Which of the following indicates the function of sodium bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas?
A. Sodium bicarbonate is a protease that digests carbohydrates.
B. Sodium bicarbonate stimulates the pyloric sphincter.
C. Sodium bicarbonate inhibits peristalsis.
D. Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
The pancreas secretes large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which protects the duodenum by neutralizing the acid that comes from the stomach.
This compound helps neutralize stomach acid generated during the digestive process.
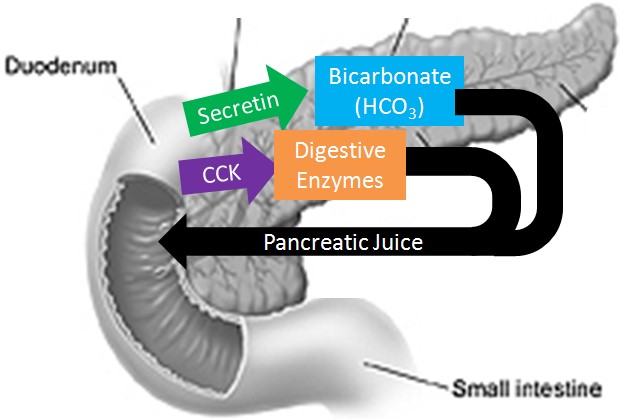
Choice A is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate is not a protease that digests carbohydrates.
Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins, while sodium bicarbonate is a chemical compound that helps neutralize stomach acid.
Choice B is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not stimulate the pyloric sphincter.
The pyloric sphincter is a ring of smooth muscle that separates the stomach from the duodenum and regulates the passage of partially digested food (chyme) into the small intestine.
Choice C is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not inhibit peristalsis.
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following is the number of protons in a lithium atom?
A. 7
B. 3
C. 12
D. 4
Answer Explanation
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
Since lithium has an atomic number of 3, it has 3 protons in its nucleus.
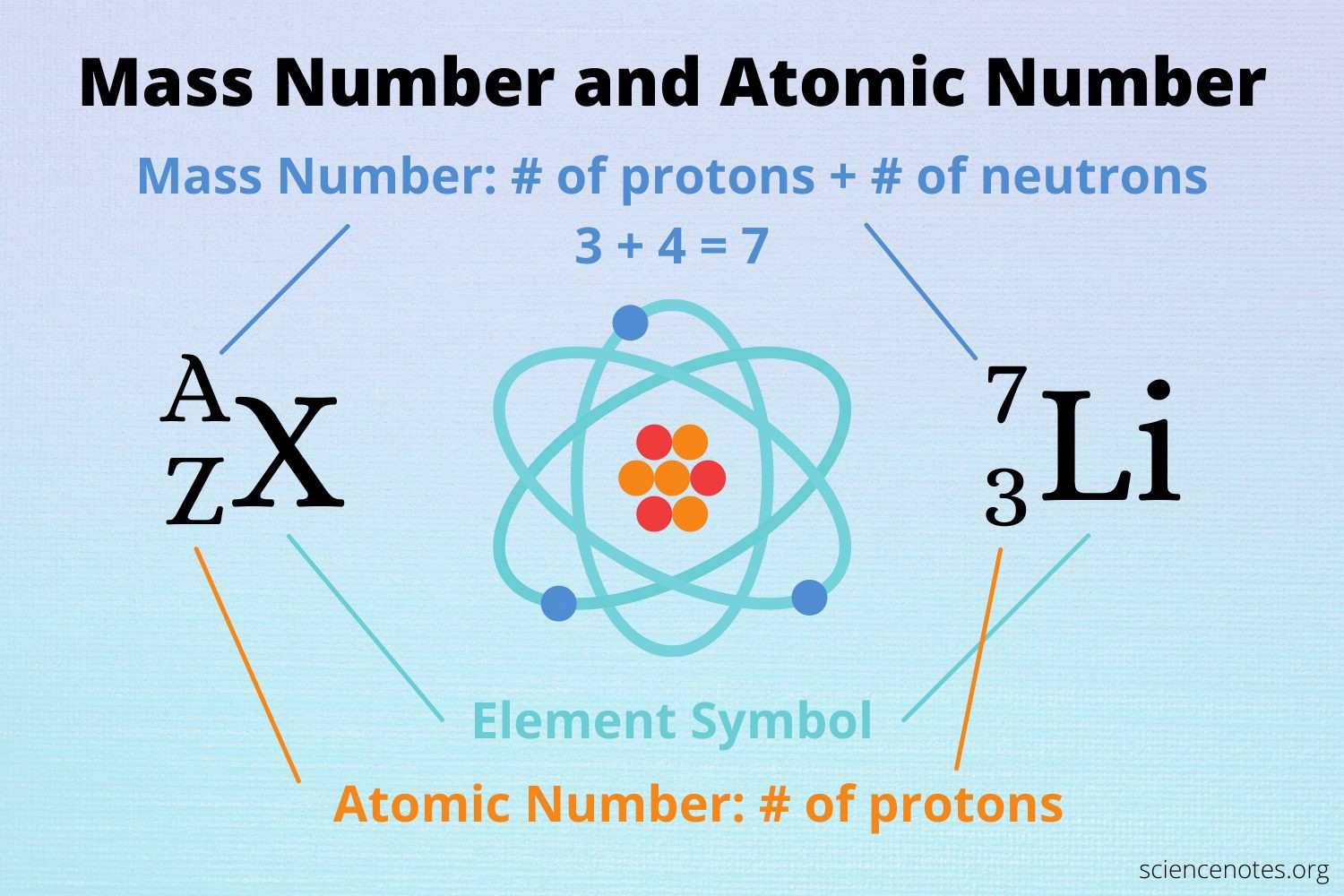
Choice A is not correct because 7 is the mass number of lithium, not the number of protons.
Choice C is not correct because 12 is not the atomic number or mass number of lithium.
Choice D is not correct because 4 is not the atomic number or mass number of lithium.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is the main function of centrosomes in animal cells?
A. . Organelle trafficking.
B. Pathogen digestion.
C. Cytoplasm formation
D. Microtubule organization
Answer Explanation
Microtubule organization.
Centrosomes are organelles that serve as the main microtubule-organizing centers for animal cells.
They regulate the movement of microtubules and other cytoskeletal structures, thereby facilitating changes in the shapes of the membranes of animal cells.
