Which of the following statements best supports the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer?
A. Cancerous and normal cells share genetic sequences
B. Cellular DNA has sequences related to viral sequences
C. Viruses and cancer cells both replicate rapidly.
D. Genes that regulate cell division are found in some viruses
Genes that regulate cell division are found in some viruses.
When viruses cause an infection, they spread their DNA, affecting healthy cells’ genetic makeup and potentially causing them to turn into cancer.
For instance, HPV infections cause the virus’ DNA to combine with the host’s DNA, disrupting the normal function of cells.
Choice A is not correct because cancerous and normal cells sharing genetic sequences does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Choice B is not correct because cellular DNA having sequences related to viral sequences does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Choice C is not correct because viruses and cancer cells both replicating rapidly does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following glands synthesizes antidiuretic hormone?
A. Pineal gland
B. Thymus
C. Hypothalamus
D. Pancreas
Answer Explanation
The hypothalamus is a region of the brain that synthesizes antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin.
ADH is then transported to the posterior pituitary gland via neurohypophysial capillaries, where it is stored until it is ready to be secreted into the circulation.
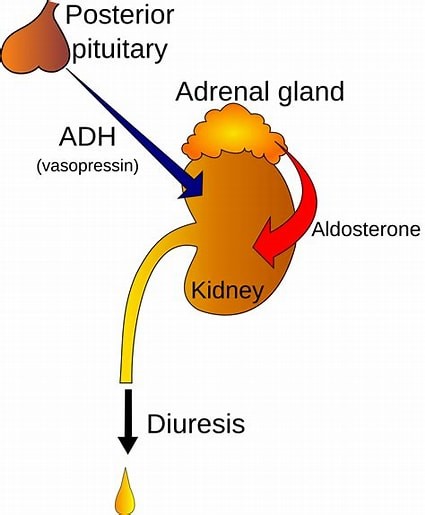
Choice A.
Pineal gland is not correct because it is a small endocrine gland located in the brain that secretes the hormone melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles, but it does not synthesize ADH.
Choice B.
Thymus is not correct because it is a gland located in the chest that produces hormones involved in immune system development, but it does not synthesize ADH.
Choice D.
Pancreas is not correct because it is a gland located behind the stomach that secretes hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels, but it does not synthesize ADH.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is used to determine a person's DNA sequence?
A. Enzymes
B. Blood types
C. Hormones
D. Genes
Answer Explanation
Genes are used in the process of DNA sequencing to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
Choice B.
Blood types is not the correct answer because blood types are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells and are not directly related to DNA sequencing.
Choice C.
Hormones is not the correct answer because hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the body and are not directly involved in DNA sequencing.
Choice D.
Genes is the correct answer because genes are used in the process of DNA sequencing to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
-
Q #3: Which of the following physiological responses is caused by the release of antidiuretic hormone?
A. Increase in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus.
B. Increase in water reabsorption in the collecting duct
C. Decrease in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus.
D. Decrease in water reabsorption in the collecting duct
Answer Explanation
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, is a hormone that helps regulate the amount of water in your body.
It works to control the amount of water your kidneys reabsorb as they filter out waste from your blood.
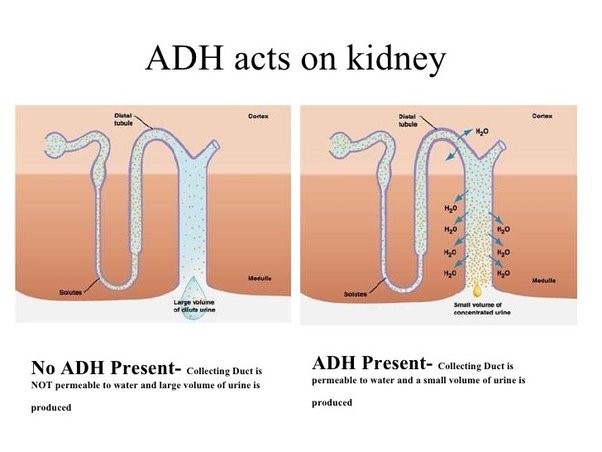
Choice A is not correct because an increase in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus is not a physiological response caused by the release of antidiuretic hormone.
