Which of the following immune system molecules creates holes in the cell membranes of their target cells in order to destroy the cell?
A. Perforins
B. Interferons
C. Cytokines
D. Lymphotoxins
Perforins are immune system molecules that create holes in the cell membranes of their target cells in order to destroy the cell. Perforins are proteins that are released by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells
They form pores in the target cell membrane, allowing water and ions to enter the cell and causing it to swell and burst.
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe the immune system molecules that create holes in the cell membranes of their target cells. Interferons, cytokines, and lymphotoxins do not create holes in cell membranes.
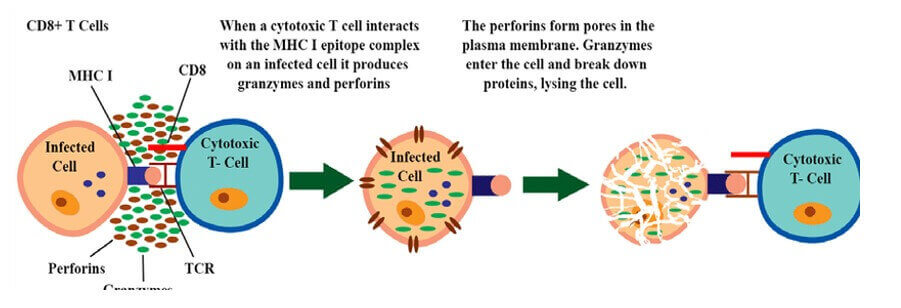
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: A researcher wants to gather data on the average wing strength of all birds found in the American Northwest. The researcher only has one small net, so all large birds were excluded from the study. The researcher's results were different than expected, but he believes his data include enough birds to estimate the strength of all birds. For which of the following reasons should this data be rejected?
A. Data contradict the control group
B. Data were different than expected
C. Data are biased by the methodology
D. Data cannot be displayed graphically
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is c. Data are biased by the methodology. The researcher's data should be rejected because they are biased by the methodology used to gather them. By only using a small net, the researcher excluded all large birds from the study. This means that the data do not accurately represent the average wing strength of all birds found in the American Northwest.
A. The data contradicting the control group is not a reason to reject the data in this case.
B. The data being different than expected is not a reason to reject the data in this case.
D. The data not being able to be displayed graphically is not a reason to reject the data in this case.
-
Q #2: Which of the following immune system molecules creates holes in the cell membranes of their target cells in order to destroy the cell?
A. Perforins
B. Interferons
C. Cytokines
D. Lymphotoxins
Answer Explanation
Perforins are immune system molecules that create holes in the cell membranes of their target cells in order to destroy the cell. Perforins are proteins that are released by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells
They form pores in the target cell membrane, allowing water and ions to enter the cell and causing it to swell and burst.
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe the immune system molecules that create holes in the cell membranes of their target cells. Interferons, cytokines, and lymphotoxins do not create holes in cell membranes.

-
Q #3: Which of the following properties does soap, an emulsifier, have that make it useful for washing dirt off one’s hands with water?
A. Soap’s dual polar and nonpolar nature helps bond oil and water
B. Soap’s acidity causes grime to precipitate into the water
C. Soap’s enzymatic action helps to dissolve grime into small particles
D. Soap’s rough texture physically scours grime off surfaces
Answer Explanation
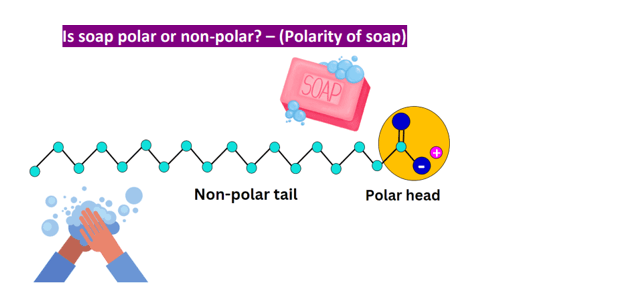
The correct answer is a. Soap’s dual polar and nonpolar nature helps bond oil and water. Soap is an emulsifier, which means that it has both polar and nonpolar regions. The polar regions of soap molecules are atracted to water, while the nonpolar regions are atracted to oil and grease. This allows soap to bond with both water and oil, helping to remove dirt and grime from surfaces.
B. Soap’s acidity does not cause grime to precipitate into the water.
C. Soap does not have enzymatic action that helps to dissolve grime into small particles.
D. Soap’s texture does not physically scour grime off surfaces.
-
Q #4: Which of the following describes a genetic mutation that results in uncontrolled division of a single cell within the body?