Choice A, Organelle trafficking, is not the correct answer because while centrosomes do play a role in intracellular trafficking during interphase by organizing an astral ray of microtubules, their main function is microtubule organization.
Choice B, Pathogen digestion, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in pathogen digestion.
Choice C, Cytoplasm formation, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in cytoplasm formation.
-
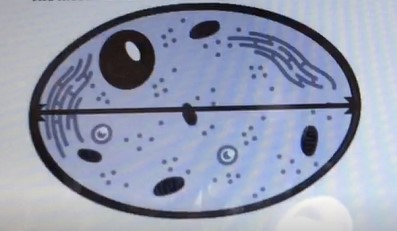
Q #3: The measurement indicated by the line across the center of the cell is best referred to as which of the following?
A. Area.
B. Diameter.
C. Volume.
D. Radius.
Answer Explanation
Diameter.
The diameter is the measurement of a straight line passing through the center of a circle and connecting two points on its circumference.
In this case, the line across the center of the cell represents the diameter of the cell.
Choice A, Area, is not the correct answer because area refers to the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape.
Choice C, Volume, is not the correct answer because volume refers to the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object.
Choice D, Radius, is not the correct answer because radius refers to the distance from the center of a circle to its circumference and is half the length of the diameter.
-
Q #4: Which of the following substances protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation?
A. Melanin
B. Perspiration
C. Sebum
D. Keratin
Answer Explanation
Melanin.
Melanin is a pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in the skin.
It protects the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation by absorbing and dissipating over 99.9% of absorbed UV radiation.
This helps to prevent DNA damage and other adverse effects of UV radiation on the skin.
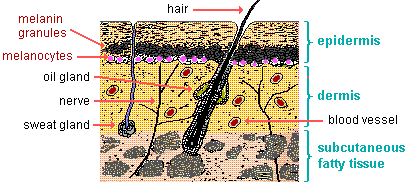
Choice B.
Perspiration is not correct because it is a fluid produced by sweat glands in the skin that helps to regulate body temperature, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
Choice C.
Sebum is not correct because it is an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands in the skin that helps to lubricate and protect the skin, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
Choice D.
