Which of the following is a consequence of increased viscosity of a fluid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. The fluid will have a lower density.
C. The fluid will have a higher flow rate.
D. The fluid will have a higher pressure.
The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: A nurse is caring for a patient who has been declared brain dead and is awaiting organ donation. Which of the following interventions is most important to preserve the viability of the organs?
A. Administering antibiotics to prevent infection.
B. Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
C. Providing emotional support to the family members.
D. Applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
Early identification and management of potential organ donors must take into consideration specific pathophysiologic changes for medical optimization 1.
The VIPPS (ventilation, infusion and pumping, pharmacological treatment, and specificities) strategy is a mnemonic method that brings together key aspects of the restoration of oxygen delivery to tissues during hemodynamic instability plus organ optimization strategies.
Choice A is incorrect because administering antibiotics to prevent infection is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Choice C is incorrect because providing emotional support to family members, while important, is not an intervention that directly affects organ viability.
Choice D is incorrect because applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
-
Q #2: Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
Answer Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
-
Q #3: Which process involves the fusion of male and female gametes resulting in the formation of a zygote?
A. Oogenesis.
B. Fertilization.
C. Meiosis.
D. Mitosis.
Answer Explanation
Fertilization.
Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
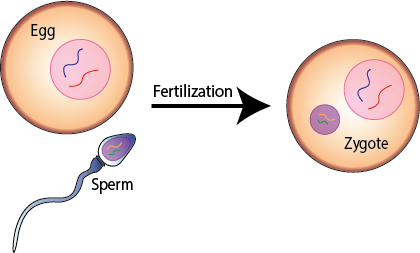
Oogenesis (choice A) is the process by which female gametes, or eggs, are produced.
Meiosis (choice C) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of gametes.
Mitosis (choice D) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
-
Q #4: How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
-
Q #5: Which factor is primarily responsible for the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis?
A. Hydrostatic pressure of the solution.
B. Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
C. Temperature of the solution.
D. Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules .
Answer Explanation
Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
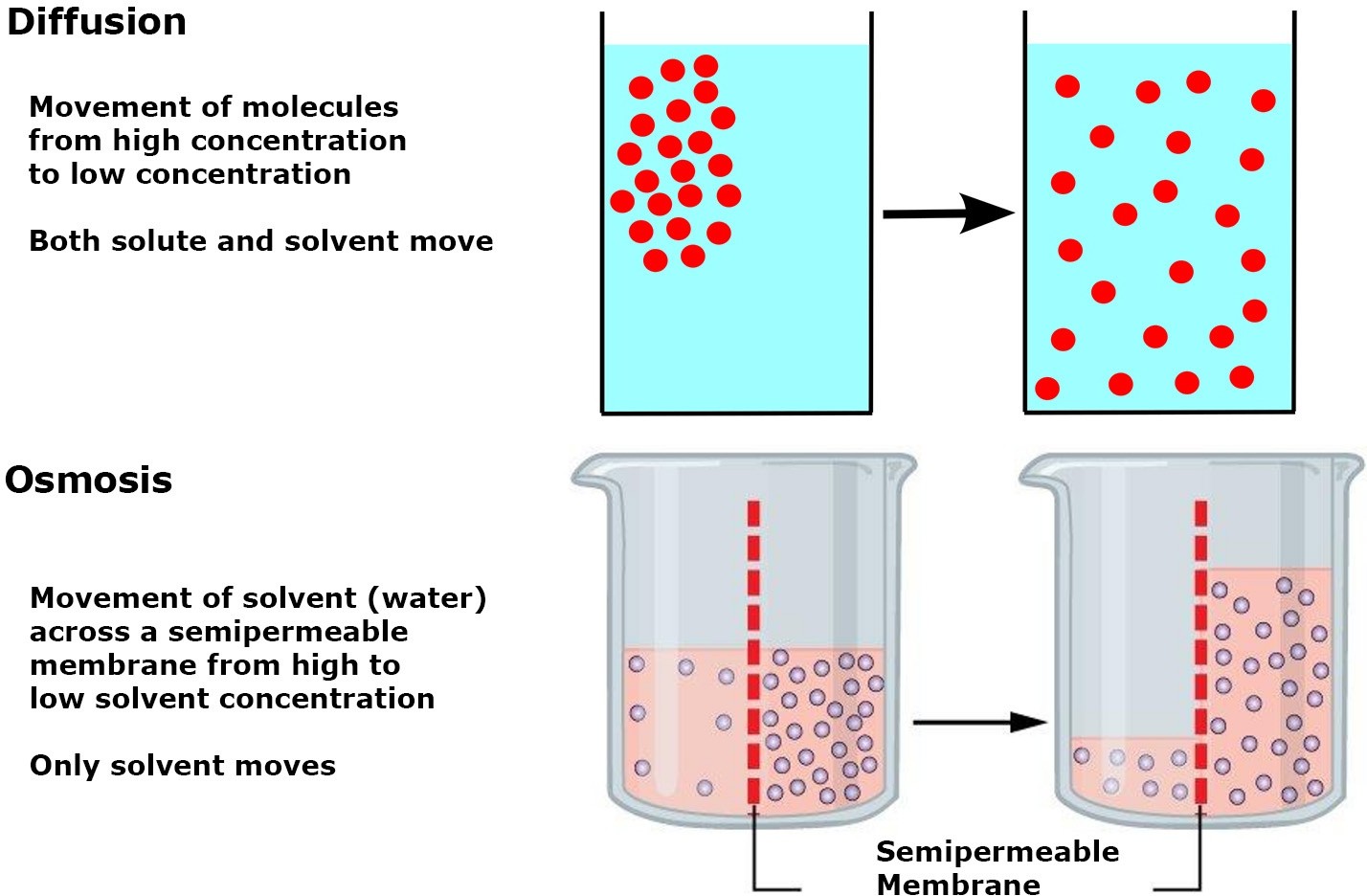
The concentration of solute particles in the solution is the primary factor that determines the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis.
