Which of the following refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand?
A. Orthopnea
B. Hypoxia
C. Tachypnea
D. Bradypnea
The correct answer is choice A. Orthopnea.
Orthopnea refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand.
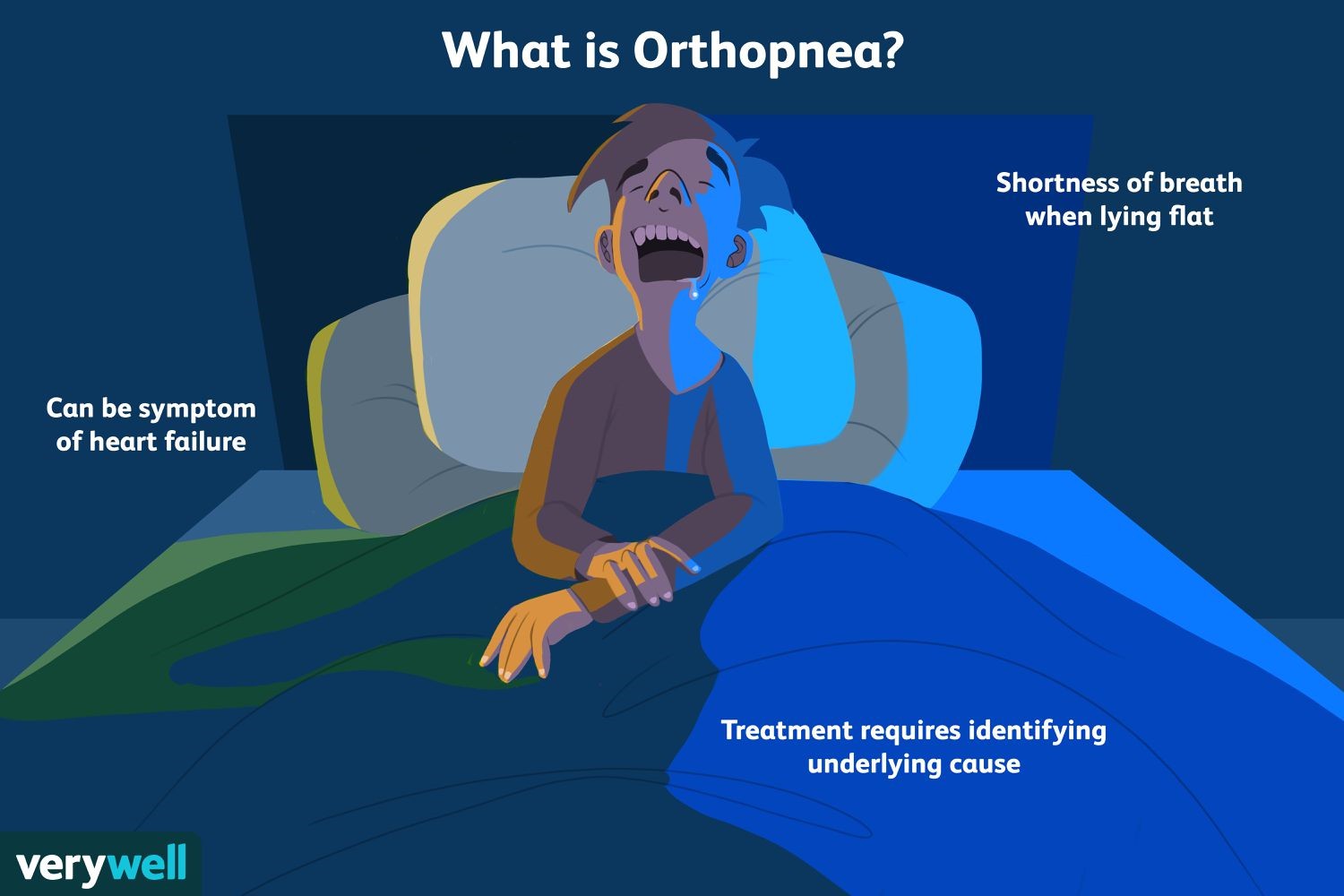 |
Choice B, Hypoxia, is not the correct answer because it refers to a condition in which there is a lack of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Choice C, Tachypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to rapid breathing.
Choice D, Bradypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to abnormally slow breathing.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
-
Q #2: Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
-
Q #3: A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder. The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
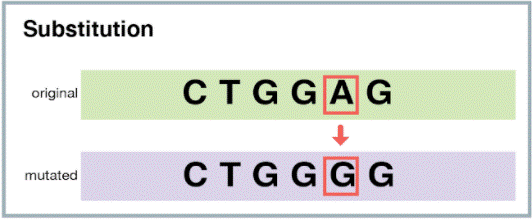
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
-
Q #4: Which of the following is an example of a storage form of glucose in the human body?
A. Starch
B. Glycogen
C. Fructose
D. Cellulose
Answer Explanation
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the human body.