Keratin is not correct because it is a fibrous protein that provides strength and durability to the skin, hair and nails, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
-
Q #5: Which of the following microorganisms lack their own metabolic pathways and can only reproduce inside of a host cell?
A. Bacteria
B. Protozoa
C. Helminths
D. Viruses
Answer Explanation
Viruses.
Viruses lack essential machinery needed to reproduce by themselves.
In fact, viruses can only reproduce after infecting a living cell - a process called viral replication.
Once inside a living cell, viruses re-program the cell’s machinery to produce viral proteins and genetic material to make new copies of themselves.
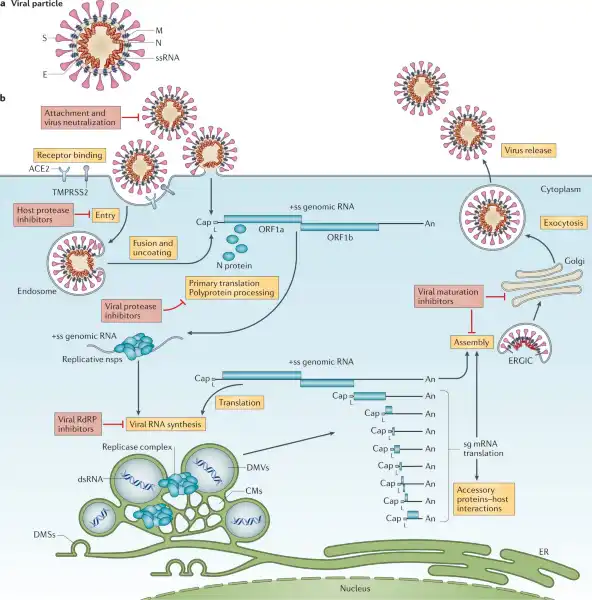
Choice A, Bacteria, is not the correct answer because bacteria have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice B, Protozoa, is also not the correct answer because protozoa are singlecelled eukaryotes that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice C, Helminths, is not the correct answer because helminths are multicellular parasitic worms that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
-
Q #6: What is the approximate threshold value for mammalian neurons?
A. -55 mV
B. -80 mV
C. +35 mV
D. 0 mV
Answer Explanation
The approximate threshold value for mammalian neurons is -55 mV.
The threshold potential is the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential.
Most often, the threshold potential is a membrane potential value between –50 and –55 mV
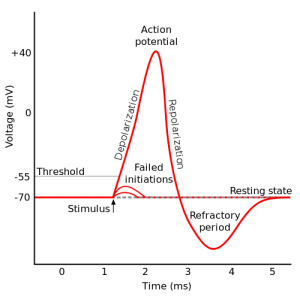
The membrane potential of a neuron is determined by the distribution of ions across the cell membrane.
At rest, the inside of a neuron is more negative than the outside due to the presence of negatively charged proteins and other molecules.
The movement of ions across the cell membrane can change the membrane potential.
For example, when sodium ions enter the cell, they make the inside of the cell more positive (less negative), causing depolarization.
Choice B is incorrect because -80 mV is below the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
Choice C is incorrect because +35 mV is above the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
Choice D is incorrect because 0 mV is above the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
-
Q #7: In a plant in which fuzzy leaves (F) are dominant over smooth leaves (f), which of the following crosses will produce only offspring with smooth leaves?
A. FF x FF
B. Ff x Ff
C. ff x ff
D. Ff x ff
Answer Explanation
ff.
In this cross, both parents are homozygous recessive for the smooth leaf trait
(ff).
This means that all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the recessive allele (f) and will therefore have smooth leaves.
Choice A.
FF x FF is not correct because both parents are homozygous dominant for the fuzzy leaf trait (FF) and all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the dominant allele (F) and will therefore have fuzzy leaves.
Choice B.
Ff x Ff is not correct because both parents are heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) and their offspring can inherit either one dominant allele (F) or one recessive allele (f) from each parent, resulting in a 3:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves. Choice D.
Ff x ff is not correct because one parent is heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) while the other is homozygous recessive (ff), resulting in a 1:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves in their offspring.
-
Q #8: Which of the following structures is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Cell membrane
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Chloroplasts
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer Explanation
The cell membrane is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment.
