Which part of the respiratory system is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth?
A. Bronchi
B. Alveoli
C. Diaphragm
D. Trachea
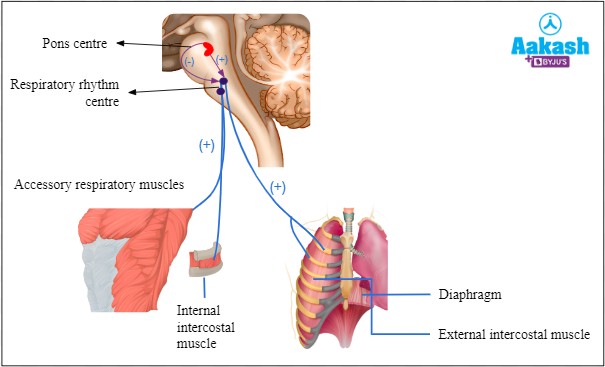
Diaphragm is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the
bottom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
 |
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following substances is excreted by the kidneys to regulate blood pressure?
A. renin
B. erythropoietin
C. calcitriol
D. urobilinogen
Answer Explanation
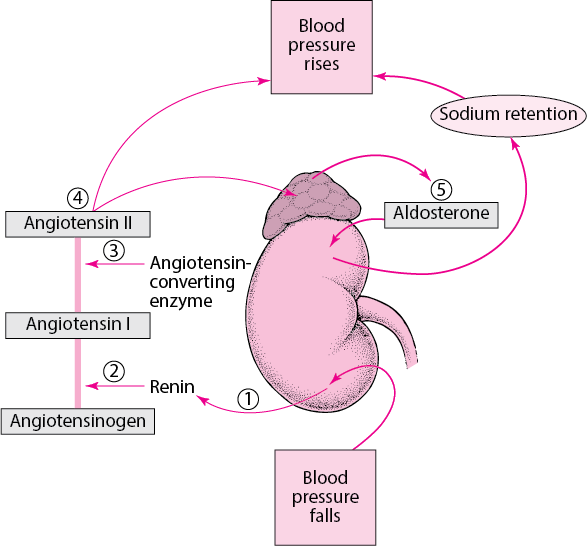
Renin is an enzyme that is produced by the kidneys and it acts to elevate blood pressure. When blood pressure falls, the kidneys secrete renin into the bloodstream ³.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis?
A. tRNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. DNA
Answer Explanation
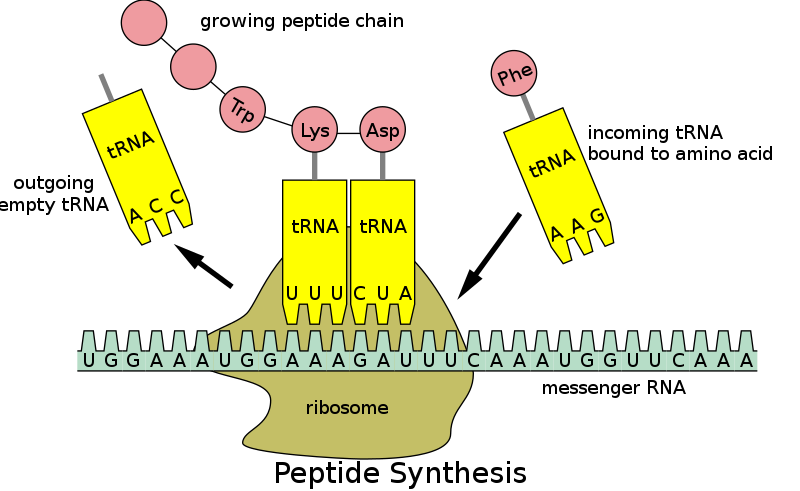
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific anticodon that matches a codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA codon and brings the corresponding amino acid to the ribosome, where it is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
-
Q #3: Which of the following is NOT one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body?
