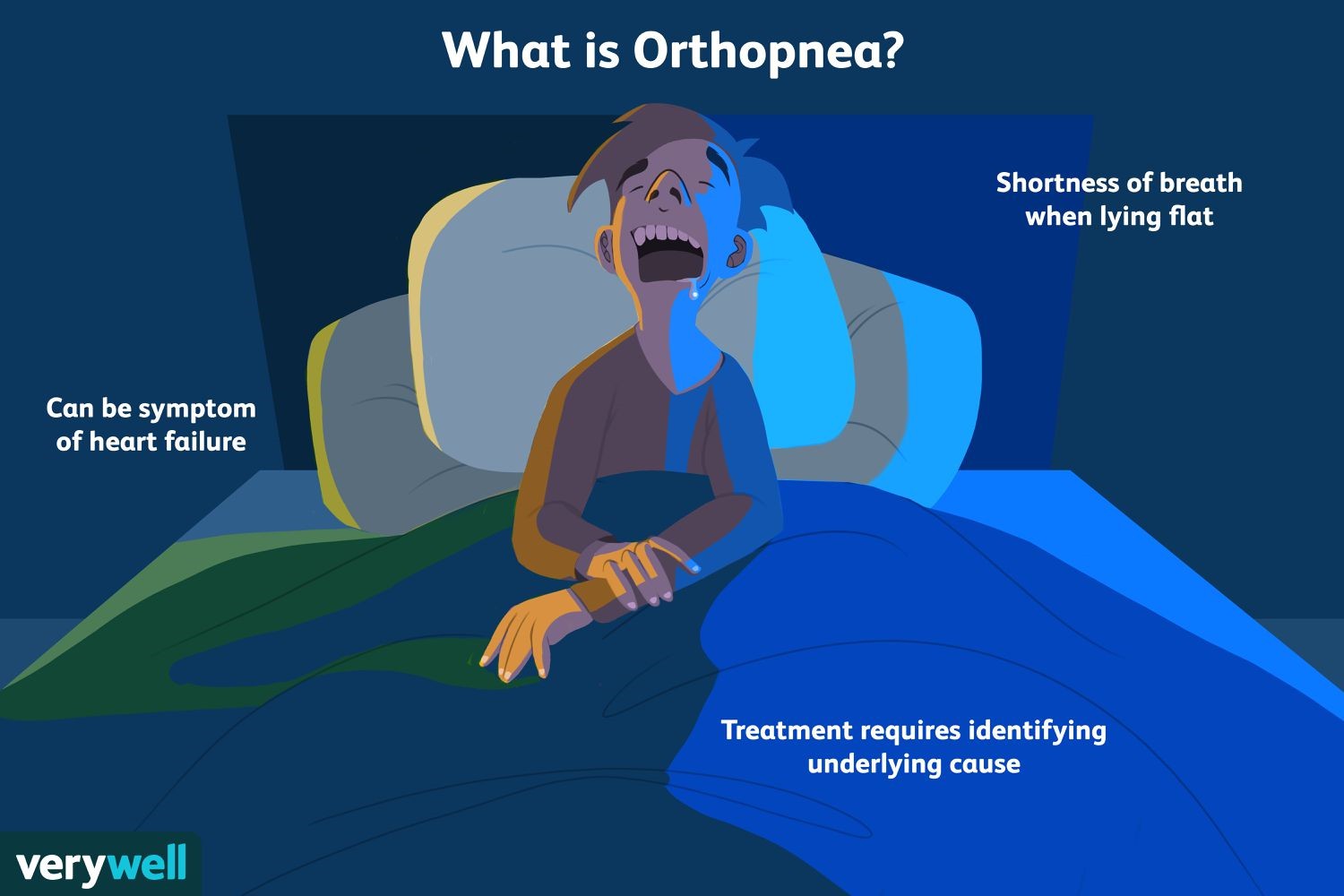
The correct answer is choice A. Orthopnea.
Orthopnea refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand.
Choice B, Hypoxia, is not the correct answer because it refers to a condition in which there is a lack of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Choice C, Tachypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to rapid breathing.
