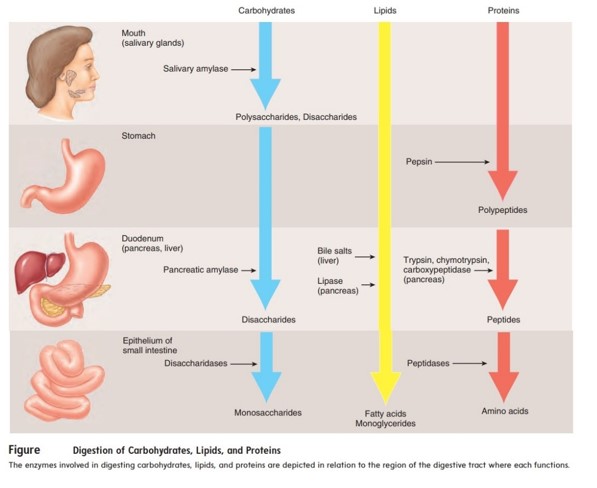
Which of the following correctly orders structures from simple to complex?
A. Cells, tissues, atoms, organs
B. Atoms, organs, tissues, cells
C. Atoms, cells, tissues, organs
D. Organs, tissues, cells, atoms
The correct answer is c. Atoms, cells, tissues, organs. This is the correct order of structures from simple to complex. Atoms are the smallest and simplest units of mater. Cells are made up of atoms and are the basic units of life.
Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Organs are made up of different types of tissues and perform more complex functions.
A. Cells, tissues, atoms, organs is not the correct order from simple to complex.
B. Atoms, organs, tissues, cells is not the correct order from simple to complex.
D. Organs, tissues, cells, atoms is not the correct order from simple to complex.
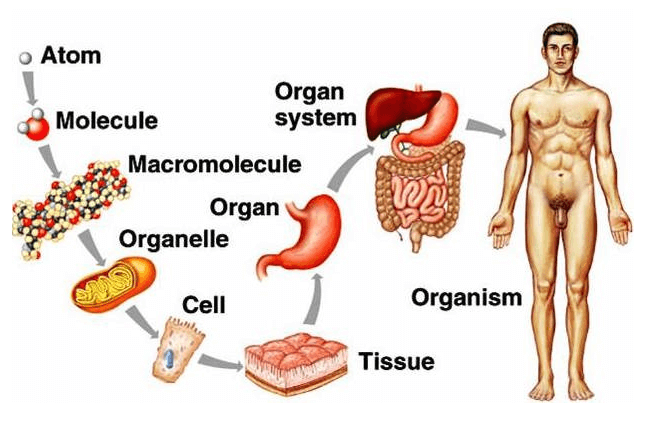
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.