Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
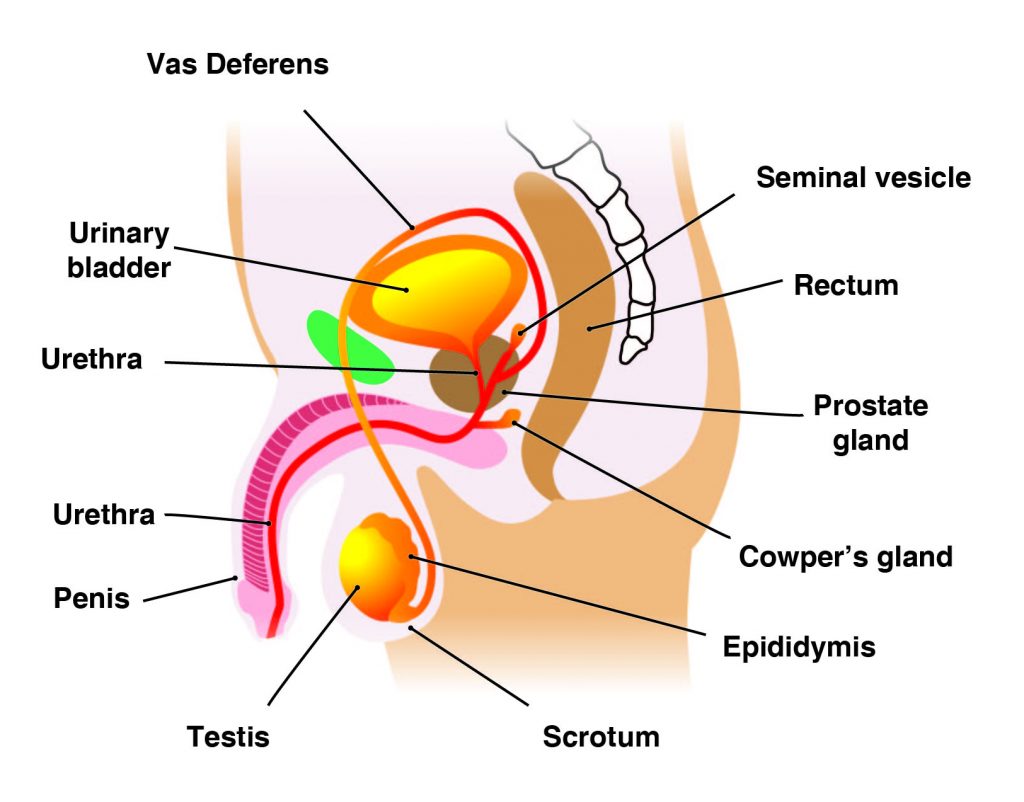
The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
Answer Explanation
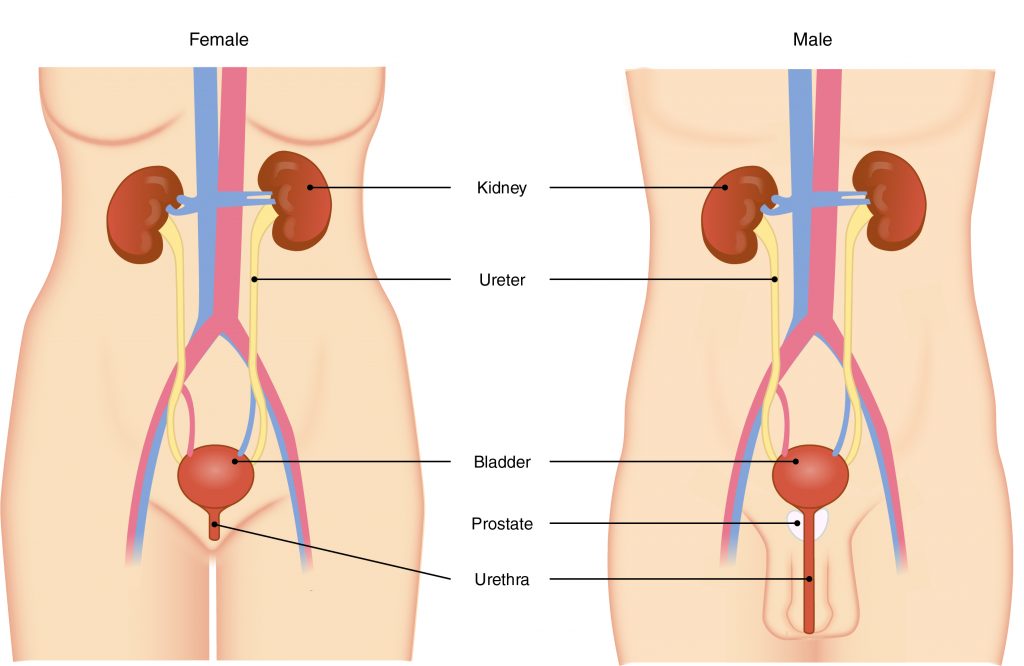
The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
-
Q #2: While hiking, a person is startled after encountering a bear. Her palms get sweaty and her heart starts racing. Which part of her nervous system was directly stimulated?
A. Central
B. Parasympathetic
C. Somatic
D. Sympathetic
Answer Explanation
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for activities that are nonvoluntary and under unconscious control. This system controls glands and the smooth muscles of internal organs, heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the following:
- Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system focuses on emergency situations by preparing the body for fight or flight. (Sympathetic = Stress)
- Parasympathetic nervous system: The parasympathetic nervous system controls involuntary processes unrelated to emergencies. This system deals with “rest or digest” activities. (Parasympathetic = Peace)
The somatic nervous system primarily controls voluntary activities such as walking and riding a bicycle. Thus, this system sends information to the CNS and motor nerve fibers that are attached to skeletal muscle.
-
Q #3: Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
Answer Explanation
Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
-
Q #4: Mendel discovered the pattern associated with _____after developing a series of rules in genetics.
A. epigenetics
B. heredity
C. heterogeneity
D. taxonomy
Answer Explanation
