Which process involves the fusion of male and female gametes resulting in the formation of a zygote?
A. Oogenesis.
B. Fertilization.
C. Meiosis.
D. Mitosis.
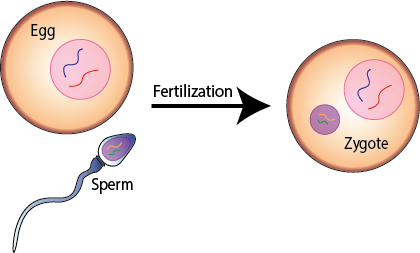
Fertilization.
Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
 |
Oogenesis (choice A) is the process by which female gametes, or eggs, are produced.
Meiosis (choice C) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of gametes.
Mitosis (choice D) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science
-
Q #1: Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
Answer Explanation
Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
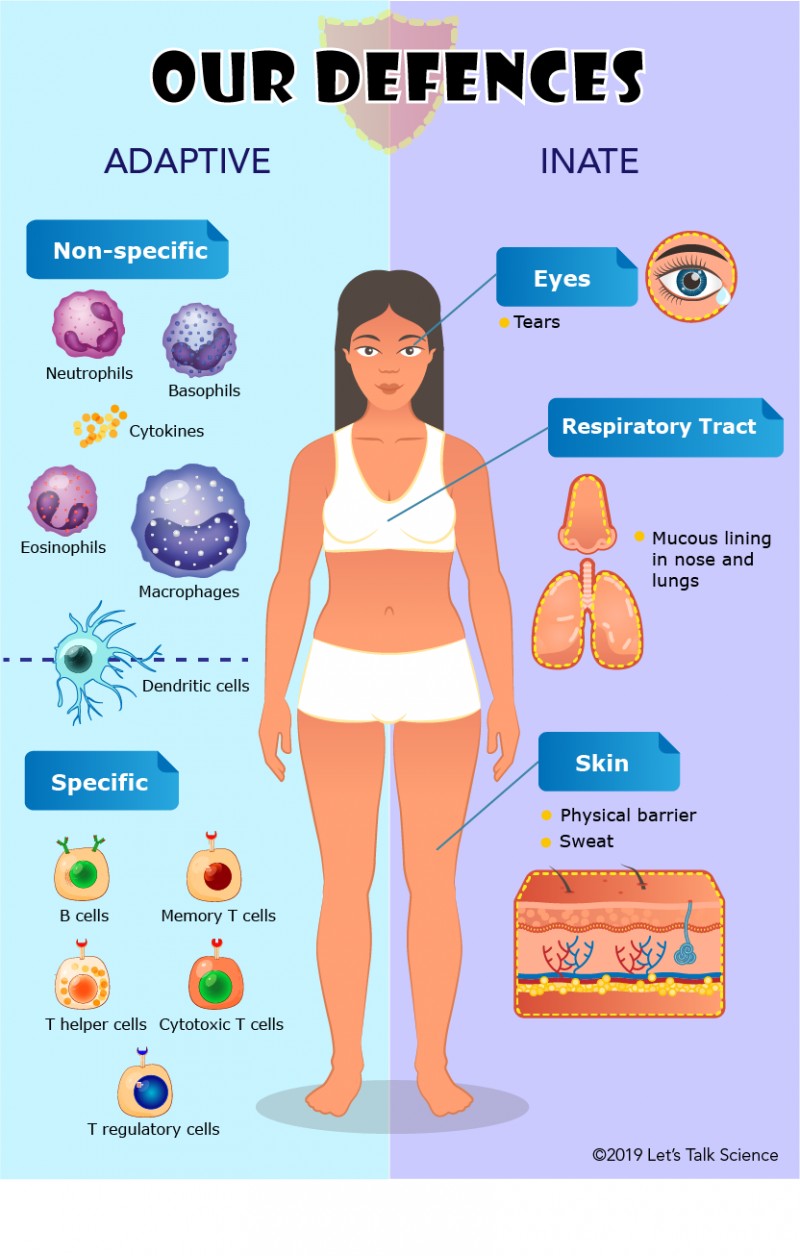
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
-
Q #2: Which of the following is a consequence of increased viscosity of a fluid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. The fluid will have a lower density.
