Which choice best describes homeostasis?
A. A functional system of the body
B. Blood flow to every cell in the body
C. A relatively constant environment within the body
D. Neural pathways that have integrated into the body
Homeostasis is the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body. Each cell of the body is surrounded by a small amount of fluid, and the normal functions of each cell depend on the maintenance of its fluid environment within a narrow range of conditions, including temperature, volume, and chemical content. These conditions are known as variables. For example, body temperature is a variable that can increase in a hot environment or decrease in a cold environment.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms in the human body: negative and positive.
- Negative Feedback: Most systems of the body are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, which maintain homeostasis. Negative means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted. The maintenance of normal blood pressure is a negative-feedback mechanism. Normal blood pressure is important because it is responsible for moving blood from the heart to tissues.
- Positive Feedback: Positive-feedback mechanisms are not homeostatic and are rare in healthy individuals. Positive means that when a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response of the system is to make the deviation even greater. Positive feedback therefore usually creates a cycle leading away from homeostasis and, in some cases, results in death. Inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of positive feedback.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which is true regarding the Urinary system?
A. Kidneys makes urine, Kidney help regulate water balance.
B. As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium.
C. Eliminates metabolic wastes., Kidneys makes urine., Kidney help regulate water balance.
D. Kidney help regulate water balance, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, Eliminates metabolic wastes
Answer Explanation
Kidneys makes urine is incorrect. Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase is incorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance is correct. Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is correct. There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes is correct. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
-
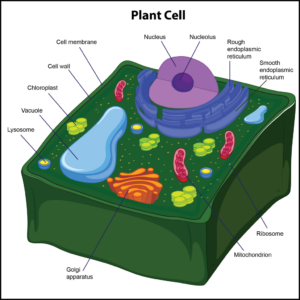
Q #2: What organelle is only associated with plant cells?
A. Cell wall
B. Ribosome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Golgi apparatus
Answer Explanation
Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells. Chloroplasts are photosynthetic compounds used to make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
-
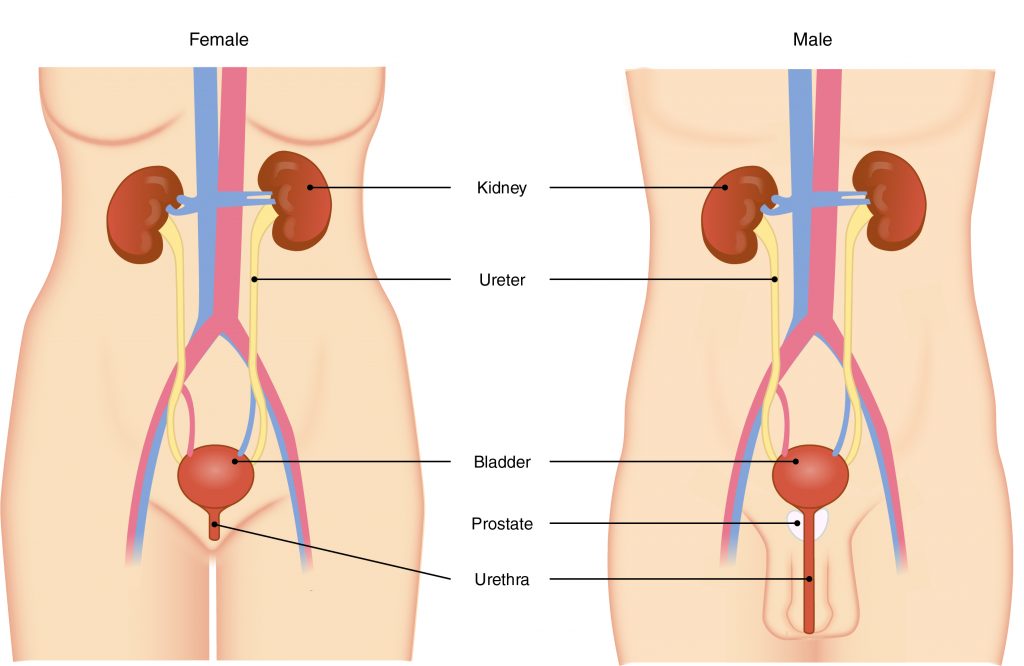
Q #3: What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
Answer Explanation
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
-
Q #4: What type of reaction is described by the following equation? ZnBr2(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2KBr(aq)
A. Synthesis
B. Decomposition
C. Single-Replacement
D. Double-Replacement
Answer Explanation
In this reaction, two elements are trading places hence double-replacement. In the reactants, zinc and bromide ions are together, and potassium and hydroxide ions are together. In the products, zinc and hydroxide ions are together, and potassium and bromide ions are together.