A. Epithelial
B. Nervous
C. Connective
D. Exocrine glandular
Answer Explanation
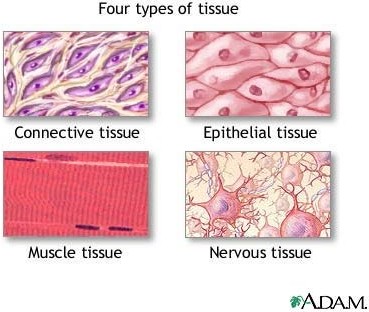
Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body. The four primary tissue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
-
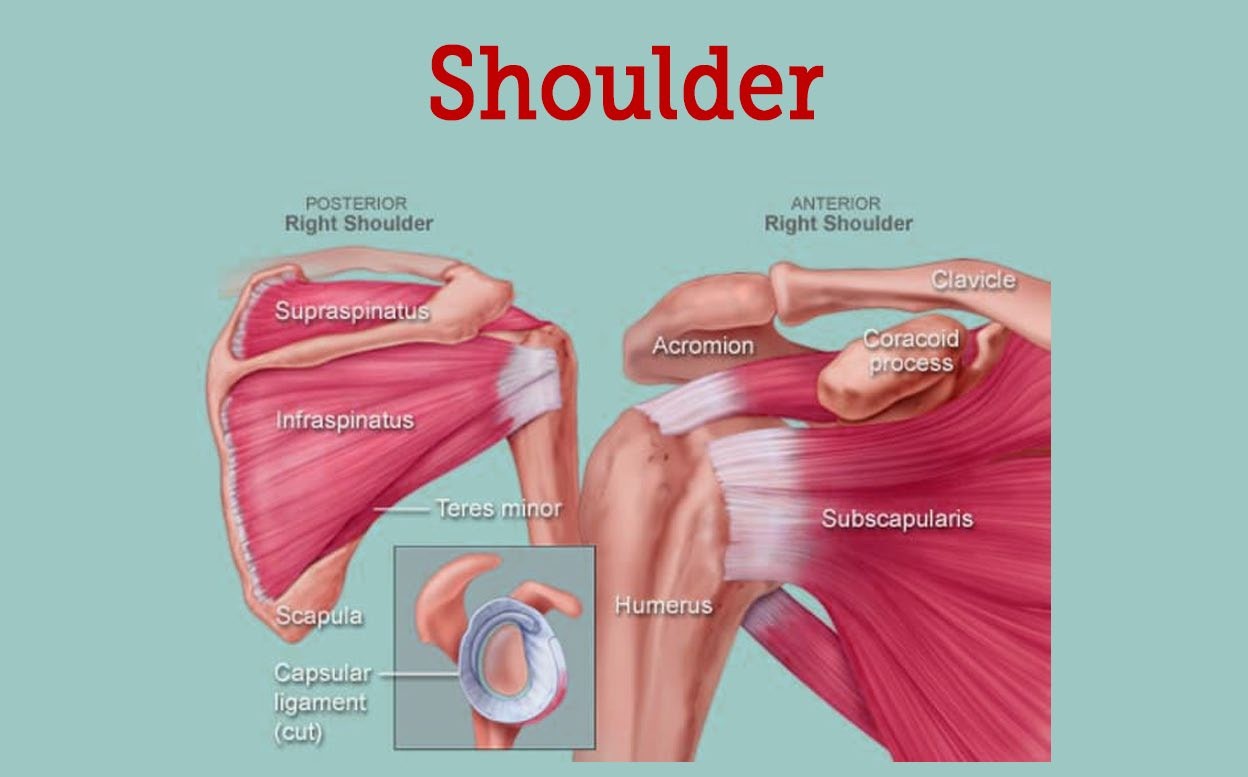
Q #4: What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
A. Elbow joint
B. Hip joint
C. Knee joint
D. Shoulder joint
Answer Explanation
-
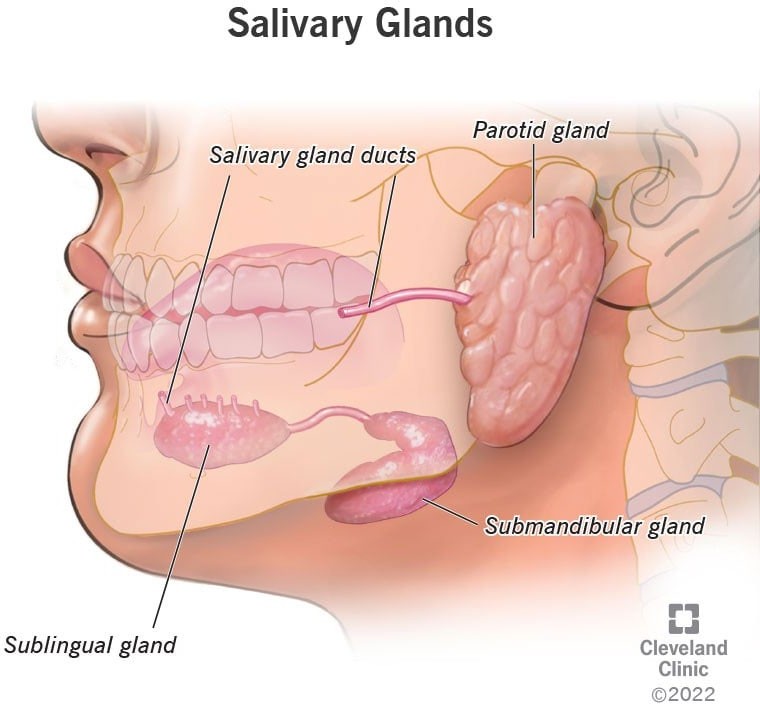
Q #5: What are the three types of salivary glands and where are they located in the mouth?
A. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the cheeks, tongue, and roof of the mouth, respectively.
B. Sublingual, submandibular, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
C. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the roof of the mouth, cheeks, and under the jawbone, respectively.
D. Sublingual, parotid, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
Answer Explanation