Choice C is not correct because a decrease in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus is not a physiological response caused by the release of antidiuretic hormone.
Choice D is not correct because a decrease in water reabsorption in the collecting duct is not a physiological response caused by the release of antidiuretic hormone.
-
Q #4: To separate genomic DNA fragments by size, which of these laboratory methods is most useful?
A. Titration
B. Electrophoresis
C. Filtration
D. Spectrophotometry
Answer Explanation
Electrophoresis is the most useful laboratory method for separating genomic DNA fragments by size.
Electrophoresis is a technique that uses an electric field to separate charged molecules, such as DNA fragments, based on their size and charge.
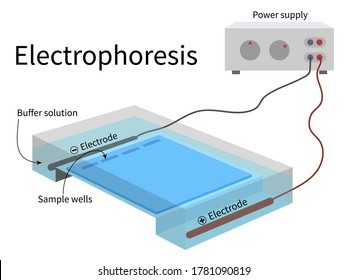
Choice A is not correct because titration is a laboratory method used to determine the concentration of a solution.
Choice C is not correct because filtration is a laboratory method used to separate solids from liquids.
Choice D is not correct because spectrophotometry is a laboratory method used to measure the absorbance of light by a solution.
-
Q #5: Which of the following substances is responsible for donating H+ ions to act as a buffer when blood pH rises?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Carbon monoxide
C. Carbonic acid
D. Oxygen
Answer Explanation
Carbonic acid.
In the human body, maintaining the pH of the blood within a narrow range is critical for proper physiological functioning.
One of the buffering systems that helps to regulate blood pH involves the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into carbonic acid (H2CO3), which then dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
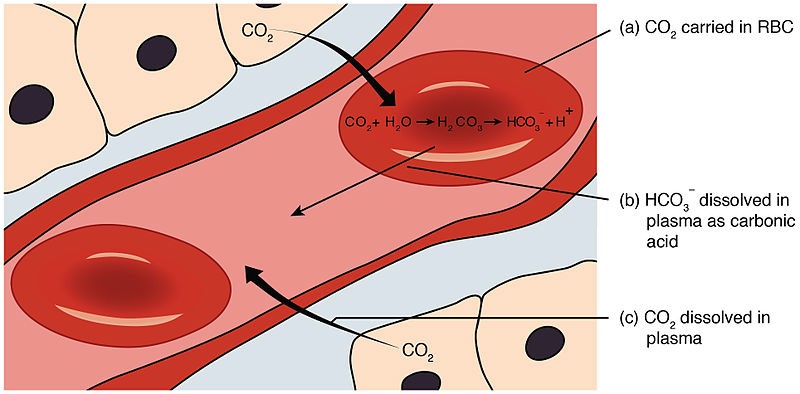
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is responsible for donating H+ ions to act as a buffer when blood pH rises.
When blood pH rises (becomes more alkaline), carbonic acid dissociates, and the H+ ions combine with bicarbonate ions to form more carbonic acid.
This helps to remove excess H+ ions from the blood and prevent the pH from rising too much.
Option A, carbon dioxide, is involved in the buffering system through its conversion to carbonic acid.
However, it does not directly donate H+ ions to act as a buffer when blood pH rises.
Option B, carbon monoxide, is a toxic gas that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, preventing them from carrying oxygen.
It is not involved in the buffering system and does not donate H+ ions.
Option D, oxygen, is carried by hemoglobin in red blood cells and is essential for respiration.
It is not involved in the buffering system and does not donate H+ ions.
-
Q #6: Which of the following are the two major parts of the nervous system?
A. Autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous system.
B. Peripheral nervous system and somatic nervous system
C. Peripheral nervous system and central nervous system.
D. Autonomic nervous system and central nervous system.
Answer Explanation
The two major parts of the nervous system are the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
The CNS is made up of the brain and spinal cord and acts as the integration and command center of the body.