Choice D, Bradypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to abnormally slow breathing.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
-
Q #3: What are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA?
A. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
B. Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine.
C. Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine.
D. Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine.
Answer Explanation
These are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA1.
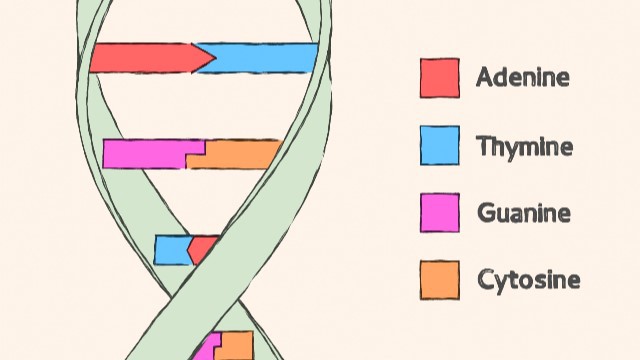
Choice B) Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine is incorrect because Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice C) Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine and Guanosine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice D) Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine, Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
-
Q #4: What is the purpose of using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) in the laboratory?
A. To separate DNA fragments by size.
B. To amplify specific regions of DNA.
C. To sequence DNA fragments.
D. To analyze protein expression levels.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
To amplify specific regions of DNA.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a laboratory technique used to make many copies of a specific region of DNA.

The goal of PCR is to make enough of the target DNA region that it can be analyzed or used in some other way.
PCR has many research and practical applications, including DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
Choice A is incorrect because PCR does not separate DNA fragments by size. Choice C is incorrect because PCR does not sequence DNA fragments.
Choice D is incorrect because PCR does not analyze protein expression levels.
-
Q #5: What is the organelle that encapsulates the contents of the cell and plays a vital role in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell?.
A. Ribosome
B. Nucleus
C. Mitochondria
D. Plasma membrane.
Answer Explanation
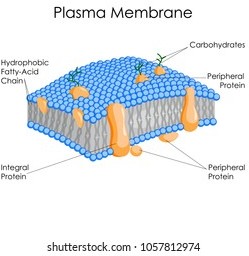
The plasma membrane is the organelle that encapsulates the contents of the cell and plays a vital role in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
It is a selectively permeable barrier that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment.
Choice A is incorrect because ribosomes are organelles involved in protein synthesis, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Choice B is incorrect because the nucleus is an organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because mitochondria are organelles involved in energy production, not in regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
-
Q #6: Which of the following hormones is responsible for regulating the body's metabolism and energy levels?
A. Estrogen
B. Progestin
C. Thyroxine
D. Androgen
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Thyroxine.
Thyroxine (T4) is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that controls your body’s metabolism, the process in which your body transforms the food you eat into energy.
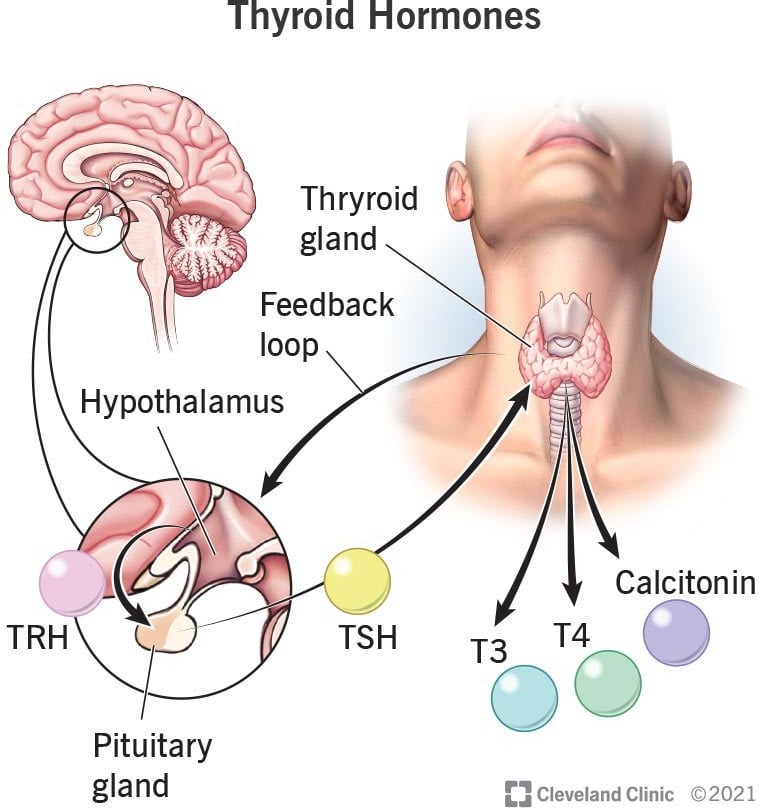
Choice A, Estrogen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Choice B, Progestin, is not the correct answer because it is a synthetic form of progesterone used in hormonal birth control and hormone replacement therapy.