It is a polysaccharide that is stored primarily in the liver and muscle tissue and can be broken down into glucose when the body needs energy.
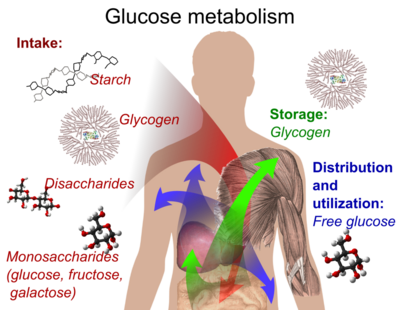
Choice A is incorrect because starch is a storage form of glucose in plants, not in the human body.
Choice C is incorrect because fructose is a simple sugar, not a storage form of glucose.
Choice D is incorrect because cellulose is a structural carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, not a storage form of glucose in the human body.
-
Q #5: What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
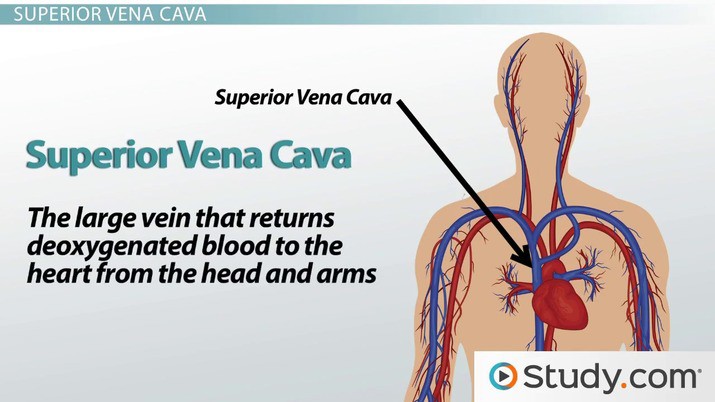
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
-
Q #6: A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis. What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
Answer Explanation
Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
-
Q #7: How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
-
Q #8: Which of the following allows a limited range of immune cells to detect and respond rapidly to a wide range of pathogens that share common structures?
A. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
B. Cytokines
C. Chemokines
D. T cells .
Answer Explanation
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are a class of receptors that can directly recognize the specific molecular structures on the surface of pathogens.
PRRs play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system and are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens.
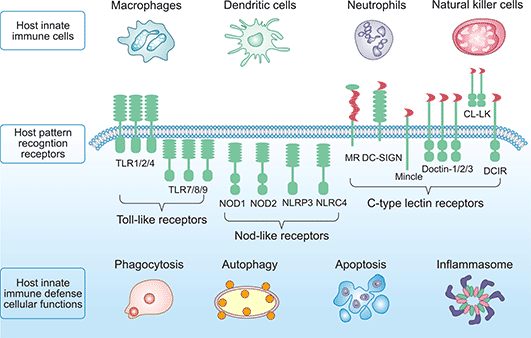
Choice B is incorrect because cytokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that regulate immunity.
Choice C is incorrect because chemokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that attract immune cells to sites of infection.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are not receptors but rather white blood cells that assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
-
Q #9: Which organ in the human body is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells?
A. Spleen
B. Kidneys
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
The spleen is an organ in the human body that is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells.
Choice B is incorrect because the kidneys are responsible for filtering waste from the blood and regulating electrolyte balance.
Choice C is incorrect because the pancreas produces hormones and enzymes that aid in digestion.
Choice D is incorrect because the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
-
Q #10: What is the relationship between atomic mass and mass number?
A. They are the same.
B. Atomic mass is always greater than mass number.
C. Atomic mass and mass number are not related.
D. Atomic mass is very close to mass number but with some deviation in the decimal places.
Answer Explanation
Atomic mass is very close to mass number but with some deviation in the decimal places.
Atomic mass is also known as atomic weight and is the weighted average mass of an atom of an element based on the relative natural abundance of that element’s isotopes.
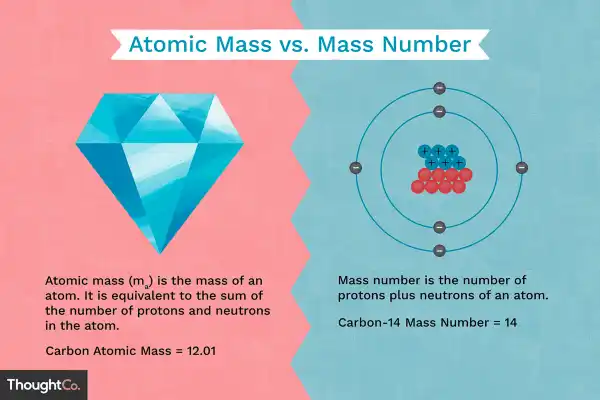
The mass number, on the other hand, is a count of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Choice A is incorrect because atomic mass and mass number do not mean the same thing.
Choice B is incorrect because atomic mass is not always greater than mass number.
Choice C is incorrect because atomic mass and mass number are related.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
