Which is true regarding the Urinary system?
A. Kidneys makes urine, Kidney help regulate water balance.
B. As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium.
C. Eliminates metabolic wastes., Kidneys makes urine., Kidney help regulate water balance.
D. Kidney help regulate water balance, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, Eliminates metabolic wastes
Kidneys makes urine is incorrect. Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase is incorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance is correct. Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is correct. There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes is correct. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Where is skeletal muscle found?
A. Inside the heart
B. Attached to bone
C. Lining the walls of the bladder
D. Within the gastrointestinal tract
Answer Explanation
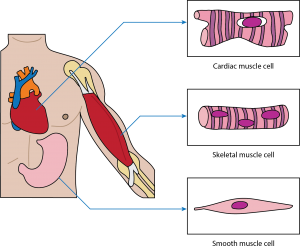
Skeletal muscle: This muscle cell is striated, long, and cylindrical. There are many nuclei in a skeletal muscle cell. Attached to bones in the body, skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily, meaning that it is under conscious control.
Smooth muscle: This muscle consists of nonstriated muscle cells that are spindle-shaped. Like cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contain one nucleus. This muscle type is found in the walls of internal organs like the bladder and stomach. Smooth muscle contraction is involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle: This muscle consists of muscle cells that are striated, short, and branched. These cells contain one nucleus, are branched, and are rectangular. Cardiac muscle contraction is an involuntary process, which is why it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. This muscle is found in the walls of the heart.
-
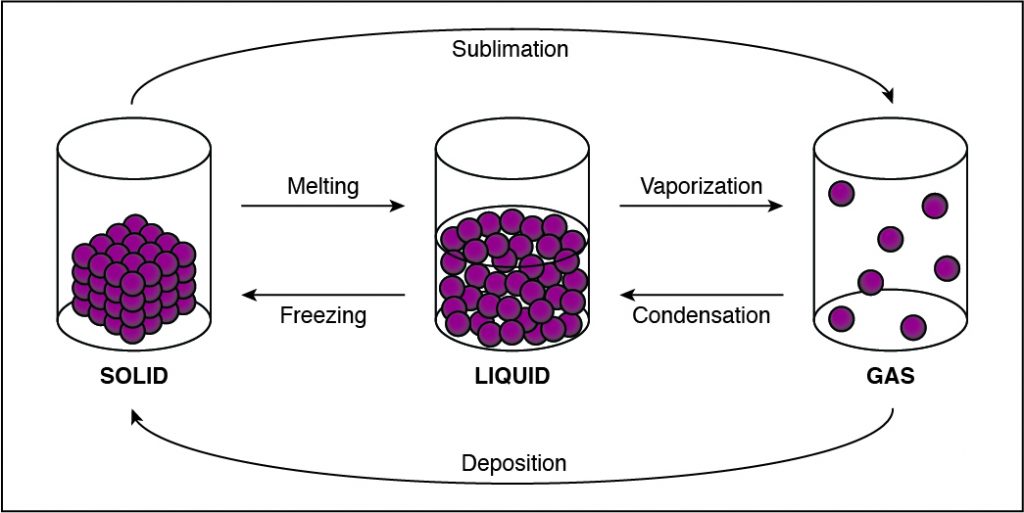
Q #2: During which of the following phase changes will the cohesion between the particles in a substance decrease?
A. Condensation
B. Deposition
C. Freezing
D. Vaporization
Answer Explanation
If the cohesion between particles decreases, then the particles must be undergoing a phase change that allows particles to move farther apart. This happens when a substance vaporizes and turns from liquid to gas. Any phase change that moves to the right in the diagram above requires energy to be added to the system because the substance has more energy at the end of the phase change. The phase changes are melting, vaporization (boiling), and sublimation. When energy is added, particles move faster and can break away from each other more easily as they move to a state of matter with a higher amount of energy. This is most commonly done by heating the substance.
-
Q #3: If a person smells something sweet, what form of information is this initially perceived as in the nervous system?
A. Cognitive
B. Integrative
C. Motor
D. Sensory
Answer Explanation
A sensory nerve is a nerve that carries sensory signals from the external environment to the brain to the central nervous system. It is also an afferent nerve, long dendrites of sensory neurons, which sends sensory information towards the central nervous system (CNS). This information is what is sensed, using the five senses from external environment, sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch.
Motor nerves have only efferent fibers, long axons of motor neurons, that carry impulses away from the CNS to the effectors, which are typically tissues and muscles of the body.
Interneurons are nerve cells that act as a bridge between motor and sensory neurons in the CNS. These neurons help form neural circuits, which helps neurons communicate with each other.
-
Q #4: During the aging process, not all hormone levels decrease; some actually increase. Which of the following is a hormone that may increase as a person ages?
A. Cortisol
B. Insulin
C. Luteinizing
D. Thyroid
Answer Explanation
The aging process affects hormone activity in one of three ways: their secretion can decrease, remain unchanged, or increase.