It is composed of a lipid bilayer and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
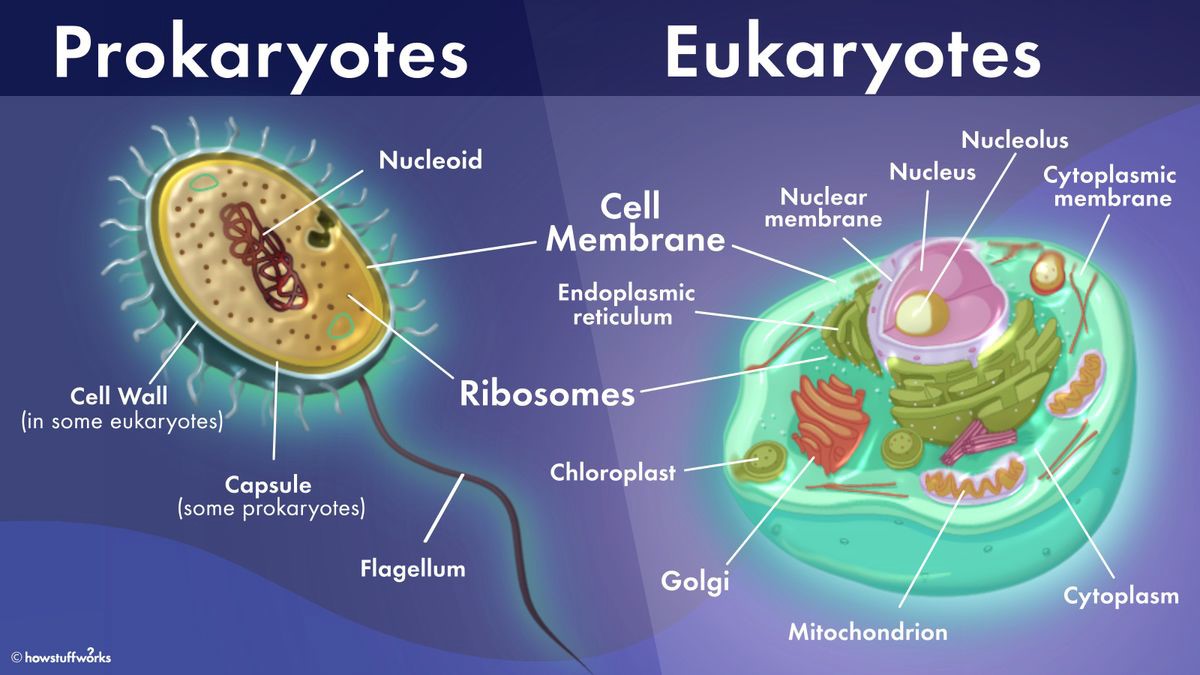
Choice B is incorrect because the Golgi apparatus is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to other parts of the cell or to be secreted outside the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because chloroplasts are not present in prokaryotic cells.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae that are responsible for photosynthesis.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
-
Q #9: Parasitic worm infestation is hypothesized to be damaging to the host. However, scientists have recently discovered that worm infestation can relieve the effects of certain autoimmune disorders. In which of the following ways should the hypothesis be modified, given the new findings?
A. Worm infestation prevents the body from immune malfunction
B. Worm infestation reduces the severity of certain autoimmune disorders
C. Worm infestations exacerbate the body's immune reactions
D. Lack of worm infestations is the cause of some autoimmune disorders
Answer Explanation
The hypothesis should be modified to include the new findings that worm infestation can relieve the effects of certain autoimmune disorders.
A possible modification could be: “Parasitic worm infestation can have both damaging and beneficial effects on the host.
While it can cause harm, it has also been found to reduce the severity of certain autoimmune disorders.”
Choice A.
Worm infestation prevents the body from immune malfunction is not correct because it overstates the findings and implies that worm infestation completely prevents immune malfunction, which is not supported by the evidence.
Choice C.
Worm infestations exacerbate the body’s immune reactions is not correct because it contradicts the new findings that worm infestation can relieve the effects of certain autoimmune disorders.
Choice D.
Lack of worm infestations is the cause of some autoimmune disorders is not correct because it overstates the findings and implies a causal relationship between lack of worm infestations and autoimmune disorders, which is not supported by the evidence.
-
Q #10: Which of the following organic molecules contain both an amine and carboxyl group?
A. Lipids
B. Chitin
C. Cellulose
D. Proteins
Answer Explanation
Proteins.