Hydrostatic pressure (choice A) can affect the movement of water across cell membranes but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Temperature (choice C) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules (choice D) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
-
Q #6: During the menstrual cycle, which structure in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation?
A. Corpus luteum.
B. Fimbriae
C. Follicle
D. Ovarian ligament.
Answer Explanation
Corpus luteum.
During the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation.
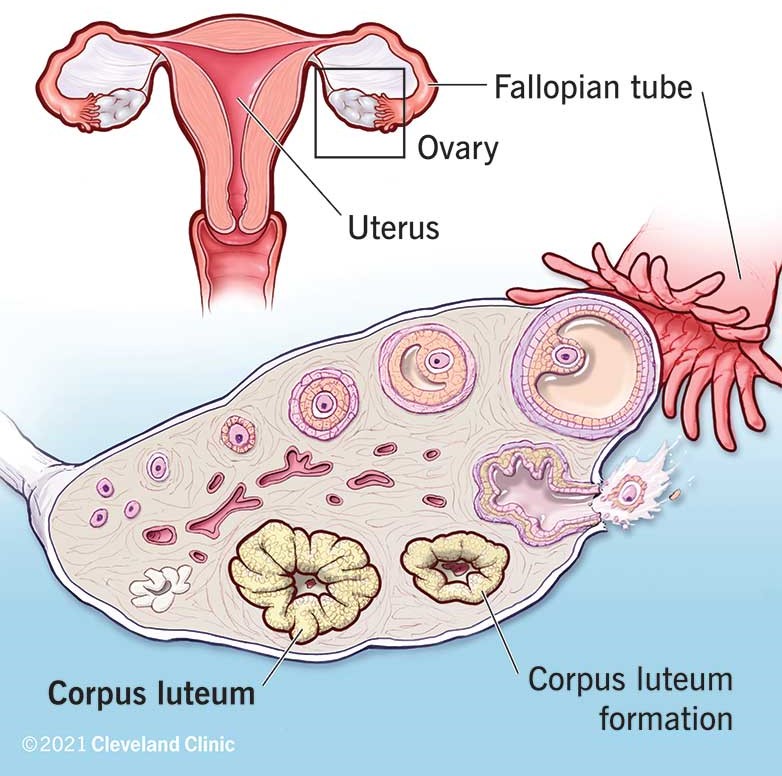
Choice B is incorrect because fimbriae are finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube.
Choice C is incorrect because a follicle is a sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Choice D is incorrect because the ovarian ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the uterus.
-
Q #7: Which hormone is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development, menstrual cycle, and widening of hips?
A. Progesterone
B. Testosterone
C. Estrogen
D. FSH
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Estrogen.
Estrogen is a steroid hormone responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development, menstrual cycle, and widening of hips.
Choice A, Progesterone, is not the correct answer because it is required to maintain pregnancy and delivery.
Choice B, Testosterone, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone produced by the testes which controls the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Choice D, FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone), is not the correct answer because it stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles in females and regulates spermatogenesis in males.
-
Q #8: Which of the following structures in the nephron is responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients?
A. Distal tubule
B. Proximal tubule
C. Glomerulus
D. Loop of Henle
Answer Explanation
Proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is responsible for reabsorbing all the nutrients and most of the water.
