What is the role of ribosomes?
A. Make proteins
B. Waste removal
C. Transport
D. Storage
A ribosome is a structure of eukaryotic cells that makes proteins.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of these does NOT match the nitrogenous base to the nucleobase?
A. Purine: Adenine
B. Purine: Thymine
C. Pyrimidine: Uracil
D. Pyrimidine: Cytosine
Answer Explanation
There are two types of nitrogenous bases: purine and pyrimidine bases. Purine bases have two rings in their structure and consist of adenine and guanine. Pyrimidine bases only have one ring in their structure and consist of thymine and cytosine (DNA) and uracil and cytosine (RNA). Therefore, the correct answer is B since thymine is a pyrimidine.
-
Q #2: Which structure of the nervous system carries action potential in the direction of a synapse?
A. Cell body
B. Axon
C. Neuron
D. Myelin
Answer Explanation
Axons carry action potential in the direction of synapses. Axons are the long, fiber-like structures that carry information from neurons. Electrical impulses travel along the body of the axons, some of which are up to a foot long.
A neuron is a type of cell that is responsible for sending information throughout the body. There are several types of neurons, including muscle neurons, which respond to instructions for movement; sensory neurons, which transmit information about the external world; and interneurons, which relay messages between neurons. Myelin is a fat that coats the nerves and ensures the accurate transmission of information in the nervous system.
-
Q #3: Which of the following statements concerning the states of matter is NOT true?
A. Plasmas are high-temperature collections of ions and free electrons.
B. Solids are the least compressible due to the more rigid positions of the particles.
C. Gases have no definite volume and expand to fill their containers
D. Liquids have no definite shape and no definite volume.
Answer Explanation
Liquids have no definite shape, but they do have a definite volume. While the particles of liquids move more freely than those in solids, they do maintain a definite volume.
-
Q #4: Which of the following is a carbohydrate?
A. Cellulose
B. Hemoglobin
C. Estrogen
D. ATP
Answer Explanation
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that composes the better part of the cell wall.
Hemoglobin is a protein and is found in red blood cells. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a compound used by living organisms to store and use energy. Estrogen is a steroid hormone that stimulates the development of female sex characteristics.
-
Q #5: How many tissue layers does the uterus have?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Answer Explanation
The uterus has three layers. The inner layer is called the endometrium. The middle layer is called the myometrium. The outer layer of the uterus is called the serosa or perimetrium.
-
Q #6: Which of the following are formed when the plasma membrane surrounds a particle outside of the cell?
A. Golgi bodies
B. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
C. Secretory vesicles
D. Endocytic vesicles
Answer Explanation
Endocytosis is a process by which cells absorb larger molecules or even tiny organisms, such as bacteria, that would not be able to pass through the plasma membrane. Endocytic vesicles containing molecules from the extracellular environment often undergo further processing once they enter the cell.
-
Q #7: Which section of the digestive system is responsible for receiving chyme and further digesting it?
A. The large intestine
B. The duodenum
C. The jejunum
D. The gallbladder
Answer Explanation
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine. It receives partially digested food (also called chyme) from the stomach, further digesting it with the help of enzymes released by the gall bladder. Then, the food enters into the jejunum, then the ileum. The large Intestine's main function is the reabsorption of water into the body to form solid waste. It also allows for the absorption of vitamin K produced by microbes living inside the large intestine.
-
Q #8: What is a hypothetical explanation for an occurrence that is based on prior knowledge called?
A. Independent variable
B. Dependent variable
C. Trial
D. Hypothesis
Answer Explanation
A hypothesis is the use of prior knowledge in order to provide a hypothetical explanation for why something may or may not occur. A hypothesis can be proved wrong or right based on the results of the experiment and repeated trials.
-
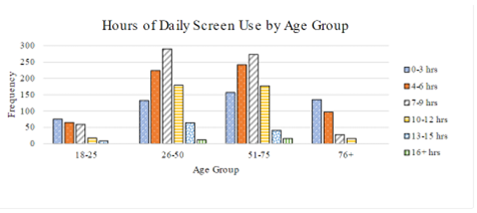
Q #9: Which of the following conclusions is supported by the data from this survey?
A. Dally screen usage in the United States decreases with age
B. Daily screen usage in the United States, increases with age.
C. In the United States, most people use screens more than 3 but less than13 hours a day
D. In the United States, people over 75 generally don't use screens.
Answer Explanation
The percentage of respondents that indicated average screen usage between 4-12 hours per day is (628 +650+389) ÷ 2, 307 ≈ 0.723 or 72.3% This is indeed a significant majority of the responses and would be a reasonable conclusion. The highest screen usage is in the middle two groups with both the younger and older groups indicating less screen usage, so the daily usage neither increases nor decreases with age. While the oldest group shows the least usage per day, the survey data indicates that some of the Individuals over 75 do indeed use screens.
-
Q #10: What type of mutation is represented by the following sequence? Original: 123456 Mutated: 154326
A. Breakage
B. Deletion
C. Insertion
D. Inversion
Answer Explanation
An inversion mutation is represented in the sequence 1 5 4 3 2 6. An inversion error is a type of mutation where an entire sequence of DNA is reversed. In this case, 2 3 4 5 has been reversed to 5 4 3 2.
Breakage, choice A, in a gene can mess up its function entirely or lead to a translocation of genetic information. Choice B, deletion, is when a section of DNA is omitted or lost.
Choice C, Insertion, is when an extra base pair is added to a DNA sequence. Deletions and insertions can lead to a frameshift effect where entire sequences are thrown off because one nucleotide is wrong.
This could result in coding for the wrong amino acid and non-functioning proteins.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
