Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
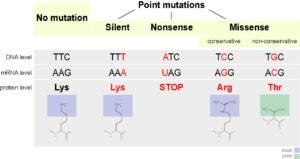
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.