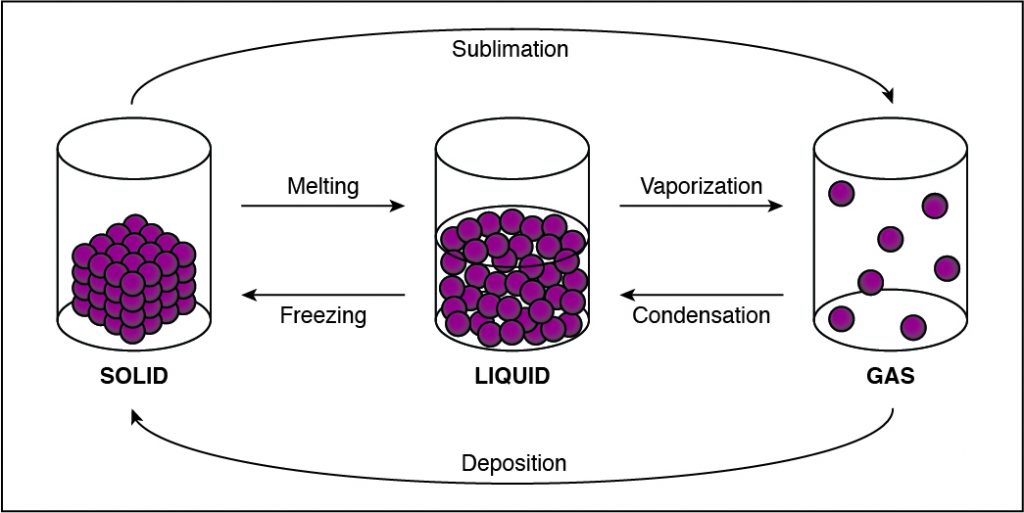
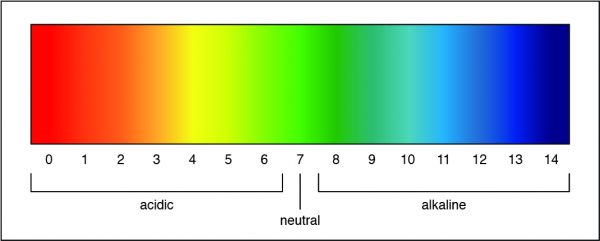
What raw inorganic material would an autotroph most likely use to create chemical energy for growth?
A. carbon dioxide
B. minerals in soil
C. decaying matter
D. sugar molecules
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophs are organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.