What is the role of the epididymis in sperm maturation?
A. The epididymis produces sperm cells.
B. The epididymis stores and protects sperm cells until ejaculation.
C. The epididymis is responsible for the transport of sperm cells from the testes to the urethra.
D. The epididymis provides nourishment to sperm cells.
The epididymis is a coiled tube located at the back of each testicle where the sperm mature and are stored until ejaculation. Sperm are produced in the testes and then transported to the epididymis where they undergo maturation and become motile. The epididymis provides a protective environment for the sperm, allowing them to mature and become more resilient to external stressors. During ejaculation, the sperm are transported from the epididymis to the vas deferens and then to the urethra for ejaculation.
 |
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What are the steps involved in the scientific method?
A. Observation, hypothesis, prediction, experimentation, analysis, conclusion.
B. Hypothesis, observation, prediction, experimentation, analysis, conclusion.
C. Prediction, observation, experimentation, analysis, conclusion, hypothesis.
D. Observation, data collection, analysis, experimentation, hypothesis, conclusion.
Answer Explanation
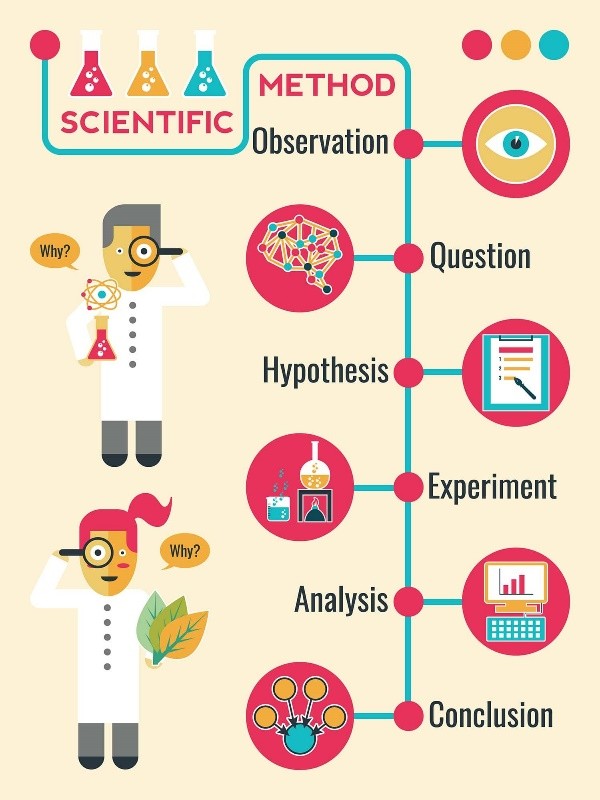
The scientific method is a systematic approach used to answer questions or test hypotheses about the natural world. The steps involved in the scientific method are:
- Observation: This is the first step in the scientific method. It involves observing a phenomenon or a problem and gathering information about it.
- Hypothesis: After making an observation, a scientist forms a hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the phenomenon or problem.
- Prediction: Based on the hypothesis, the scientist makes a prediction about what will happen in an experiment or what they will observe.
- Experimentation: The scientist designs and conducts an experiment to test the hypothesis and prediction.
- Analysis: The data collected from the experiment are analyzed to determine if they support or refute the hypothesis.
- Conclusion: Based on the analysis of the data, the scientist draws a conclusion about whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted.
Option b) is incorrect because it starts with hypothesis before observation. Option c) is incorrect because prediction comes before experimentation. Option d) is incorrect because hypothesis comes after observation and data collection.
-
Q #2: A researcher collects data on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month. This data would be most useful to analyze which of the following:
A. traffic paterns during rush hour
B. pedestrian movement during the day
C. air pollution levels in the area
D. noise levels in the area
Answer Explanation
The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic paterns during rush hour.
-
Q #3: Which of the following substances is excreted by the kidneys to regulate blood pressure?