Mendel was accurately able to predict the patterns of heredity by studying rules related to genetics. These rules helped shape his theory of heredity. Heredity is the characteristics offspring inherit from their parents.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants either self-pollinate or cross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are either dominant or recessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information called genes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual is homozygous for that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual is heterozygous for that trait. Each copy of a factor, or gene, is called an allele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, or phenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is its genotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
-
Q #5: Which is classified as a type of acid-base reaction that produces a salt?
A. Combination
B. Decomposition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Neutralization
Answer Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes, neutralization reactions also occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as an ionic compound that includes any cation except H+ and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
-
Q #6: Which part of the digestive system comes before the stomach?
A. mouth
B. esophagus
C. ileum
D. colon
Answer Explanation
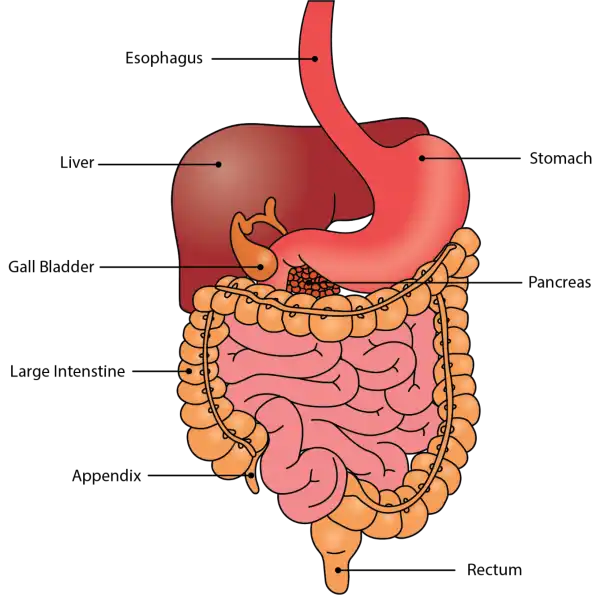
Oral Cavity is the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestine is about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colon is about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
-
Q #7: Which is true regarding the Urinary system?