Hormones that decrease secretion include the following:
- Estrogen (in women)
- Testosterone (in men)
- Growth hormone
- Melatonin
In women, the decline in estrogen levels leads to menopause. In men, testosterone levels usually decrease gradually. Decreased levels of growth hormone may lead to decreased muscle mass and strength. Decreased melatonin levels may play an important role in the loss of normal sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythms) with aging.
Hormones that usually remain unchanged or slightly decrease include the following:
- Cortisol
- Insulin
- Thyroid hormones
Hormones that may increase secretions levels include the following:
Parathyroid hormone
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine, in the very old
-
Q #5: While hiking, a person is startled after encountering a bear. Her palms get sweaty and her heart starts racing. Which part of her nervous system was directly stimulated?
A. Central
B. Parasympathetic
C. Somatic
D. Sympathetic
Answer Explanation
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for activities that are nonvoluntary and under unconscious control. This system controls glands and the smooth muscles of internal organs, heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the following:
- Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system focuses on emergency situations by preparing the body for fight or flight. (Sympathetic = Stress)
- Parasympathetic nervous system: The parasympathetic nervous system controls involuntary processes unrelated to emergencies. This system deals with “rest or digest” activities. (Parasympathetic = Peace)
The somatic nervous system primarily controls voluntary activities such as walking and riding a bicycle. Thus, this system sends information to the CNS and motor nerve fibers that are attached to skeletal muscle.
-
Q #6: After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
Answer Explanation
Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.
-
Q #7: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
Answer Explanation
Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.
-
Q #8: When would a cell most likely contain the most nucleotides?
A. S
B. G1
C. M
D. G2
Answer Explanation
A cell copies its DNA during the S phase, and nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Thus, the step preceding the S phase, the G1 phase, is the phase of the cell cycle when the cell would contain the most nucleotides.
For a cell to divide into more cells, it must grow, copy its DNA, and produce new daughter cells. The cell cycle regulates cellular division. This process can either prevent a cell from dividing or trigger it to start dividing.
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
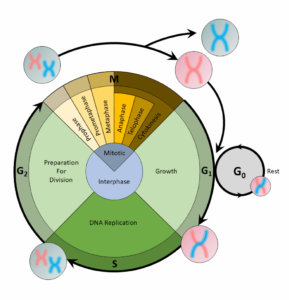
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
-
Q #9: Which statement best represents Mendel’s experiments with garden peas?
A. As a result, Mendel developed several theories that have since been disproved.
B. Mendel realized he was on an incorrect track, which led him to other experimental media
C. As a result, Mendel developed foundational conclusions that are still valued and followed today.
D. Mendel collaborated with others interested in genetics to develop heredity guidelines we still use today
Answer Explanation
Mendel developed theories of genetics that scientists around the world use today.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants either self-pollinate or cross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are either dominant or recessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information called genes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual is homozygous for that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual is heterozygous for that trait. Each copy of a factor, or gene, is called an allele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, or phenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is its genotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
-
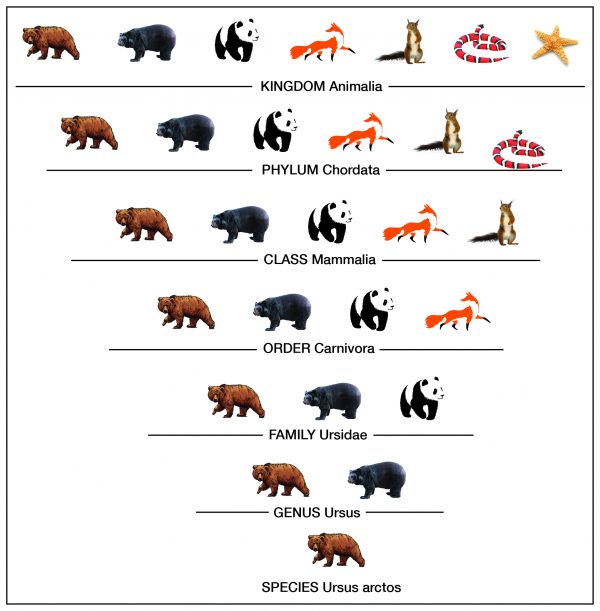
Q #10: Which sequence describes the hierarchy level of biological organization?
A. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
B. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
C. Genus, class, kingdom, species, order, phylum, and family
D. Species, kingdom, genus, class, family, phylum, and order
Answer Explanation
Taxonomy is the process of classifying, describing, and naming organisms. There are seven levels in the Linnaean taxonomic system, starting with the broadest level, kingdom, and ending with the species level. For example, in the image the genus level contains two types of bears, but the species level shows one type. Additionally, organisms in each level are found in the level above it. For example, organisms in the order level are part of the class level. This classification system is based on physical similarities across living things. It does not account for molecular or genetic similarities.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