A. Cancer
B. Gene therapy
C. Stem cell
D. Translation
Answer Explanation
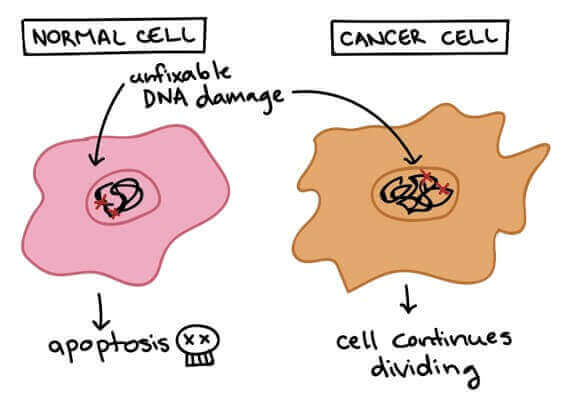
A genetic mutation that results in uncontrolled division of a single cell within the body describes cancer ¹. Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell division ¹. Its development and progression are usually linked to a series of changes in the activity of cell cycle regulators ¹. In most cases, these changes in activity are due to mutations in the genes that encode cell cycle regulator proteins ¹.
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe a genetic mutation that results in uncontrolled division of a single cell within the body. Gene therapy, stem cells, and translation are not processes that result in uncontrolled cell division.
-
Q #5: Which of the following ions binds to the troponin complex, initiating the contraction of a muscle?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Calcium
D. Phosphorus
Answer Explanation
When a muscle cell is stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm. The calcium ions bind to the troponin complex, which is a protein that regulates the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. The binding of calcium to troponin causes a conformational change that exposes the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments. This allows the myosin heads to attach to the actin and pull the filaments past each other, resulting in muscle contraction.
-
Q #6: The mitochondrial inner membrane carries out the same function in cellular respiration as the ________ membrane of chloroplasts in photosynthesis. Which of the following correctly completes the sentence above?
A. Thylakoid
B. Epithelial
C. Nuclear
D. Tonoplast
Answer Explanation
The thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts is where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place, while the mitochondrial inner membrane is where the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis occur during cellular respiration.
The tonoplast is the membrane that surrounds the central vacuole in plant cells. It is not involved in cellular respiration or photosynthesis.
The other options, epithelial and nuclear, are not related to these processes.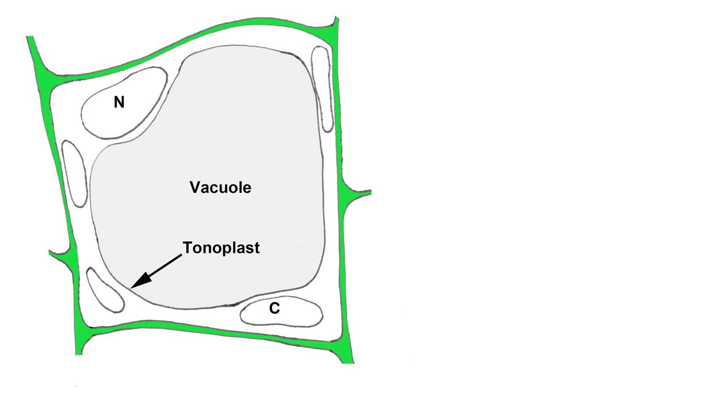
-
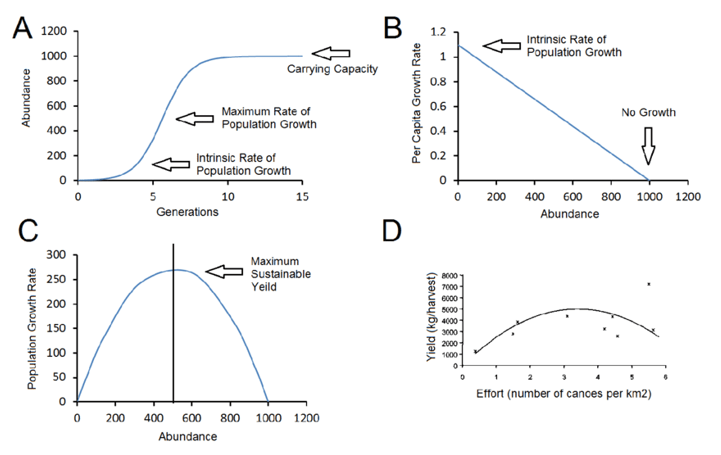
Q #7: Which of the following growth curves shows a population that is at its carrying capacity?
A. B
B. C
C. A
D. D
Answer Explanation
A population is said to be at its carrying capacity when it has reached the maximum number of individuals that can be sustained in a particular environment over a prolonged period of time, given the available resources and the prevailing environmental conditions.