The PNS represents the conduit between the CNS and the body and is further subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
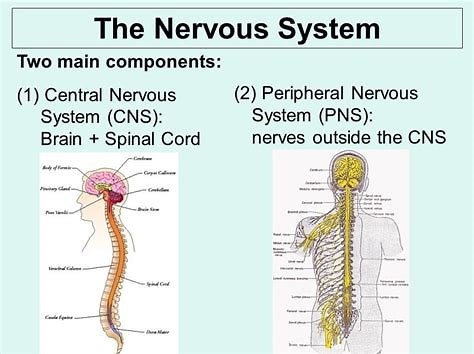
Choice A is incorrect because it only mentions two subdivisions of the PNS, which are the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and somatic nervous system (SNS).
Choice B is incorrect because it only mentions one major part of the nervous system, which is the PNS, and one subdivision of it, which is the SNS.
Choice D is incorrect because it only mentions one major part of the nervous system, which is the CNS, and one subdivision of the PNS, which is the ANS.
-
Q #7: What is the approximate threshold value for mammalian neurons?
A. -55 mV
B. -80 mV
C. +35 mV
D. 0 mV
Answer Explanation
The approximate threshold value for mammalian neurons is -55 mV.
The threshold potential is the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential.
Most often, the threshold potential is a membrane potential value between –50 and –55 mV
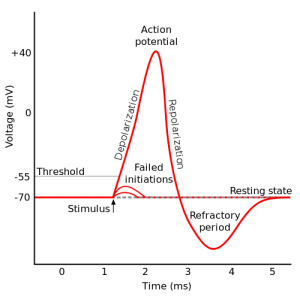
The membrane potential of a neuron is determined by the distribution of ions across the cell membrane.
At rest, the inside of a neuron is more negative than the outside due to the presence of negatively charged proteins and other molecules.
The movement of ions across the cell membrane can change the membrane potential.
For example, when sodium ions enter the cell, they make the inside of the cell more positive (less negative), causing depolarization.
Choice B is incorrect because -80 mV is below the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
Choice C is incorrect because +35 mV is above the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
Choice D is incorrect because 0 mV is above the typical threshold value for mammalian neurons.
-
Q #8: Which of the following indicates the function of sodium bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas?
A. Sodium bicarbonate is a protease that digests carbohydrates.
B. Sodium bicarbonate stimulates the pyloric sphincter.
C. Sodium bicarbonate inhibits peristalsis.
D. Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
Answer Explanation
Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
The pancreas secretes large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which protects the duodenum by neutralizing the acid that comes from the stomach.
This compound helps neutralize stomach acid generated during the digestive process.
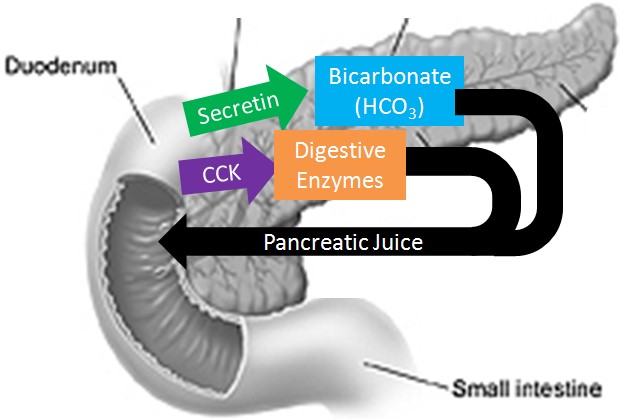
Choice A is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate is not a protease that digests carbohydrates.
Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins, while sodium bicarbonate is a chemical compound that helps neutralize stomach acid.
Choice B is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not stimulate the pyloric sphincter.
The pyloric sphincter is a ring of smooth muscle that separates the stomach from the duodenum and regulates the passage of partially digested food (chyme) into the small intestine.
Choice C is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not inhibit peristalsis.
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
-
Q #9: Which of the following is the main function of centrosomes in animal cells?