Proteins are made up of amino acids which are organic molecules that contain both an amine functional group (–NH2) and a carboxylic acid functional group (– COOH).
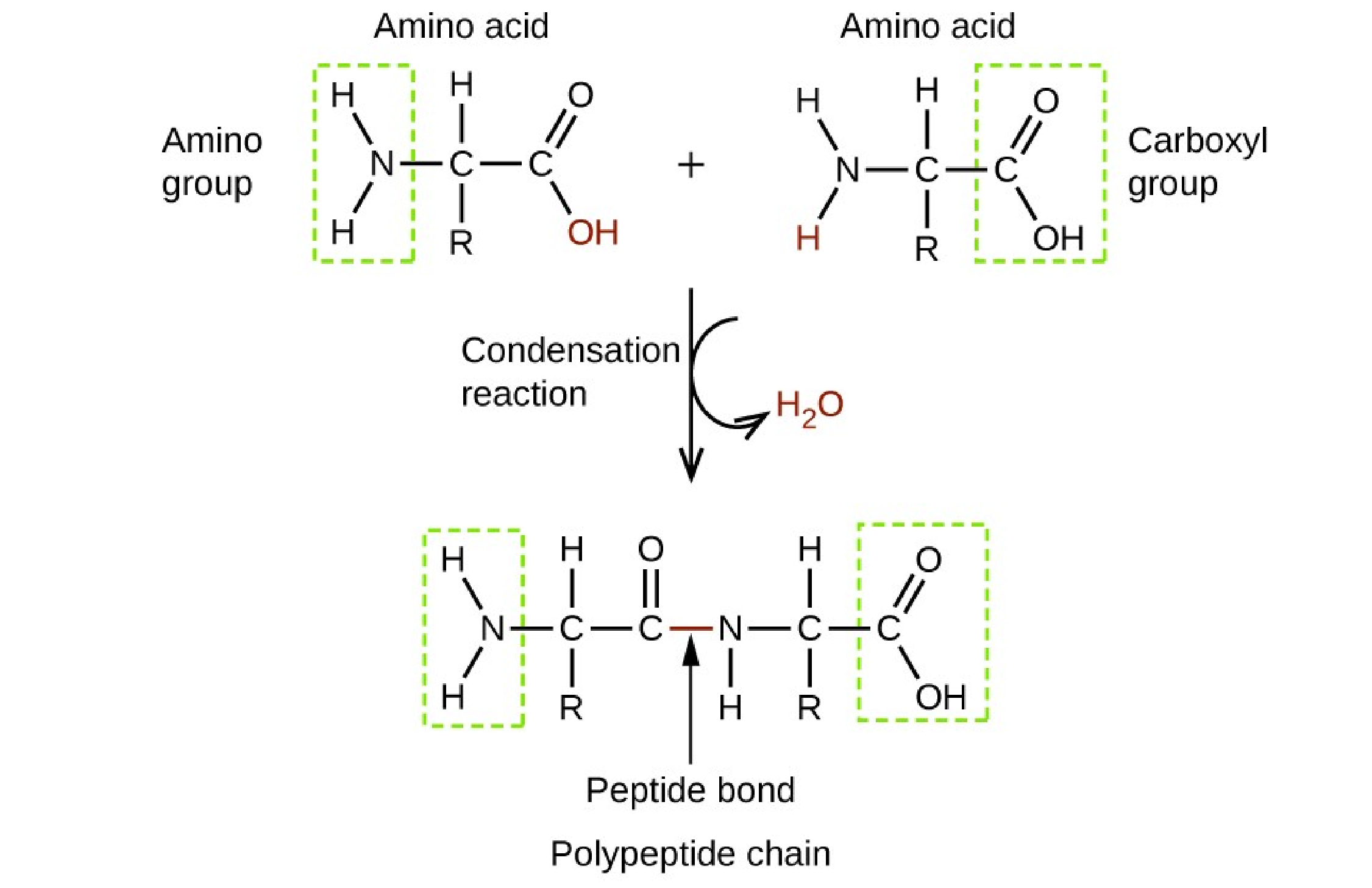
Choice A, Lipids, is not the correct answer because lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others.
They do not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice B, Chitin, is not the correct answer because chitin is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice C, Cellulose, is not the correct answer because cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C6H10O5)n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