Choice D, Androgen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
-
Q #7: What is a primer in DNA sequencing?
A. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
B. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a "starter" for the template.
C. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
D. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a "starter" for the template.
Answer Explanation
A primer is a short single-stranded DNA fragment used in certain laboratory techniques, such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
In the PCR method, a pair of primers hybridizes with the sample DNA and defines the region that will be amplified.
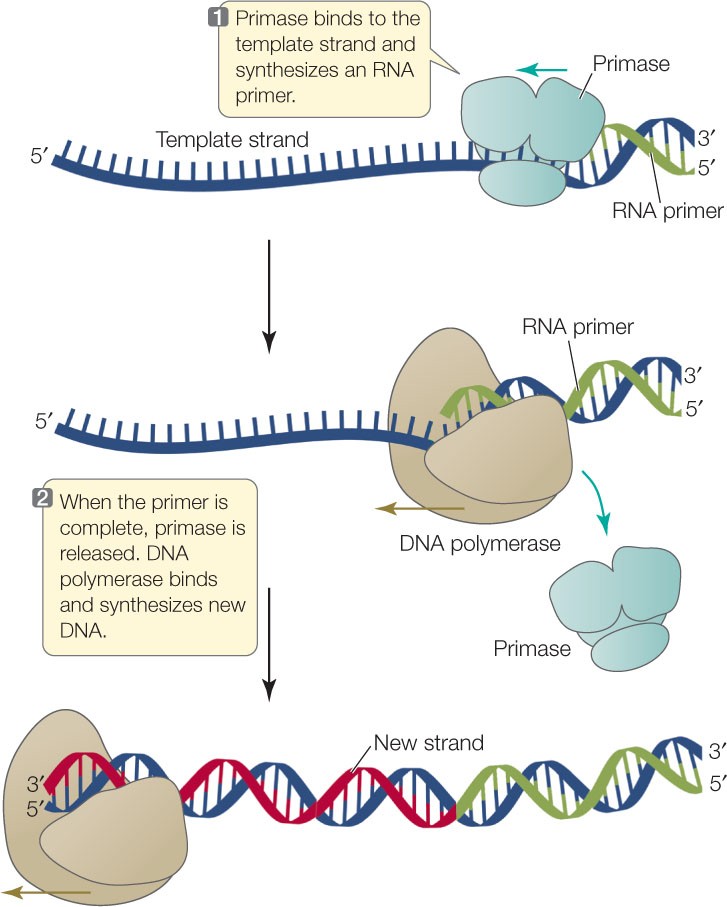
Choice A) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a “starter” for the polymerase is incorrect because primers are single-stranded, not double-stranded.
Choice B) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because it does not make sense for a primer to bind to itself.
Choice D) A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because primers bind to the template DNA, not to the polymerase.
Note: DNA primers are used instead of RNA primers in DNA sequencing and PCR because DNA is more stable, specific, and compatible with the enzymes and processes involved in these techniques.
-
Q #8: Which cytotoxic lymphocyte granules contain serine proteases that induce apoptosis in target cells?.
A. Perforins.
B. Cytokines.
C. Granzymes.
D. Interferons.
Answer Explanation
Granzymes.