C. The fluid will have a higher flow rate.
D. The fluid will have a higher pressure.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
-
Q #3: A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder. The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
Answer Explanation
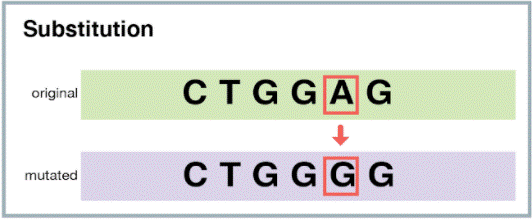
The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
-
Q #4: A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis. What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
Answer Explanation
Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
-
Q #5: Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
-
Q #6: What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
Answer Explanation
Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
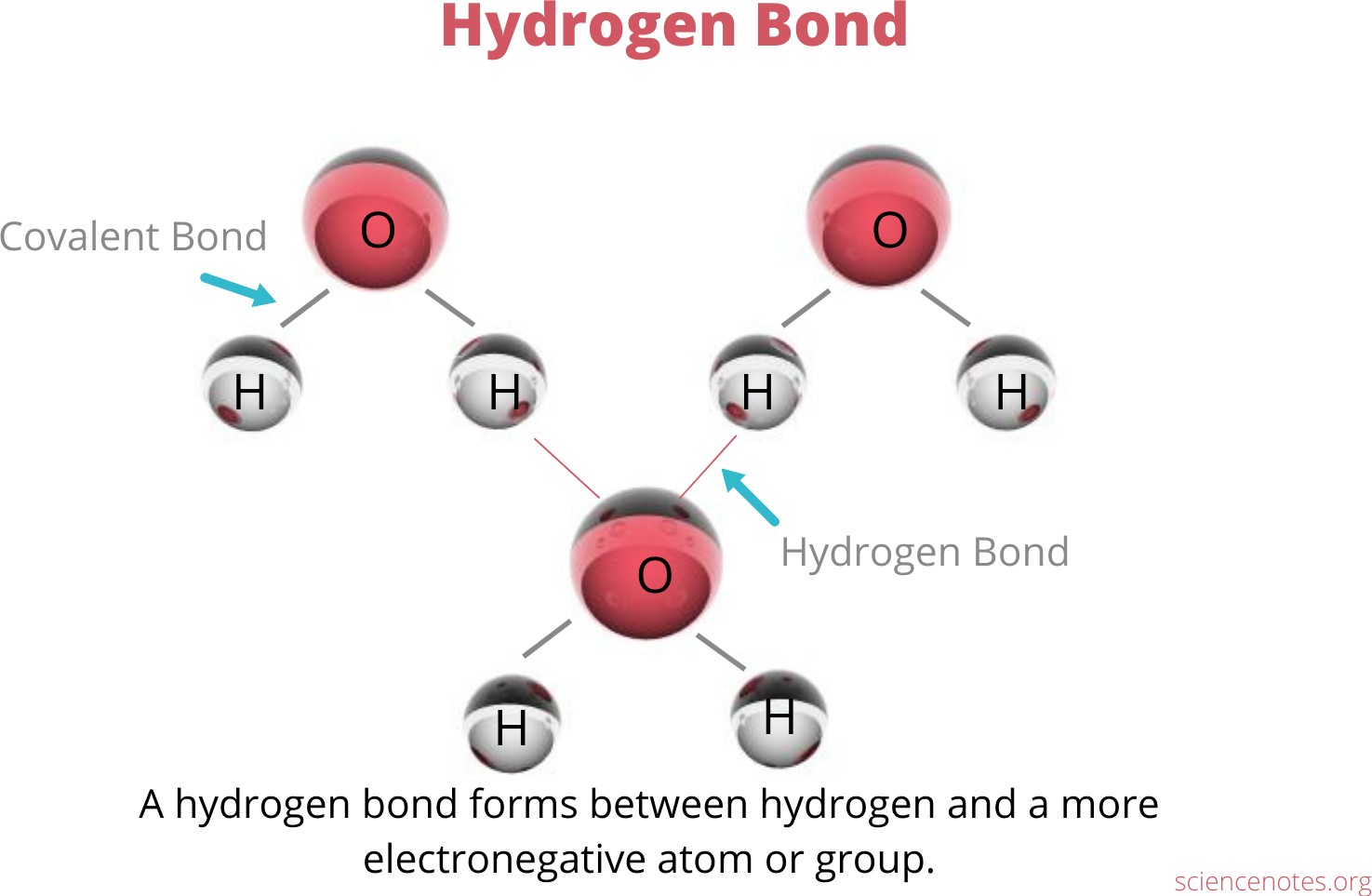
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
-
Q #7: How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
-
Q #8: A nurse is caring for a patient who has been declared brain dead and is awaiting organ donation. Which of the following interventions is most important to preserve the viability of the organs?