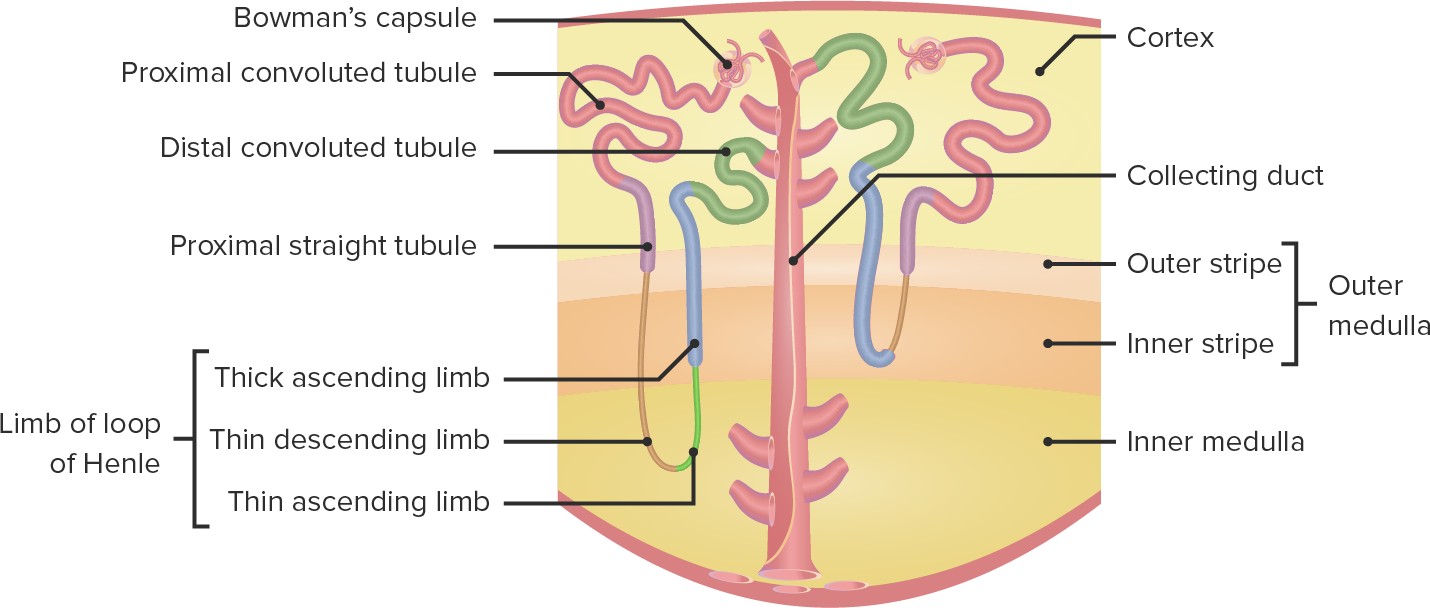
Choice A is incorrect because the distal tubule is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
Choice C is incorrect because the glomerulus is responsible for filtering fluid and solutes out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate.
Choice D is incorrect because the Loop of Henle is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
-
Q #9: A nurse is conducting a research study to compare the effects of two different pain medications on postoperative patients. The nurse randomly assigns the patients to either receive medication A or medication B. Which of the following is the best way to ensure that the study is valid and reliable?
A. Use a large sample size and a standardized procedure for administering the medications.
B. Use a placebo group and a double-blind technique for giving the medications.
C. Use a matched-pairs design and a crossover technique for switching the medications.
D. Use a convenience sample and a pretest-posttest design for measuring the pain levels.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
Using a placebo group and a double-blind technique for giving the medications is the best way to ensure that the study is valid and reliable.
A placebo group helps control for the placebo effect, which can influence the results of a study.
A double-blind technique means that neither the patients nor the researchers know which medication is being given, reducing bias.
Choice A is not the best answer because while a large sample size and standardized procedure can increase reliability, they do not address validity.
Choice C is not the best answer because a matched-pairs design and crossover technique are useful for reducing variability but do not address validity.
Choice D is not the best answer because a convenience sample may not be representative and a pretest-posttest design does not control for extraneous variables.
-
Q #10: Which subatomic particle contributes to the positive charge of an atom?
A. Proton
B. Neutron
C. Electron
D. Nucleon
Answer Explanation
Protons contribute to the positive charge of an atom.
Protons are subatomic particles with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom.
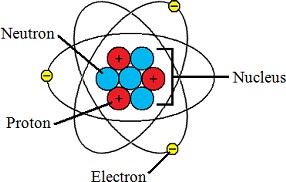
Choice B is incorrect because neutrons are neutral and do not have a charge. Choice C is incorrect because electrons have a negative charge.
Choice D is incorrect because nucleons refer to both protons and neutrons, but only protons contribute to the positive charge of an atom.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
