What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
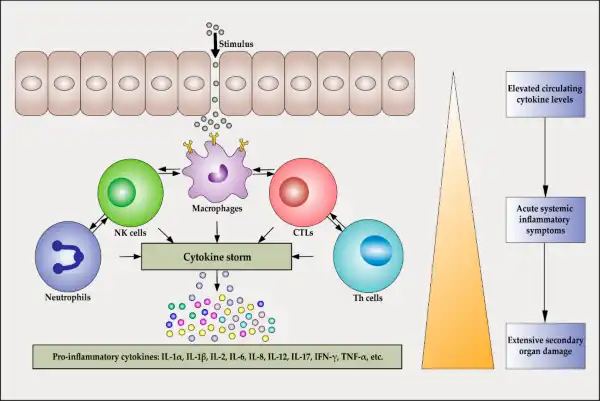
Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.
Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.