A. renin
B. erythropoietin
C. calcitriol
D. urobilinogen
Answer Explanation
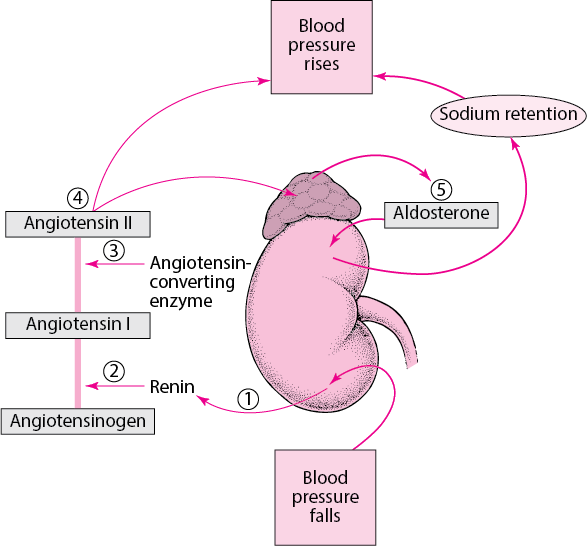
Renin is an enzyme that is produced by the kidneys and it acts to elevate blood pressure. When blood pressure falls, the kidneys secrete renin into the bloodstream ³.
-
Q #4: Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
A. Transport of nutrients to the body
B. Pumping of blood to the lungs
C. Exchange of gases between the body and the environment
D. Digestion of food in the stomach
Answer Explanation
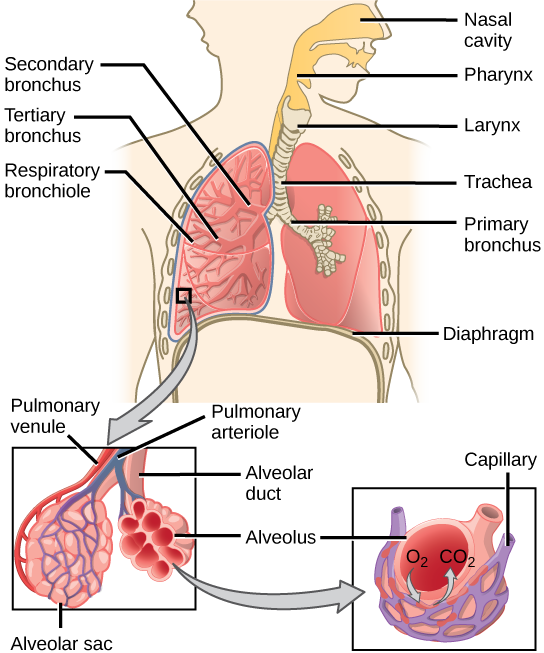
One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
-
Q #5: What is the role of the epididymis in sperm maturation?
A. The epididymis produces sperm cells.
B. The epididymis stores and protects sperm cells until ejaculation.
C. The epididymis is responsible for the transport of sperm cells from the testes to the urethra.
D. The epididymis provides nourishment to sperm cells.
Answer Explanation
The epididymis is a coiled tube located at the back of each testicle where the sperm mature and are stored until ejaculation. Sperm are produced in the testes and then transported to the epididymis where they undergo maturation and become motile. The epididymis provides a protective environment for the sperm, allowing them to mature and become more resilient to external stressors. During ejaculation, the sperm are transported from the epididymis to the vas deferens and then to the urethra for ejaculation.

-
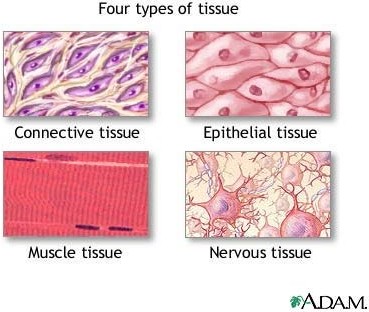
Q #6: Which of the following is NOT one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body?
A. Epithelial
B. Nervous
C. Connective
D. Exocrine glandular
Answer Explanation
Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body. The four primary tissue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
-
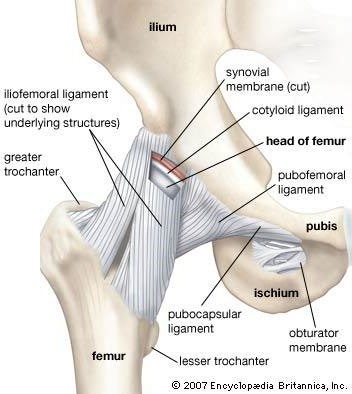
Q #7: Which of the following describes the function of ligaments?
A. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to bone
B. Ligaments attach two bones
C. Ligaments attach bones to tendons
D. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to tendons
Answer Explanation
Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, preventing excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.
-
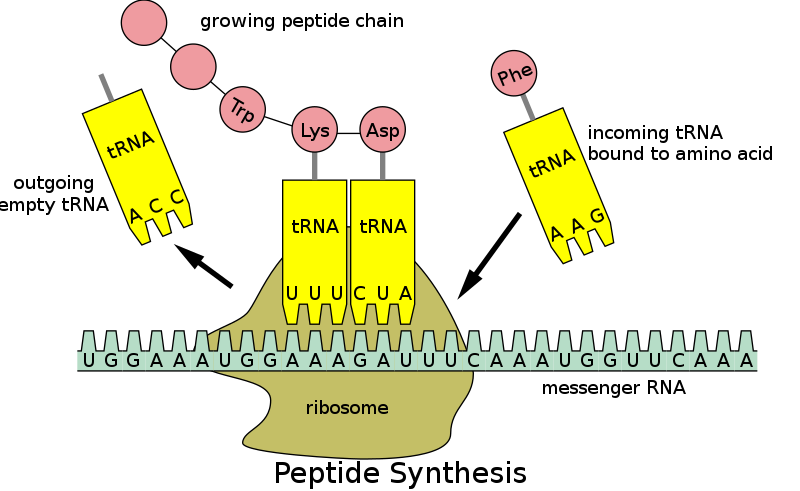
Q #8: Which of the following is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis?
A. tRNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. DNA
Answer Explanation
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific anticodon that matches a codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA codon and brings the corresponding amino acid to the ribosome, where it is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
-
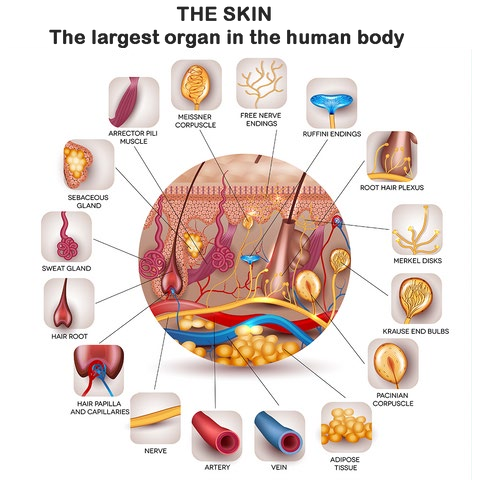
Q #9: What is the largest organ in the human body by surface area?
A. Brain
B. Heart
C. Liver
D. Skin
Answer Explanation
The largest organ in the human body by surface area is the skin. It covers the entire external surface of the body and has an average surface area of about 20 square feet in adults.
-
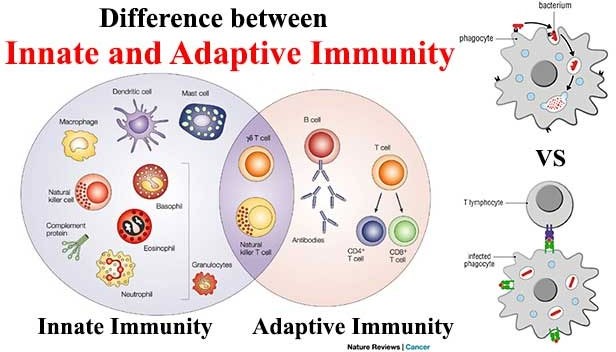
Q #10: What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
A. Innate immunity is present at birth while adaptive immunity is acquired after exposure to pathogens.
B. Innate immunity is specific to particular pathogens while adaptive immunity is nonspecific.
C. Innate immunity is mediated by antibodies while adaptive immunity is mediated by T cells.
D. Innate immunity provides long-term protection while adaptive immunity provides only short-term protection.
Answer Explanation
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