A. Kidneys makes urine, Kidney help regulate water balance.
B. As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium.
C. Eliminates metabolic wastes., Kidneys makes urine., Kidney help regulate water balance.
D. Kidney help regulate water balance, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, Eliminates metabolic wastes
Answer Explanation
Kidneys makes urine is incorrect. Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase is incorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance is correct. Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is correct. There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes is correct. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
-
Q #8: Why did it take many years for the cell theory to be developed?
A. Advancements in microscopy took place slowly.
B. Cells were difficult to isolate for experimental analysis
C. Researchers believed a cell formed from preexisting cells
D. Scientists already proved that cells were essential for life.
Answer Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
-
Q #9: Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
Answer Explanation
The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.

-
Q #10: The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines
A. the primary structure of a codon
B. the primary structure of a protein
C. the primary structure of a nucleotide
D. the primary structure of a nucleic acid.
Answer Explanation
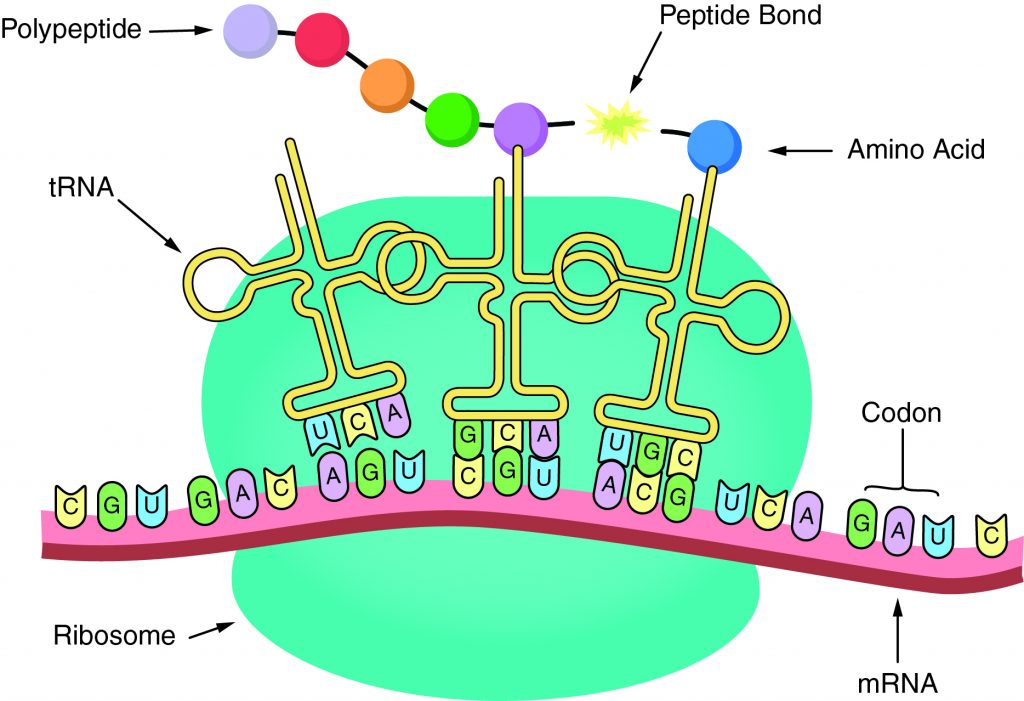
The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines the primary structure of a protein. The components necessary for translation are located in the cytoplasm. Translation is the making of proteins by mRNA binding to a ribosome with the start codon that initiates the production of amino acids. A peptide bond forms and connects the amino acids together. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s structure, which determines its function.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