The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands.
- Parotid glands are located just in front of your ears.
- Sublingual glands are located below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth.
- Submandibular glands are located below your jaw.
-
Q #6: Which of the following is a chemical property of a substance?
A. Density
B. Melting point
C. Boiling point
D. Reactivity with acid
Answer Explanation
Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance.
Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance. Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
-
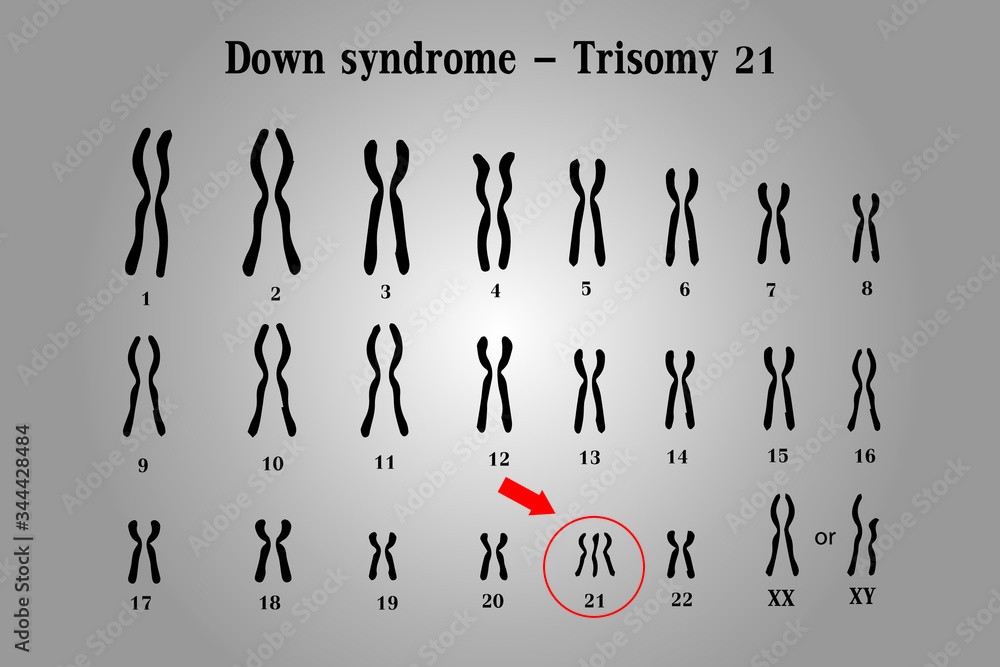
Q #7: What is the name of the genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Klinefelter syndrome
C. Down syndrome
D. Huntington's disease
Answer Explanation
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is also known as trisomy 21, because affected individuals have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two.
The extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome occurs due to a random error in cell division, which leads to the production of an abnormal gamete (egg or sperm) with an extra copy of the chromosome. When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, and develops into a fetus with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is characterized by a range of physical and intellectual symptoms, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, heart defects, and increased risk of certain medical conditions such as leukemia and Alzheimer's disease. However, the severity and expression of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
-
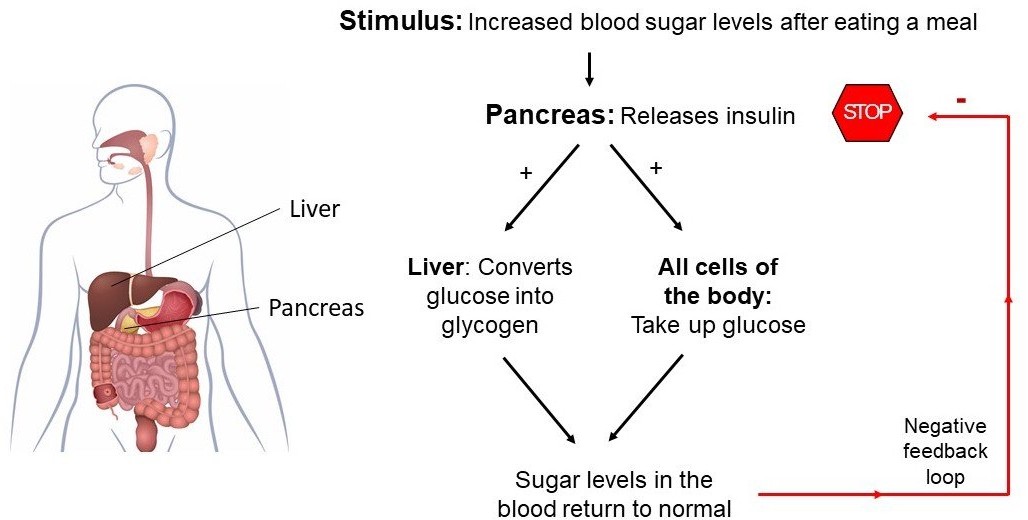
Q #8: What is the name of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the human body?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Estrogen
D. Testosterone
Answer Explanation
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. After a person eats a meal, the levels of glucose in the blood rise, which stimulates the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts on various cells in the body, particularly those in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue, to promote the uptake, use, and storage of glucose.
Insulin helps to lower the levels of glucose in the blood by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells, stimulating the liver and muscle cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen, and inhibiting the production and release of glucose by the liver. This process is known as glucose homeostasis, and it helps to keep the levels of glucose in the blood within a normal range.
Deficiencies or abnormalities in insulin production or function can lead to a range of metabolic disorders, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
-
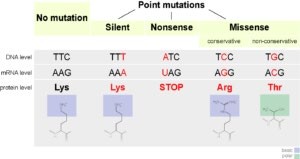
Q #9: Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
Answer Explanation
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
-
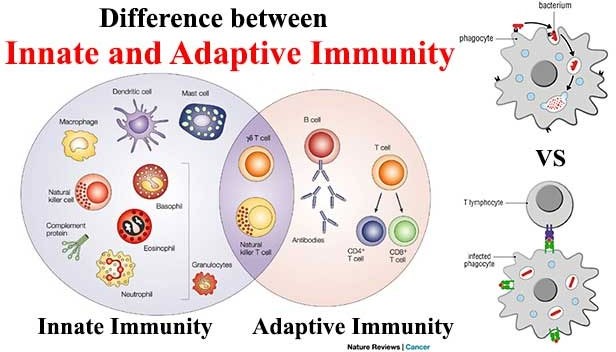
Q #10: What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
A. Innate immunity is present at birth while adaptive immunity is acquired after exposure to pathogens.
B. Innate immunity is specific to particular pathogens while adaptive immunity is nonspecific.
C. Innate immunity is mediated by antibodies while adaptive immunity is mediated by T cells.
D. Innate immunity provides long-term protection while adaptive immunity provides only short-term protection.
Answer Explanation
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