Granzymes are a family of serine proteases that are stored in and secreted from the cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells.
They work in synergy with perforin, a pore-forming toxin, to induce apoptosis in target cells.
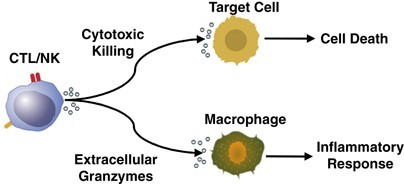
Perforin is necessary for the delivery of granzyme B to the target cell cytosol where caspase-dependent and -independent pathways to apoptosis are activated.
Perforins (choice A) are pore-forming toxins that work in synergy with granzymes to induce apoptosis in target cells.
Cytokines (choice B) are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
Interferons (choice D) are a type of cytokine that play a role in immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
-
Q #9: What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
Answer Explanation
Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
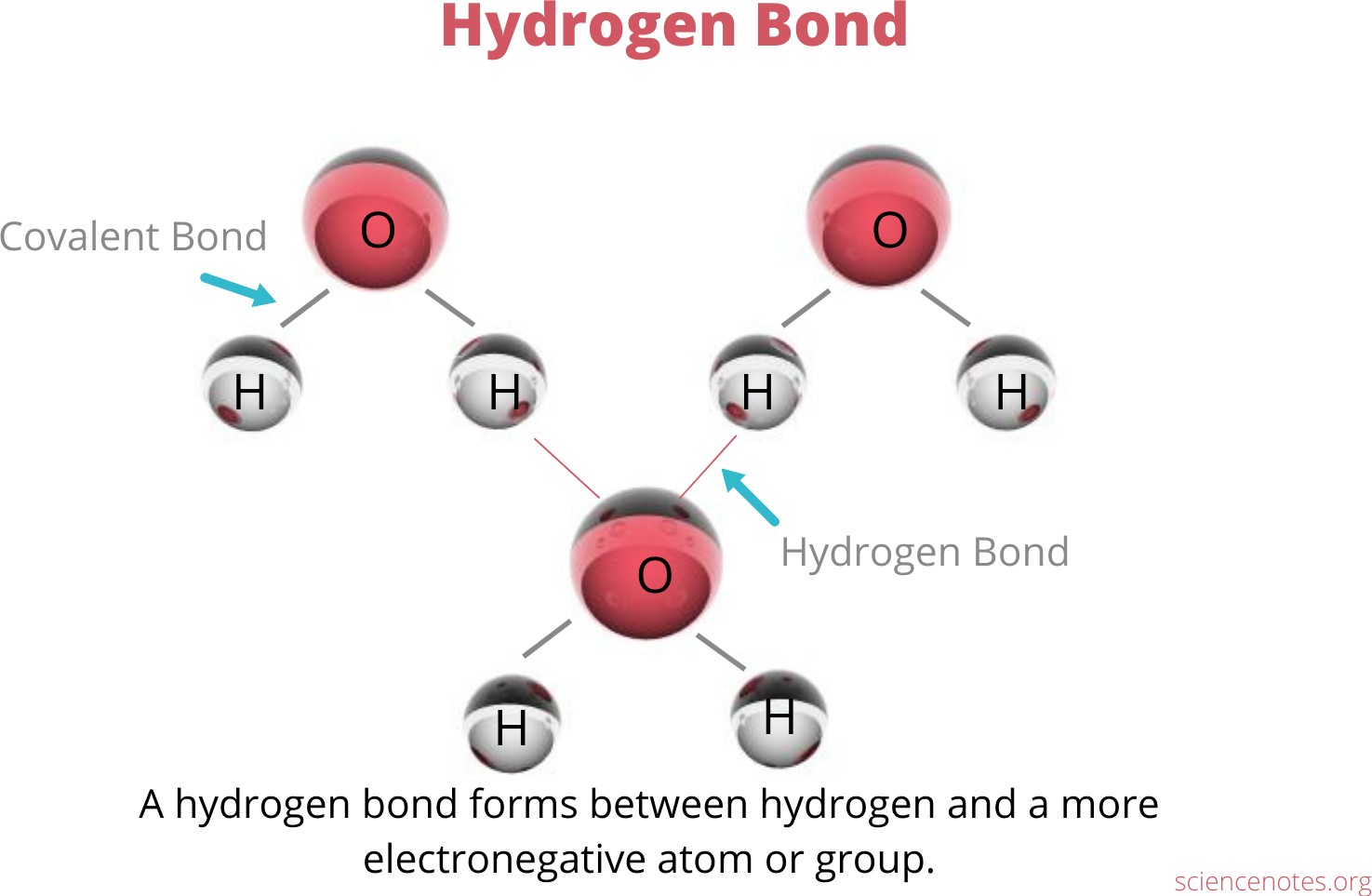
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
-
Q #10: Which of the following structures in the nephron is responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients?
