What solution has a pH of 7?
A. Aniline
B. Pyridine
C. Pure water
D. Sodium hydroxide
A pH of 7 is a neutral solution, which is how pure water is classified. Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
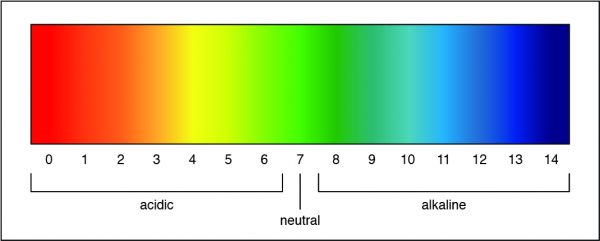
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
Answer Explanation
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
-
Q #2: After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
Answer Explanation
Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.
-
Q #3: Which sequence describes the hierarchy level of biological organization?
A. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
B. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
C. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
D. Species, kingdom, genus, class, family, phylum, and order
Answer Explanation
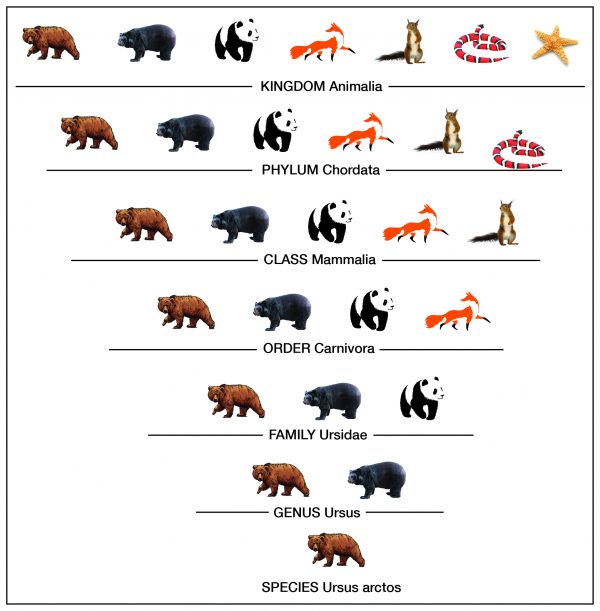
Taxonomy is the process of classifying, describing, and naming organisms. There are seven levels in the Linnaean taxonomic system, starting with the broadest level, kingdom, and ending with the species level. For example, in the image the genus level contains two types of bears, but the species level shows one type. Additionally, organisms in each level are found in the level above it. For example, organisms in the order level are part of the class level. This classification system is based on physical similarities across living things. It does not account for molecular or genetic similarities.
-
Q #4: Fertilization (the fusing of one sperm and an ovum) results in a(n) _____.
A. embryo
B. fetus
C. infant
D. zygote
Answer Explanation
Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating a zygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
-
Q #5: What is the correct order of the stages of the cell cycle?
A. G1,S,G2,M
B. G2,S,G1,M
C. M,S,G2,G1
D. S,M,G1,G1
Answer Explanation
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
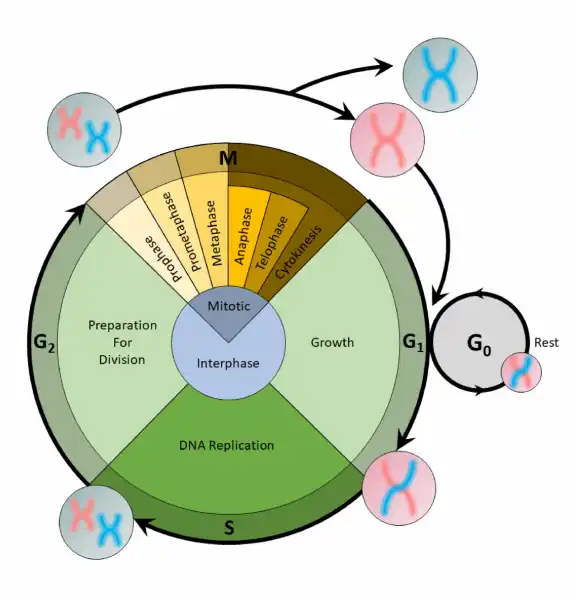
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
-
Q #6: What organelle is only associated with plant cells?
A. Cell wall
B. Ribosome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Golgi apparatus
Answer Explanation
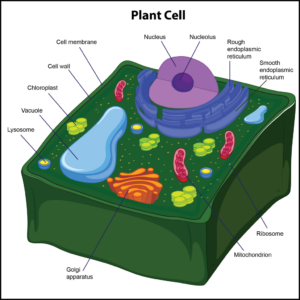
Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells. Chloroplasts are photosynthetic compounds used to make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
-
Q #7: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
Answer Explanation
Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.
-
Q #8: A spoonful of sugar is added to a hot cup of tea. All the sugar dissolves. How can the resulting solution be described?
A. Saturated and homogeneous
B. Saturated and heterogeneous
C. Unsaturated and homogeneous
D. Unsaturated and heterogeneous
Answer Explanation
Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- A mixture is when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- A homogeneous mixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. A heterogeneous mixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. An unsaturated solution has the ability to dissolve more solute and a saturated solution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
-
Q #9: The diffusion of nutrients through the walls of the digestive system is critical to homeostasis in the body. Where does the majority of this diffusion take place in the digestive system?
A. Stomach
B. Esophagus
C. Oral cavity
D. Small intestine
Answer Explanation
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestines, located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestines (jejunum). Once food has mixed with acid in the stomach, it moves into the duodenum, where it then mixes with bile from the gallbladder and digestive juices secreted from the pancreas. In the duodenum, absorption of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients begins.
-
Q #10: What type of reaction is described by the following equation? ZnBr2(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2KBr(aq)
A. Synthesis
B. Decomposition
C. Single-Replacement
D. Double-Replacement
Answer Explanation
In this reaction, two elements are trading places hence double-replacement. In the reactants, zinc and bromide ions are together, and potassium and hydroxide ions are together. In the products, zinc and hydroxide ions are together, and potassium and bromide ions are together.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
