What phase is the cell cycle part of?
A. Interphase
B. Metaphase
C. Prophase
D. Telophase
Before mitosis or meiosis occurs, interphase must happen. This is when the cell cycle takes place. The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
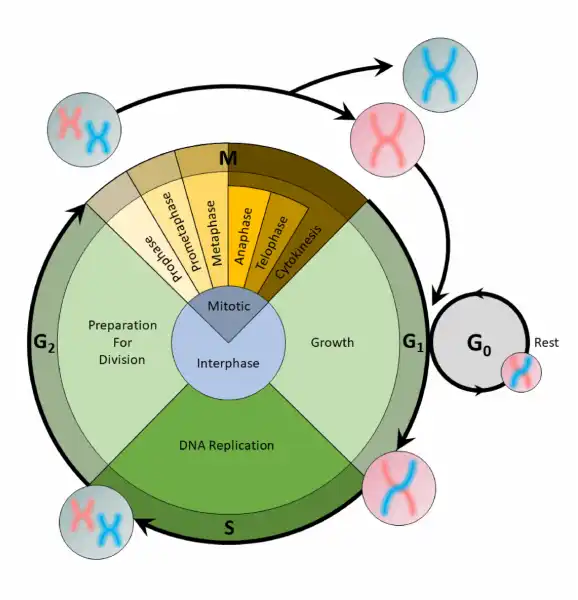
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which sequence describes the hierarchy level of biological organization?
A. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
B. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
C. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
D. Species, kingdom, genus, class, family, phylum, and order
Answer Explanation
Taxonomy is the process of classifying, describing, and naming organisms. There are seven levels in the Linnaean taxonomic system, starting with the broadest level, kingdom, and ending with the species level. For example, in the image the genus level contains two types of bears, but the species level shows one type. Additionally, organisms in each level are found in the level above it. For example, organisms in the order level are part of the class level. This classification system is based on physical similarities across living things. It does not account for molecular or genetic similarities.
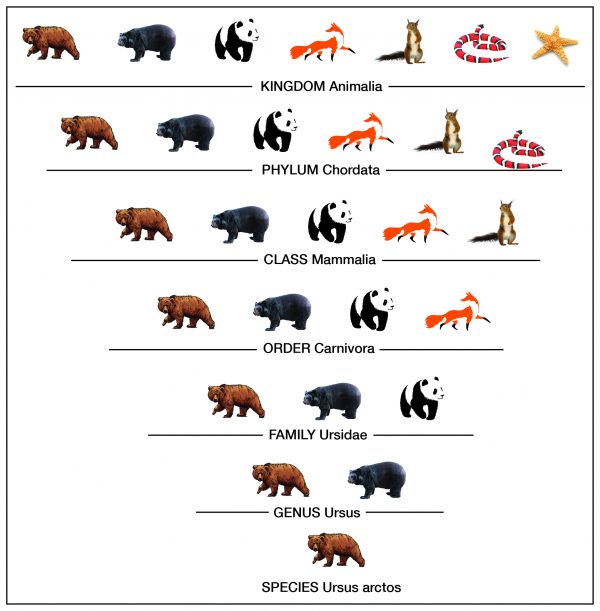
-
Q #2: An intracellular chemical signal can be produced in the cell membrane. Once it is produced, where does it go?
A. To a different cell
B. To another part of the same cell
C. To a region right outside the cell
D. To an area with a high ion concentration
Answer Explanation
There are two major types of receptor molecules that respond to an intercellular chemical signal:
- Intracellular receptors: These receptors are located in either the cytoplasm or the nucleus of the cell. Signals diffuse across the cell membrane and bind to the receptor sites on intracellular receptors, of the same cell.
- Membrane-bound receptors: These receptors extend across the cell membrane, with their receptor sites on the outer surface of the cell membrane. They respond to intercellular chemical signals that are large, water-soluble molecules that do not diffuse across the cell membrane.
-
Q #3: What structure plays a role in air conduction?
A. Alveolus
B. Capillary
C. Lung
D. Trachea
Answer Explanation
The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
-
Q #4: Where is skeletal muscle found?