-
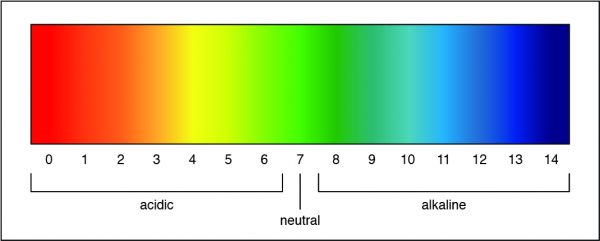
Q #5: What solution has a pH of 7?
A. Aniline
B. Pyridine
C. Pure water
D. Sodium hydroxide
Answer Explanation
A pH of 7 is a neutral solution, which is how pure water is classified. Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
-
Q #6: A spoonful of sugar is added to a hot cup of tea. All the sugar dissolves. How can the resulting solution be described?
A. Saturated and homogeneous
B. Saturated and heterogeneous
C. Unsaturated and homogeneous
D. Unsaturated and heterogeneous
Answer Explanation
Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- A mixture is when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- A homogeneous mixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. A heterogeneous mixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. An unsaturated solution has the ability to dissolve more solute and a saturated solution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
-
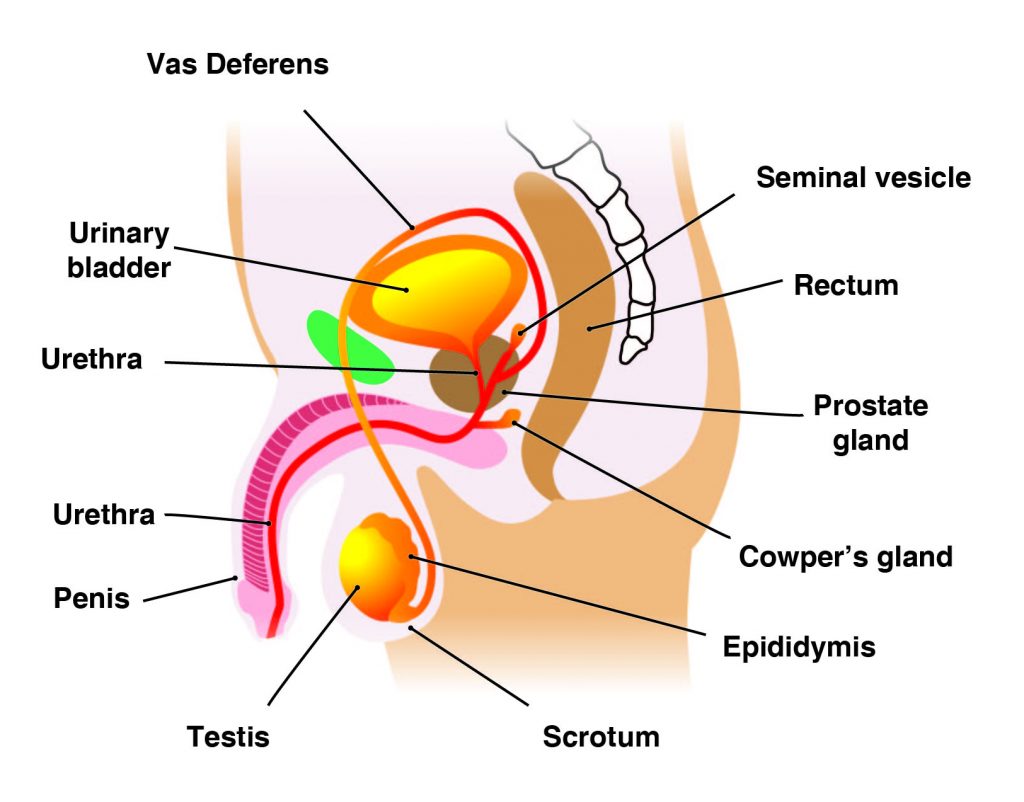
Q #7: Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
Answer Explanation
The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
-
Q #8: What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
Answer Explanation
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
-
Q #9: What structure plays a role in air conduction?
A. Alveolus
B. Capillary
C. Lung
D. Trachea
Answer Explanation
The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
-
Q #10: What raw inorganic material would an autotroph most likely use to create chemical energy for growth?
A. carbon dioxide
B. minerals in soil
C. decaying matter
D. sugar molecules
Answer Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophs are organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