A. Administering antibiotics to prevent infection.
B. Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
C. Providing emotional support to the family members.
D. Applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying.
Answer Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
Early identification and management of potential organ donors must take into consideration specific pathophysiologic changes for medical optimization 1.
The VIPPS (ventilation, infusion and pumping, pharmacological treatment, and specificities) strategy is a mnemonic method that brings together key aspects of the restoration of oxygen delivery to tissues during hemodynamic instability plus organ optimization strategies.
Choice A is incorrect because administering antibiotics to prevent infection is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Choice C is incorrect because providing emotional support to family members, while important, is not an intervention that directly affects organ viability.
Choice D is incorrect because applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
-
Q #9: Which of the following is an example of a storage form of glucose in the human body?
A. Starch
B. Glycogen
C. Fructose
D. Cellulose
Answer Explanation
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the human body.
It is a polysaccharide that is stored primarily in the liver and muscle tissue and can be broken down into glucose when the body needs energy.
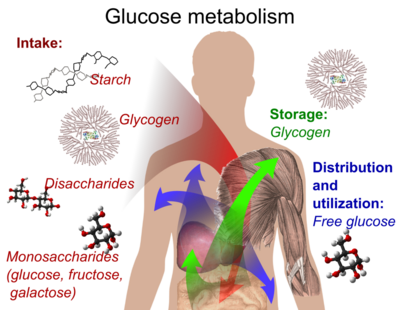
Choice A is incorrect because starch is a storage form of glucose in plants, not in the human body.
Choice C is incorrect because fructose is a simple sugar, not a storage form of glucose.
Choice D is incorrect because cellulose is a structural carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, not a storage form of glucose in the human body.
-
Q #10: Which of the following statements about bacteria and archaea is true?
A. A. Bacteria have a true nucleus while archaea do not
B. B. Archaea reproduce by spores while some bacteria reproduce by fission.
C. C. Bacteria can perform photosynthesis while archaea cannot.
D. D. Archaeal and bacterial flagella are constructed similarly.
Answer Explanation
Bacteria can perform photosynthesis while archaea cannot. Many types of bacteria can generate oxygen from sunlight through photosynthesis, while archaea cannot perform this process.
Choice A is incorrect because neither bacteria nor archaea have a true nucleus. Both are prokaryotic organisms. Choice B is incorrect because archaea reproduce by fission, fragmentation, or budding, while bacteria can produce spores and divide sexually or asexually. Choice D is incorrect because archaeal and bacterial flagella are constructed differently.
Free Access on TEAS 7 Exams and Study Notes
- Access to all TEAS 7 Exams
- Performance Tracking and Analysis
- Well Documented and Explained Questions and Answers
- 2000+ Questions and Correct Answers: Answers Well Explained
- Libary of Detailed StudyNotes
- Topical Questions and Answers on Examinable topics
TEAS 7 Exams (Q&A)
TEAS 7 Study Notes
TEAS 7 Topical Tests

TEAS 7 Study Guides
Quick Links
Refer a Friend
Refer a friend and claim free unlimited access

© 2024 ExamGates Made with by ExamGates