A. Distal tubule
B. Proximal tubule
C. Glomerulus
D. Loop of Henle
Answer Explanation
Proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is responsible for reabsorbing all the nutrients and most of the water.
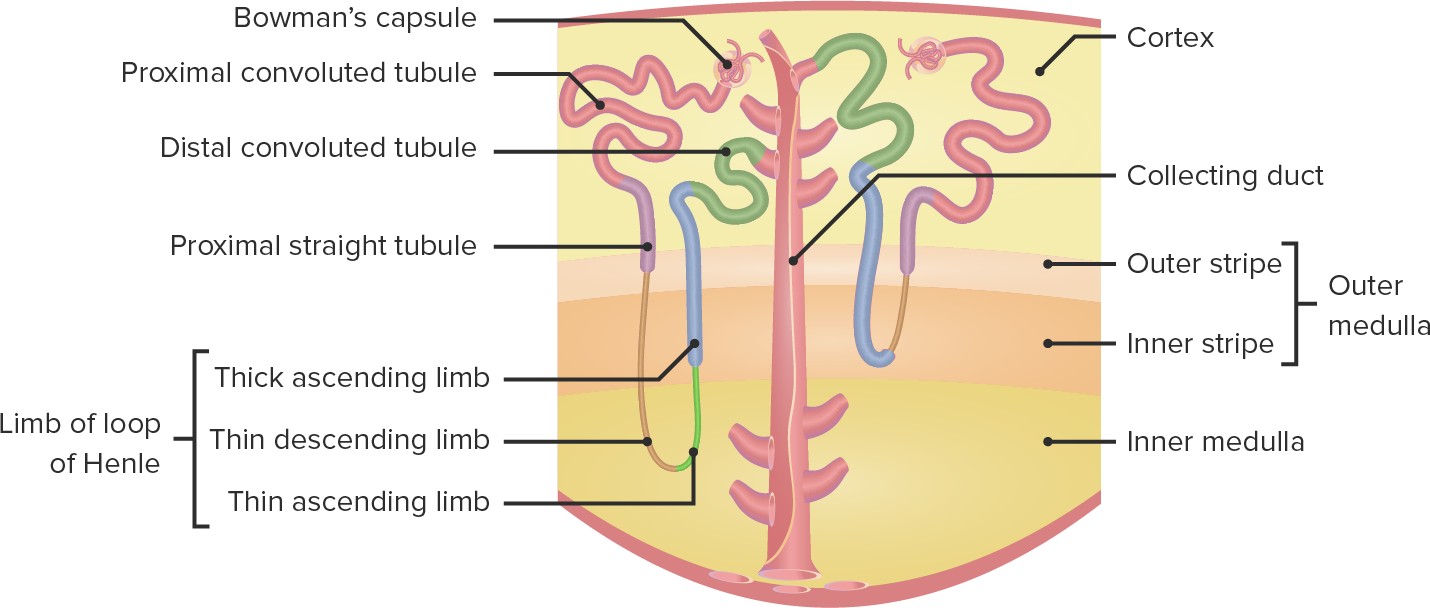
Choice A is incorrect because the distal tubule is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
Choice C is incorrect because the glomerulus is responsible for filtering fluid and solutes out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate.
Choice D is incorrect because the Loop of Henle is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