A. Inside the heart
B. Attached to bone
C. Lining the walls of the bladder
D. Within the gastrointestinal tract
Answer Explanation
Skeletal muscle: This muscle cell is striated, long, and cylindrical. There are many nuclei in a skeletal muscle cell. Attached to bones in the body, skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily, meaning that it is under conscious control.
Smooth muscle: This muscle consists of nonstriated muscle cells that are spindle-shaped. Like cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contain one nucleus. This muscle type is found in the walls of internal organs like the bladder and stomach. Smooth muscle contraction is involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle: This muscle consists of muscle cells that are striated, short, and branched. These cells contain one nucleus, are branched, and are rectangular. Cardiac muscle contraction is an involuntary process, which is why it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. This muscle is found in the walls of the heart.
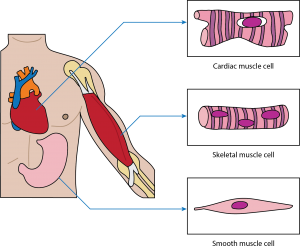
-
Q #5: Which choice best describes homeostasis?
A. A functional system of the body
B. Blood flow to every cell in the body
C. A relatively constant environment within the body
D. Neural pathways that have integrated into the body
Answer Explanation
Homeostasis is the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body. Each cell of the body is surrounded by a small amount of fluid, and the normal functions of each cell depend on the maintenance of its fluid environment within a narrow range of conditions, including temperature, volume, and chemical content. These conditions are known as variables. For example, body temperature is a variable that can increase in a hot environment or decrease in a cold environment.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms in the human body: negative and positive.
- Negative Feedback: Most systems of the body are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, which maintain homeostasis. Negative means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted. The maintenance of normal blood pressure is a negative-feedback mechanism. Normal blood pressure is important because it is responsible for moving blood from the heart to tissues.
- Positive Feedback: Positive-feedback mechanisms are not homeostatic and are rare in healthy individuals. Positive means that when a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response of the system is to make the deviation even greater. Positive feedback therefore usually creates a cycle leading away from homeostasis and, in some cases, results in death. Inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of positive feedback.
-
Q #6: What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
Answer Explanation
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
-
Q #7: A student notices a pattern of stripes on five tigers. Each of the five tigers has the same stripe pattern. Using his inductive reasoning, what does he logically assume based on this information?
A. The pattern continues to change over time.
B. Natural adaptations cause this pattern to occur
C. Each offspring will have the same stripe pattern
D. Ancestors of the tigers have different stripe patterns
Answer Explanation
Inductive reasoning involves making specific observations and using them to make broad statements. The student observes that all of the tigers have the same stripe pattern. He can use this observation to make the broad statement that all the tigers’ offspring will have the same stripe pattern.
Inductive reasoning involves drawing a general conclusion from specific observations. This form of reasoning is referred to as the “from the bottom up” approach. Information gathered from specific observations can be used to make a general conclusion about the topic under investigation. In other words, conclusions are based on observed patterns in data.
-
Q #8: Which of the following is a component of a chromosome?
A. Centromere
B. Gamete
C. Homologue
D. Ribose
Answer Explanation
The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
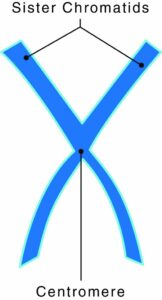
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
-
Q #9: In which state of matter do the particles of iron have the lowest amount of cohesion?
A. Solid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
B. Liquid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
C. Gaseous iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
D. The particles have the same amount of cohesion in all states of matter.
Answer Explanation
The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
-
Q #10: When would a cell most likely contain the most nucleotides?
A. S
B. G1
C. M
D. G2
Answer Explanation
A cell copies its DNA during the S phase, and nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Thus, the step preceding the S phase, the G1 phase, is the phase of the cell cycle when the cell would contain the most nucleotides.
For a cell to divide into more cells, it must grow, copy its DNA, and produce new daughter cells. The cell cycle regulates cellular division. This process can either prevent a cell from dividing or trigger it to start dividing.
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
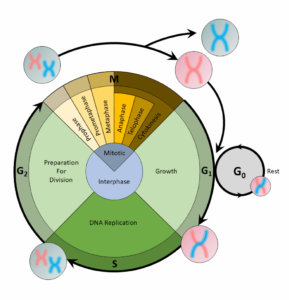
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