A. . Organelle trafficking.
B. Pathogen digestion.
C. Cytoplasm formation
D. Microtubule organization
Answer Explanation
Microtubule organization.
Centrosomes are organelles that serve as the main microtubule-organizing centers for animal cells.
They regulate the movement of microtubules and other cytoskeletal structures, thereby facilitating changes in the shapes of the membranes of animal cells.
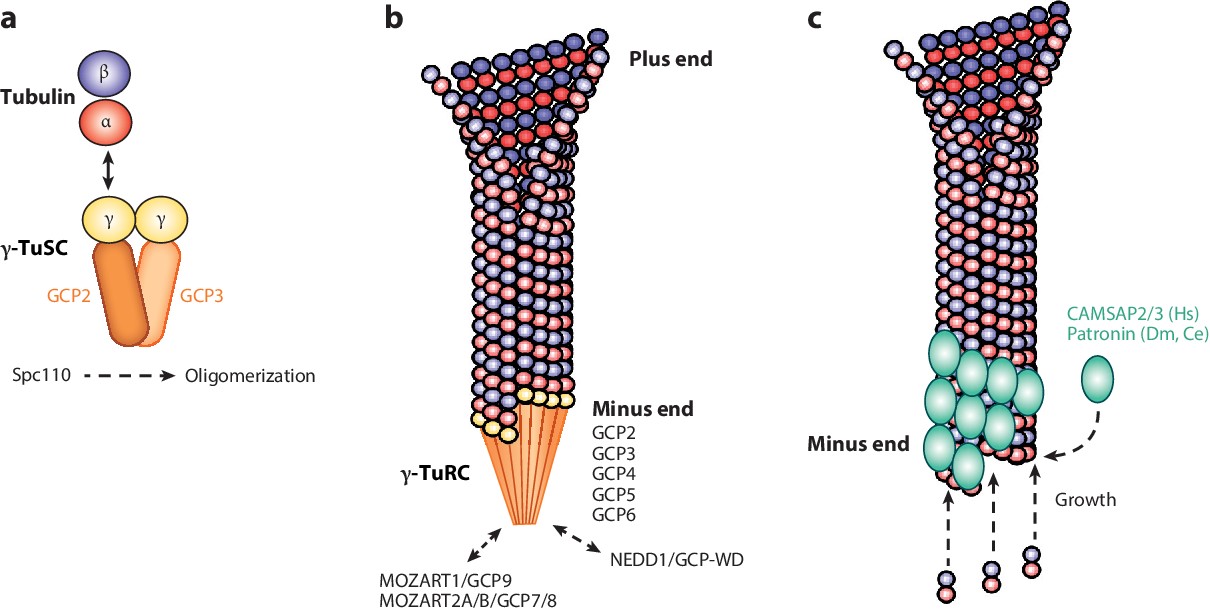
Choice A, Organelle trafficking, is not the correct answer because while centrosomes do play a role in intracellular trafficking during interphase by organizing an astral ray of microtubules, their main function is microtubule organization.
Choice B, Pathogen digestion, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in pathogen digestion.
Choice C, Cytoplasm formation, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in cytoplasm formation.
-
Q #10: In the following data table of an experiment carried out at 4°C (39.2 F) over 4 hours Solution in bag Solution outside bag Bag mass change (g): water Water -0.2 20% sucrose Water +2.4 , 40% sucrose Water +4.3 , 60% sucrose water +5.8 Which of the following options represents the dependent variable?
A. Duration
B. Temperature
C. Bag mass change
D. Solution used outside
Answer Explanation
Bag mass change is the dependent variable in this experiment.
In an experiment, the dependent variable is the variable that is being measured and is expected to change in response to changes in the independent variable(s).
In this case, the bag mass change is being measured and is expected to change in response to changes in the independent variable (sucrose concentration).
Choice A is incorrect because duration is not a variable in this experiment.
Choice B is incorrect because temperature is not a variable in this experiment.
Choice D is incorrect because sucrose concentration is an independent variable, not a dependent variable.
An independent variable is a variable that is manipulated by the experimenter to see how it affects the dependent
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
