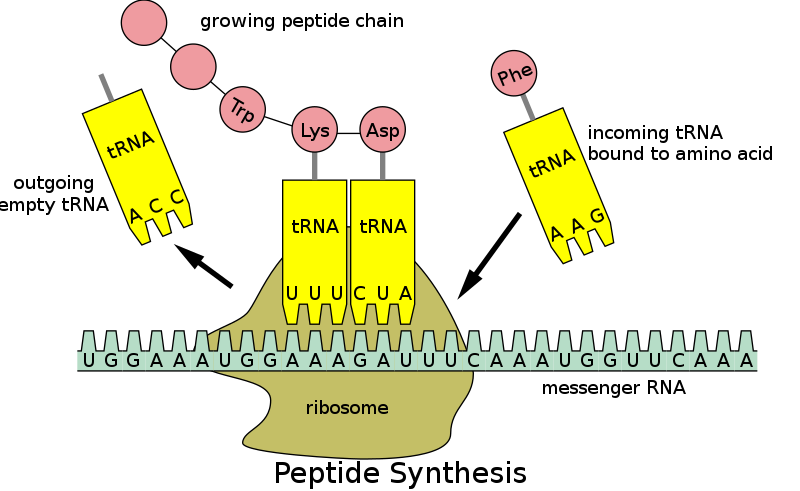
Which of the following is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis?
A. tRNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. DNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific anticodon that matches a codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA codon and brings the corresponding amino acid to the ribosome, where it is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
 |
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.