In other words, carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that a given ecosystem can support without being depleted of resources or experiencing environmental degradation. Once a population reaches its carrying capacity, its growth rate slows down and stabilizes, as individuals start to compete more intensely for resources such as food, water, and shelter, and mortality rates increase.
Carrying capacity is an important concept in ecology and population biology because it helps to explain the dynamics of natural populations and how they are influenced by changes in the environment, such as climate change, habitat loss, and human activities.
-
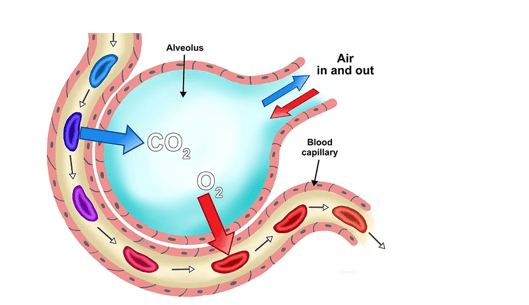
Q #8: Which of the following processes causes most of the carbon dioxide from the blood to move into the alveoli?
A. Passive transport using carrier proteins
B. Active transport using energy
C. Conversion to carbon monoxide
D. Diffusion down a concentration gradient
Answer Explanation
Most of the carbon dioxide from the blood moves into the alveoli by diffusion down a concentration gradient ¹. Carbon dioxide is always carried in the blood and is released into alveolar air during expiration ¹. Respiratory gases move from higher concentration to lower concentration ¹. In alveolar air, when carbon dioxide is less than in blood, carbon dioxide is released ¹.
The other options are incorrect because they do not accurately describe the process by which most of the carbon dioxide from the blood moves into the alveoli. Passive transport using carrier proteins, active transport using energy, and conversion to carbon monoxide is not the processes responsible for moving most of the carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli.
-
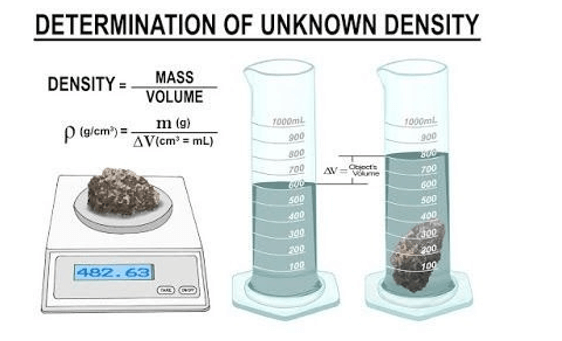
Q #9: To accurately measure the density of a series of small irregular solids made of plastic, wood, fibreglass, and glass, a student will need which of the following laboratory tools?
A. Graduated cylinder, water, weighing balance
B. Graduated cylinder, spectrophotometer, water
C. Graduated beaker, metric ruler, water
D. Weighing balance, Bunsen burner, metric ruler
Answer Explanation
To accurately measure the density of a series of small irregular solids made of plastic, wood, fiberglass, and glass, a student will need a graduated cylinder, water, and a weighing balance. The student can use the water displacement method to determine the volume of each solid by measuring the volume of water displaced when the solid is submerged in a graduated cylinder filled with water. The mass of each solid can be measured using a weighing balance. The density can then be calculated by dividing the mass by the volume.
The other options are not correct because they do not provide the necessary tools to accurately measure the density of the solids. A spectrophotometer is used to measure light absorption and is not necessary for measuring density. A graduated beaker is less accurate than a graduated cylinder for measuring volume. A Bunsen burner is used for heating and is not necessary for measuring density.
-
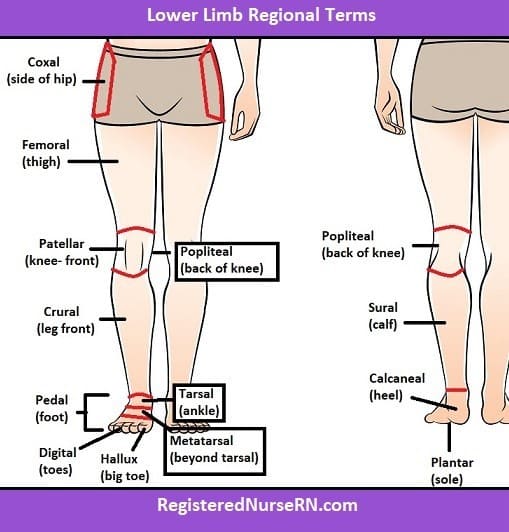
Q #10: In which of the following regions of the body are the tibia and fibula?
A. Coxal
B. Antecubital
C. Tarsal
D. Crural
Answer Explanation
The tibia and fibula are located in the crural region of the body, which is the lower leg between the knee and ankle. The coxal region refers to the hip area, the antecubital region is the front of the elbow, and the tarsal region is the ankle and foot.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
